Vocabulary for Standard 2 Objective 2, Biotic and Abiotic Factors of
advertisement
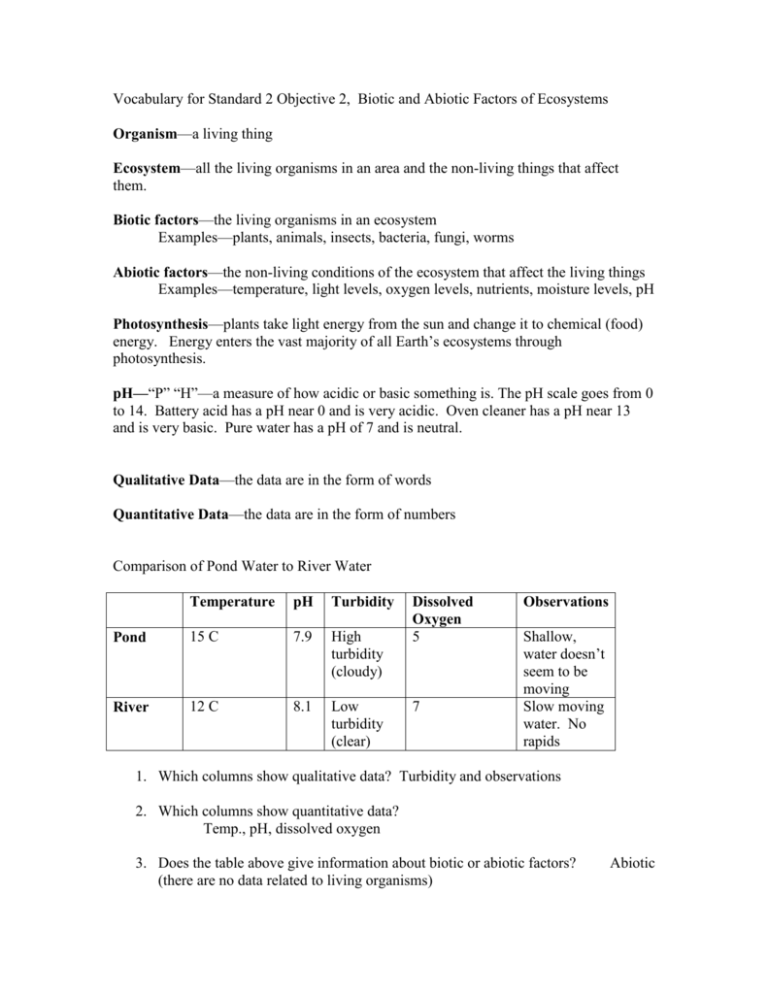
Vocabulary for Standard 2 Objective 2, Biotic and Abiotic Factors of Ecosystems Organism—a living thing Ecosystem—all the living organisms in an area and the non-living things that affect them. Biotic factors—the living organisms in an ecosystem Examples—plants, animals, insects, bacteria, fungi, worms Abiotic factors—the non-living conditions of the ecosystem that affect the living things Examples—temperature, light levels, oxygen levels, nutrients, moisture levels, pH Photosynthesis—plants take light energy from the sun and change it to chemical (food) energy. Energy enters the vast majority of all Earth’s ecosystems through photosynthesis. pH—“P” “H”—a measure of how acidic or basic something is. The pH scale goes from 0 to 14. Battery acid has a pH near 0 and is very acidic. Oven cleaner has a pH near 13 and is very basic. Pure water has a pH of 7 and is neutral. Qualitative Data—the data are in the form of words Quantitative Data—the data are in the form of numbers Comparison of Pond Water to River Water Temperature pH Turbidity Pond 15 C 7.9 High turbidity (cloudy) River 12 C 8.1 Low turbidity (clear) Dissolved Oxygen 5 7 Observations Shallow, water doesn’t seem to be moving Slow moving water. No rapids 1. Which columns show qualitative data? Turbidity and observations 2. Which columns show quantitative data? Temp., pH, dissolved oxygen 3. Does the table above give information about biotic or abiotic factors? (there are no data related to living organisms) Abiotic