Theoretical Probability – the probability of an event occurring in theory
advertisement

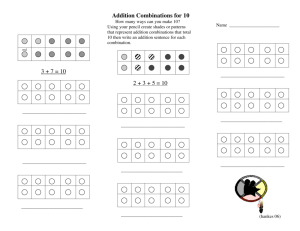
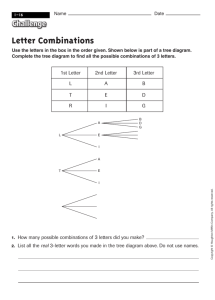
Name_________________ Probability Graphic Organizer Theoretical Probability – the probability of Example: P(sum of 7) when rolling 2 fair an event occurring in theory number cubes. Show work! Experimental Probability – the probability of an event occurring based on the results of an experiment. Remember, the more trials you run, the closer your experimental probability will get to matching the theoretical probability! Grade 6 7 8 9 10 Passing Score 2/5 1/8 1/4 1/2 3/5 What is the number of 8th graders that would have a passing score if 80 students took the test? Listing Combinations – Showing the different combinations using a systematic approach so nothing gets repeated. Example: Show the different combinations of 20 cents using dimes, nickels, and pennies? Least amount of coins used? Most? Counting Principle - To determine the number of possible outcomes. Example: 5 types of sauce, 5 choices of meat, 4 types of veggies? Name_________________ Probability Graphic Organizer Tree Diagrams – Showing the different combinations of events. Example: How many ways can you get two heads if you flip a coin three times? Independent Events – When one event does not affect the second event. Example: 5 green, 4 blue, 1 white marble. What is the probability of selecting a green, replacing it, and selecting a blue the second time? Dependent Events – When one event affects the second event. Example: 5 green, 4 blue, 1 white marble. What is the probability of selecting a green, not replacing it, and selecting a green the second time? Combinations – Order does not matter. You are eliminating the duplicates! Example: How many ways can 3 friends be chosen from a group of 8? Calculator - nCr Permutations - Order does matter. You are not eliminating the duplicates! Example: How many ways can a President, VP, and secretary be arranged from a group of 5 people? Calculator – nPr or ! How many ways can 4 racing dogs cross the finish line? Name_________________ Probability Graphic Organizer