Key Elements in Language Learning Process
advertisement

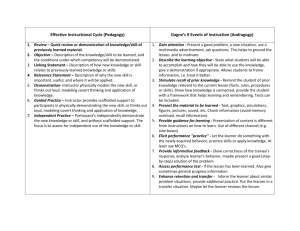
Key elements in the language learning process Learner Dependence Awareness Skills Assessment Language use Strategies Consolidation Learner Independence The purpose of the model above is to capture the inter-relationships between different elements of the language learning process, to express the dynamic nature of that learning process and to stress the choices that teachers need to make with respect to methodology and teaching and learning strategies. A key goal of the HCT is to transform our students from a state of ‘learner dependency’ into ‘independent, lifelong learners.’ The scope of the model is defined by placing the needs of the learner as paramount. A key role for language teachers (and all teachers in the HCT) is to develop the literacy skills and learning strategies which students need to make the journey from ‘learner dependence’ to ‘learner independence'. At the core of the model is effective Language Use. This reflects the overall goal of HCT language courses which is to develop in students “the linguistic ability to function effectively in an international environment''. Language Awareness (how-when-where new language is introduced), Consolidation (the range of activities necessary to move learning from ‘surface’ to ‘deeper’ learning) and Assessment (both formative and summative and supporting the learning) are inter-related and support the core. Although these elements are depicted as equal on the diagram, this is not to imply that the learning process should be structured accordingly; learner needs will be the key determinant in making decisions about emphasis and weighting of the different elements. The model highlights freedom of choice for teachers – there is no attempt to prescribe one specific methodology; rather, depending on learner needs, teachers will decide, often in collaboration with their students, the appropriate ‘mix’ of methodologies and strategies. EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES AT DIFFERENT STAGES IN THE LANGUAGE LEARNING PROCESS Language awareness elicitation Instructor presentation & explanation of a grammar point translation instructor guided discovery or noticing techniques use of picture, bilingual or monolingual dictionary to access new vocabulary self accessed computerised presentations of a grammar point peer tutor explanation of grammar point independent deduction of meaning of vocabulary or grammar from context Language consolidation Individually or in pairs groups controlled drilling /substitution techniques cloze gapfill techniques matching activities storyboard activities dictation techniques information gap tasks communicative tasks focused on grammar points or skill practice Language use and synthesis using new vocabulary/grammar in sentences timed guided writing tasks focusing on new language scaffolded writing tasks problem-based tasks competitive tasks collaborative tasks learning communities e.g. discussion boards structured integrated projects guided projects open ended integrated projects Real life use Assessment concept checking instructor made & marked tests and quizzes online tests quizzes with feedback-monitored by instructor tests,quizzes in autonomous learning situations peer correction peer editing peer mentoring peer assessment self access assessment tools self reflection EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES AT DIFFERENT STAGES IN THE LITERACY LEARNING PROCESS Literacy strategy /skill awareness Literacy strategy/skills consolidation Literacy skills use and Assessment synthesis guided writing using models – write instructor set/marked ranging from simple copying to reading/listening Instructor draws attention to LI /L2 read differences in graphological rules, essay writing from a skeleton comprehension tests speak rhetorical structure, phonic systems framework instructor created and listen assessed Instructor draws attention to ss build self correction skills through in authentic or semi knowledge of text types in L1 and deciphering error annotations and integrated projects authentic situations ranging explores similarities which are redrafting peer reading of student from short tasks to longer transferable e.g. advertisements guided speaking activities e.g. writing integrated projects Instructor presents models of EL information gap speaking pair work peer assessment of oral written texts from sentence level to presentations guided reader based activities full essay reconstruction of reading text to read independently for self assessment using Instructor helps students activate focus on recognition of text cohesion work and pleasure online reading/listening schemata by pre reading and tests questions targeted at fast/selective use spoken English to prediction activities information retrieval from text peer tutor self-reflection on SS are helped to deconstruct English effectiveness of questions targeted at extracting text to observe the underlying different literacy skills surface and embedded meaning from structure e.g. topic sentences usage, & strategies text intra text cohesion activities to strengthen linkage Instructor presentation & between spoken and written text e.g. demonstration of a reading subskill dictation, listening with a script, e.g. highlighting anaphoric reference read-aloud pronouns extensive /leisure reading activities setting up a guided reader system e.g. book /magazine reviews, exploring students interest and sustained silent reading time, self selecting appropriate reading materials access reading labs