Ch 34.4 Student notes

BIOLOGY Chapter 34: The Biosphere Name:________________________
Section Goal: The student will compare and contrast ponds, streams and estuaries, compare conditions and typical organisms in the intertidal, neritic and oceanic zones and then describe the abiotic and biotic factors that characterize coral reefs and hydrothermal vent communities.
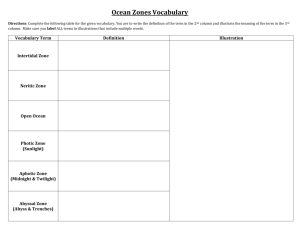
Vocabulary:
1.
photic zone-
2.
phytoplankton-
3.
aphotic zone-
4.
benthic zone-
5.
estuary-
6.
pelagic zone-
7.
intertidal zone-
8.
neritic zone-
9.
oceanic zone-
10.
zooplankton-
11.
hydrothermal vent-
Concept 34.4 Aquatic ecosystems make up most of the biosphere.
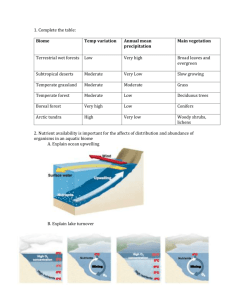
I. Ponds and Lakes
A. Freshwater bodies of water with little dissolved salts, Ex: Great lakes
B. photic zone: regions of a body of water where light penetrates, enabling photosynthesis, and lakes are divided into zones by depth
C. phytoplankton: microscopic algae and cyanobacteria that carry out photosynthesis in photic zone
D. aphotic zone: deep areas, no photosynthesis
E. benthic zone: bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
II. Streams and Rivers
A. Flowing freshwater usually empties to lake or ocean
B. near source low in nutrients, cold, major producer is algae, downstream is warmer and larger, supports more life including phytoplankton
C. trout, frogs, worms, insects, etc.
III. Estuaries
A.
estuary: area where fresh water from streams and rivers merges with salty ocean water; productive ecosystem, Ex: Chesapeake Bay, parts of Florida
B.
Have changes in salt concentration and temperature, very productive, lots of nutrients, many fish and birds, crabs, oysters, clams. Etc.
IV. Ocean Zones
A. Oceans are divided 4 zones based on depth and distance from shore
B. pelagic zone: open water above the ocean floor
C. intertidal zone: area of shore between the high-tide and low-tide lines
D. neritic zone: area of ocean that extends from the low-tide line out to the edge of the continental shelf
E. oceanic zone: Vast open ocean from the edge of the continental shelf outward, includes zooplankton: microscopic animals that swim or drift near the surface of aquatic environments
V. Coral Reefs
A. very diverse, like the rainforest of ocean, coral is an animal that builds upon hard, dead external skeletons, can be poisonous, Ex: Great Barrier Reef
B. including sponges, sea anemones, worms, sea stars, and mollusks, sea turtles, and fishes
VI. Deep-sea Vents
A. hydrothermal vent: opening in the ocean floor where hot gases and minerals escape from Earth's interior, producers (prokaryotes) use chemical energy (eat sulfur) because of no light, Ex: Mid-
Atlantic Ridge
Lesson Reflection:
Complete the Ocean Diagram. Use page 760 in your book to help you complete the handout.
Lesson Assessment:
1.
Describe the abiotic factors that affect organisms in ponds, streams, and estuaries.
Summary of Key concepts:
Complete the Summary of Key Concepts 34.4 and turn into the box.
Technology/Application/Connection to real-world:
Learn 360: Aquatic Biomes (19:08 min)