Ecology… in a Nutshell
advertisement

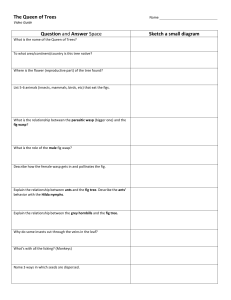
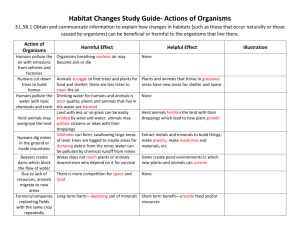
The Queen of Trees Name Video Guide Question and Answer Space What is the name of the Queen of Trees? To what area/continent/country is this tree native? Where is the flower (reproductive part) of the tree found? List 5-6 animals (insects, mammals, birds, etc) that eat the figs. What is the relationship between the parasitic wasp (bigger one) and the fig wasp? What is the role of the male fig wasp? Describe how the female wasp gets in and pollinates the fig. Explain the relationship between ants and the fig tree. Describe the ants’ behavior with the Hilda nymphs. Explain the relationship between the grey hornbills and the fig tree. Why do some insects cut through the veins in the leaf? What’s with all the licking? (Monkeys) Name 3 ways in which seeds are dispersed. Sketch a small diagram On your final exam, be prepared to address the following tasks or questions using examples from the video, The Queen of Trees. □ How the tree or other organisms within the video display evolution (provide 3-4 examples) using the following terms: □ How the tree or other organisms within the video display reproduction (provide 34 examples) using the following terms: □ How the tree or other organisms within the video display genetics □ How the tree or other organisms show energy and matter (provide 3-4 examples) □ List 4-5 various populations of organisms (i.e., species) mentioned in this ecosystem. □ List members of each trophic level shown in the video. □ Explain factors, including matter and energy, in the environment that limit the growth of plant and animal populations in natural ecosystems. □ Within the biodiversity of the tree’s environment, list 2-3 interdependencies among the organisms and explain how they depend on each other. In your journal, draw a large diagram that depicts the story in of the video, The Queen of Trees. Label your diagram using the following terms, and place a box around each term when used: Abiotic The Sycamore Fig (The Queen) Fig wasps Carbon Dioxide Water Biotic Seed Dispersal Fertilize Parasitic/Parasitism* Symbiosis* Predation Commensalism*