chapter 10: freshwater biomes 10.1 aquatic biomes
advertisement

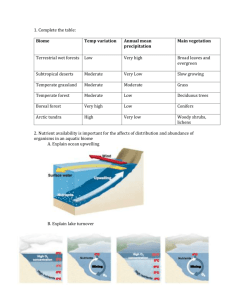
Name:_____________________________________________________ Environmental Science Note Packet Chapter 10 and 11-Aquatic Biomes (pg 154-181) 1. READ chapter 10 and 11 (pgs 154-181) in the text book. 2. Define the Vocabulary: Chapter 10 Vocabulary 1. Benthic zone: 2. Photic zone: 3. Phytoplankton: 4. Salinity: 5. Sediment: 6. Wetland: 7. Zooplankton: Chapter 11 Vocabulary 1. Continental Shelf: 2. Detritus: 3. Estuary: 4. Intertidal zone: 5. Neritic zone: 6. Oceanic zone: 7. Reef: 8. Subsidence: Ms. Marcino CHAPTER 10: FRESHWATER BIOMES 10.1 AQUATIC BIOMES Water covers _______________________________________________ surface. Aquatic habitat: Most important factors: 1. ________________________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________ Salinity Salinity: Allows us to divide water into 2 groups: 1. _______________________-30 parts per thousand. 2. _______________________-0.5 parts per thousand. Brackish water- Depth Directly related to ______________________________________ that reaches the __________________ of body of water. Sunlight determines ____________________________________________________________________________________. Bodies of water can be divided into depth zones: _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ Depth Zones Diagram Photic Zone: About 100 meters in open ocean. Aphotic Zone: Benthic Zone: CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. What characteristic distinguishes the photic zone from the aphotic zone? 2. How is salinity determined and measured? 3. Suppose a friend wants to set up an aquarium and discovers that saltwater fish are more attractive, but a freshwater aquarium is easier to maintain. Your friend decides to set up a freshwater aquarium, but buys some saltwater fish to place in it. Predict what the result of this decision would be and why. 10.2 STANDING-WATER ECOSYSTEMS Freshwater biomes: 1. _________________________________________________________ Lakes and ponds, wetlands, bogs, swamps, marshes 2. _________________________________________________________ Lake _____________________________ standing water; may have ________________________________________; may be fed by _________________________________________________________. Main producers:________________________________________________________________________________________. Pond Light reaches _________________________________________________; fed by ______________________________; may be seasonal. Main producers:________________________________________________________________________________________. Marsh Very _________________________ with land occasionally exposed; _____________________________________; very low ______________________________________________; _____________________ may vary (Florida Everglades. Plants:________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ Swamp Poor _____________________________ (__________________________________________________________________); along low ________________________________ and flat land. Large __________________________________________________________________; plants grow in ________________________________________________________________; cypress trees, willow, dogwood. Bog Inland __________________________________ with little ____________________________________________________; soil __________________________; decay _________________________. ______________________________________________ dominant; decayed moss accumulates. Standing-Water Organisms _________________________________ of water. Plankton: 1. Phytoplankton: 2. Zooplankton: ________________________________________ Scavengers Food chain: Wetlands Wetlands: Examples: Soil ____________________________________________; low in ____________________________. Water may be ___________________________________________________________________________. ___________________________________________ in the water that passes through them. _____________________________________________________________________________________ for waterfowl. ________________________ protection. Refill _______________________________________. Human Activity Destroy because we don’t like the animals there. It is not attractive to us. Like waterfront view. The Florida Everglades Use to span ________________________________________________________________________________________________. Maximum water depth ___________________________________________. Wet season from ____________________________________________________. Much drained to create farmland. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. Where would you be likely to find benthic organisms in an aquatic ecosystem? 2. What is the difference between the role of phytoplankton and the role of zooplankton in an aquatic food web? 10.3 FLOWING-WATER ECOSYSTEMS Stream Organisms Adapted to ___________________________________________________________________________________. Insects have hooks to grab hold of plants. Fish “smell” chemicals in the water to return to old breeding grounds. Stream Flow Flow to ___________________ because of _________________________________. Source (__________________________) of stream: _______________________________________________ Headwater-______________________________________________________________________________ Sediments: Accumulate on ___________________; provide place for ___________________________________________. Slow flow of _______________________________. Cause stream to change course over time. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. What condition encourages sediments to settle out of the flowing water in a stream? 2. Why are there fewer organisms in the headwater of a stream than further downstream? CHAPTER 11: THE MARINE BIOME 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN The ___________________ between the ____________________________. All oceans are _________________________________. Zones based on depth: ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Zones based on distance from shore: _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ The Oceanic Zone Oceanic Zone: ___________________________________________ below ocean surface. Not much__________________________________ Photic Zone _______________________________________________________________________________ Aphotic Zone Many organisms feed on ___________________________________________________. Detritus: Ocean Water Near __________________________________________. Near _____________________________. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ content. ____________________________________________________. Ocean currents: Driven by wind. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. What is detritus made of, and why is it important to deep sea organisms? 2. Why does the oceanic zone have no plants? What are the producers of the open ocean? 11.2 NERITIC ZONES Continental Shelf: Area between the ______________________________________________________________________________ the surface of the water. Neritic Zone: In the photic zone. Reefs and estuaries. Coral Reefs Reef: Made from __________________________________________________________________________________. In ________________________________________________________ waters. _______________________________________________________________________________________ for many fish. Protect shoreline from __________________________________________________. VERY diverse. Reef made of: ______________________________________________________________________ of corals. Symbiotic relationship between _________________________________ inside tissue of coral. Humans harm reefs: ___________________________________________________________. ______________________________________________________ for jewelry. ______________________________________________ aquariums. Water ___________________________. Estuaries Estuary: Brackish water. Neritic Zone Productivity Factors: _____________________________________________________ allows photosynthesis. High in ________________________________________________. ______________________________________ CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. Where in the ocean does the neritic zone begin and end? 2. Some types of ecosystems recover from damage more quickly than others. Would you expect coral reefs to recover quickly from the types of damage described in this section? Why or why not? 11.3 INTERTIDAL ZONES Intertidal zone: Organisms must survive: ________________________________________________________________________________. Surrounded by _____________________________________. Salt Marshes ________________________________________________________ that often surround _____________________________ ________________________________________________. ________________________________________________ tides. Support ________________________________________________________________. Support ocean ecosystem. Form when ________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________. Slowing of waters cause sediments to be deposited in ______________________________________. Sediments ______________________________________________________________________________________. Subsidence: Mangrove Swamps Coastal __________________________________ that occurs only in ________________________________________. Mangrove-____________________________________________________________________________________________. ____________________________________________________________________ Very little _________________________________________________________________. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: 1. Why are salt marshes considered part of the intertidal zone?