Spectrocolorimetry Measurements – SPEKOL
advertisement

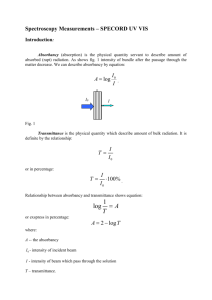
Spectrocolorimetry Measurements – SPEKOL Introduction: SPEKOL is a single-beam spectrophotometer with a grating monochromator working in the wavelength range 190-1100 nm. Together with special countershafts, this is the multifunctional device designed to measure: absorption, transmission, fluorescence and phosphorescence emission, reemission, turbidy (cloudiness) and also photometric, fluorimetric and turbidymetric of various solution. Absorbancy (absorption) is the physical quantity servant to describe amount of absorbed (rapt) radiation. As shows figure 1 intensity of bundle after the passage through the matter decrease. We can describe absorbancy by equation: A log I0 I . x I I0 Fig. 1 Transmittance is the physical quantity which describe amount of bulk radiation. It is definite by the relationship: T I I0 or in percentage: T I 100% . I0 Relationship between absorbancy and transmittance shows equation: log or exspress in percentage: where: 1 A T A 2 log T A -- the absorbancy I 0 - intensity of incident beam I - intensity of beam which pass through the solution T – transmittance. The absorption spectrum describe the relationship between amount of absorb radiation and wavelength of incidental radiation. In the visible range it could be dark lines or band on the constant emission spectrum and it is characteristic for every substance. Wavelength λ – distance between two neighboring points in the same phase. wavelengh t The most popular units express wavelength are : 1nm 10 9 m 1 m 10 6 m . 1A 10 10 m Range of wavelength of electromagnetic radiation Range of radiation Wavelenhgt [ nm] UV-C UV UV-B UV-A 100-280 280-315 315-380 VIS 380-780 IR-A IR IR-B 780-1400 1400-3000 IR-C 300010000 Others physical quantity characteristic for electromagnetic wave are: 1 Frequency ν. Frequency’s unit is Hz . It define number of vibration in time unit. s Wave number k, which describe number of wavelengths in length unit. It’s unit is Kejzer. 1K 1 cm Relationship between wave number and wavelength describe equation: k 1 . Absorption laws: Lambert law I I 0 e x where : A - the absorbancy I 0 - intensity of incident beam I - intensity of beam which pass through the thickness x α – absorption coefficient which is characteristic for every substance x - thickness of the layer Hence, I of electromagnetic radiation exponentially decreasing with the increasing length of absorber. x I0 I Fig. 1 Beer`s Lambert law- refer multicomponents solutions: I I 0e cx where c is concentration of solution. α A c c Absorption coefficient is independent of concentration of absorber. Absorption increase with the increasing concentration.. Absorption Additivity law Absorption value of several component is equal to sum of absorption values of each components. Ac A1 A2 ... An Application: NMR spectroscopy, detection of various matters 1 2 3 1. Display and Button display of data’s and control buttons for use of internal software function. 2. Sample compartment to insert accessories and samples cells. 3. Cell selector arm of the Cell change the position of he manual cell changer. Positions of the 4 cell changer Position 5 Sample nr 3 Position 4 Sample nr 2 Position 3 Sample nr 1 Position 2 Position 1 Distilled water Golas: Determine the absorption spectrum of chosen substance Check the relationship between absorption ant concentration of the substance Find concentration of the substance with the help of curve A=f(c) Procedure: Absorbance measurement 1. Set the wavelength 450 nm with the up and down button. 2. Select the operating mode ABS by using MODE button. 3. Place the cell with distilled water into the path of the beam. 4. Place the sample in the other position of cell changer. 5. Close the sample compartment cover. 6. Pull the cell holder with the distilled water in the measurement beam. 7. Measure the blank value by pressing 100%T button. 8. Using the cell holder cover the beam (position 2). 9. To calibrate device use the 0%T button. 10. Place the cell with sample into the path of beam. 11. Read the absorbance. 12. Increase the wavelength by 10 nm until 780 nm will be achieved. Make graphs A=f(λ) and T=f(λ). λ T A Repeat the measurements for other 10 different concentrations solutions. Read and tabulate only the extreme values of absorbance and transmittance. Amax Tmin c Make graphs Amax=f(c) and Tmin=f(c). Mark the value of Amax and using the graphs read it’s concentration. With the help of the SPEKOL study the substance with unknown concentration. 1. Press MODE button until the absorbance ABS is displayed. 2. Place the distilled water in the sample compartment and close the sample compartment cover. 3. Press 100%T button to measure the blank solution. 4. Cover the measurement beam (position 2). 5. Calibrate the device by using 0%T. 6. Place the standard sample into the measurements beam. 7. Press MODE button until the concentration CONC is displayed. 8. Press the FUNC button until the Input Std. CONC is displayed. 9. Use the up and down button to set the concentration of the standard on the digital display and confirm with ENT. 10. Insert the sample solution into the cell holder or cell changer. 11. Close the sample compartment cover. 12. Read the results. . Compare the received value with the value read from calibration curve.