Conductivity
advertisement

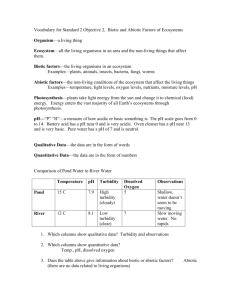
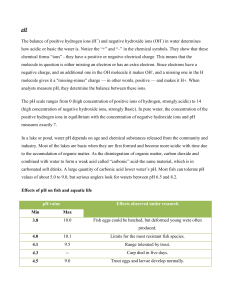
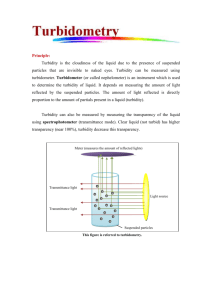
Conductivity Conductivity is a measure of the ability of water to pass an electric current. Where does it come from? Because we are testing the water in a drainage pipe, geology does not play a significant role in conductivity. Instead, salt and other forms of pollution are responsible for changes in conductivity. We have chosen to focus on salt and oil pollution because these are the main types of pollution that wash down roads and into the drainage pipe. Salt is spread on roads during the winter to melt snow and ice. Oil leaks from cars, trucks and buses. What does it do? Salt causes conductivity to go up. Oil causes it to go down. Why is it a problem? High salt concentrations can kill fish and other aquatic plants and animals. Oils can also harm these species. -Khuong Nguyen pH pH determines if the water is basic, acidic, or neutral. It has a scale of 0-14. A measurement of 7 indicates neutrality, which is a safe level of pH. In the pH scale 7-0 is increasingly acidic and 7-14 is increasingly basic. Acids come from factories and cars. Bases come from limestone. Acid is a problem because it causes deformities in young fish, which will reduce the chances for survival. It also causes metals to accumulate on gills of fish making it hard for them to breathe. It is a problem for every living thing because it causes the water to become too acidic for living. pH can be affected by acid rain. Acid rain is caused mostly by automobile and coalfueled power plant emissions. These are converted into nitric acid and sulfuric acid in the atmosphere. When nitric acid and sulfuric acid fall down on the earth in the form of rain then it is acid rain. Limestone act as a buffer to very acid precipitation. Alkaline limestone neutralizes the effect of acid. Alkaline limestone can be found in lakes and stream. Most of the areas affected by acid rain are downwind of the urban/industrial areas, where there is no buffering capacity in the form of limestone. Changes in the pH are very important because if the water is too acidic or too basic some species of fish can't live in it. In the spring, there are a lot of problems in lakes and streams because of melting acid snow. Very acidic lakes and streams cause leaching of heavy metals into water. Some of the metals include copper and aluminum. These metals accumulate on gills of fish making it hard for them to breathe. -Lam Pham Phosphate Where does it come from? Phosphate comes from some household detergents, human wastes, animal wastes, industrial wastes, and human disturbance of the land and its vegetation. What does it do? It stimulates the growth of rooted aquatic vegetation and it causes extensive growth of algae. Why is it a problem? It is a problem because it gets trapped in the sediment on the bottom of lakes and rivers and causes too much aquatic plant and algae growth. When these plants and algae die, bacteria decompose them, using up dissolved oxygen in the process. Who does it affect? It affects the fish because too much phosphate causes algae growth and low levels of dissolved oxygen for fish to breathe. It also makes the water unclear and less attractive for humans to use. What are safe levels? The safe levels of phosphate are from 0 mg/L to 0.05 mg/L. -Vinh Pham Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of the relative clarity of water. Turbidity is measured in nephlometric turbidity units. Sources of turbidity include solids such as clay, silt, plankton, industrial waste, sewage, and microorganisms. These solids come from soil erosion, waste discharge, urban runoff, algae growth, and abundant bottom feeders that stir up sediment from the bottom. Why is it a problem? As a result of turbidity, the water becomes warmer and the oxygen levels decrease. Turbidity increases as the result of suspended solids in the water that reduce the transmission of light. Because of this, photosynthesis is reduced. Who does it affect? As a result of turbidity the river loses its ability to support aquatic life. Sediments can clog fish gills, reduce growth rate, decrease resistance to disease, and prevent egg and larvae development. As particles settle they can smother the eggs of fish and insects. Particles that settle between rocks make unsuitable habitats for mayfly nymphs, stonefly nymphs, caddisfly larvae, and other insects. What are safe levels of turbidity? Natural turbidity levels in rivers vary from zero to 1.0 NTU. Except for very large, turbid, rivers, a change of 5-10 NTUs above previous levels for a river is a significant change. Measuring turbidity can also be used to assess the impacts of erosion and sedimentation over time and distance. -Nicole Shephard Velocity and Volume Velocity can be determined by a simple equation. This equation is velocity = distance/time. Velocity is important because increased velocity means increased turbidity. Heavy rain in industrialized areas, where the water is not absorbed but is simply washed over hard surfaces (pavement, gravel, etc.) and sent directly into a river, cause increases in velocity. Decreased velocity is caused by drought and the damming of rivers. The volume of flowing water is found using the manning equation. This is a complex equation that is used to find the volume of a partially filled pipe. Finding the solution of this equation includes finding the depth of the water in the pipe, the radius of the pipe, and the slope of the pipe. Volume is important because if you know the volume then you can figure the ratio of pollutant to water in parts per million. Change in velocity is caused by the amount of water running into the river. During times when it is raining and snow is melting the volume is greater but during times when there is dry weather or everything is frozen and the volume is less. -Erica Williams