04A ICA Competition rubric
advertisement

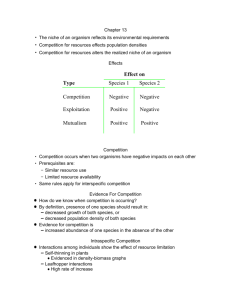
ICA 4 COMPETITION Group Name _______________ Your name _______________ PART 1 1. How does intraspecific competition relate to density-dependent regulation of population growth? Such competition increases with density and serves to dampen population growth. 16.8 What are 4 negative density-dependent growth responses? slower growth; longer time to reach sexual maturity, lower birth rate; higher death rate 2. Describe results for: Fig. 1 A Body mass increases through time, up to a point when it levels off. B The rate of increase in body mass is inversely related to population size. Fig. 2 Age to sexual maturity increases with increasing population size. Fig. 3 % of females reaching sexual maturity (having babies) declines with increasing population size. Fig. 5. Birth rate decreases and death rate increases with increasing population. When B = D, the population size stabilizes. 3 What is the effect of intraspecific competition on r? It lowers r. What is the effect of interspecific competition on K? It lowers K. Fig. 6. 16.9 How much is K of sp 1 reduced by one individual of competing sp 2? 4X…by all individuals? competition coefficient 1,2 = 4; so 4xN = 4x4 = 16 Figure 7. What is the value of 1,2? = 4 PART 2 1. How is niche breadth affected by intraspecific competition? increases breadth interspecific competition? decreases breadth What is a consequence for the community of a reduction in niche breadth due to competition? more species can exist in the community 2. What is meant by “the ghost of competition past”? Traits (niches) today may have developed from competition in the past. Today no competition is evident. How does the ghost make it hard to claim that competition explains the present-day niche space of a species? Competition is no longer occurring because past competition has resulted in a shift in niche to reduce competition. 3. What types of evidence are used to deduce that interspecific competition has occurred in the past? Explain each. A. niche separation; reduced or no niche overlap between species B. habitat shift: no habitat sharing by close competitors;weaker species has changed habitats. C. character displacement; traits evolve to be different when two competing species coexist. D. competitor exclusion; only one species exists where two existed in the past E. competitor release; competitor population size increases when a competitor has been eliminated. 6. Fig. 9.What happens to niche overlap when closely related species co-occur? Each species specializes on a unique part of the niche space. Fig. 10. What happens to habitat use when closely related species co-occur? One species moves to a different habitat How would you test the hypothesis that 2 species don’t use the same part of the habitat because of competition? remove species and see if other species moves in Fig. 11. 17.16, 17.18 How do traits of two species compare when they co-occur vs. when they do not? similar when non-co-occurring; different when co-occurring Fig. 12. 16.7 What is the Competitive Exclusion Hypothesis? 2 species can’t coexist on the same limiting resource; the better competitor will eliminate the weaker one. Fig. 12A. 16.10 Under what conditions can two species coexist? Two species can coexist if they are limited by different resources. Fig. 14. Krill, shrimp-like organisms, are fed on by all large marine animals. What does the killing of whales do to seal and penguin populations? They increase. How does this illustrate ‘competitive release’? Whales, seals, and penguins compete for same limited resource; with whales gone, others are released from competiton and increase in size. 7. Figure 15. 16.17 Starfish feed on species of herbivores (barnacles, mussels, limpets, and chitons). Does its presence control diversity of these herbivores? If…starfish control control competition among herbivores and maintain their diversity, then when fish is removed, dominant competitors exclude other species and reduce species number. In an experiment in which starfish were removed, the number of herbivore species rapidly declined from 15 to eight. How does the result relate to competition? The starfish normally keeps most dominant competitor at low population size, so other herbivores can persist. What is a keystone predator? Predator that has a disproportionate effect on species composition of a community. HOMEWORK DUE THURSDAY: PROBLEMS 3 AND 4 AT END OF PPT FOR COMPETITION; USE WORKSHEET ON WEBSITE = ICA 5 COMPETITION PROBLEMS