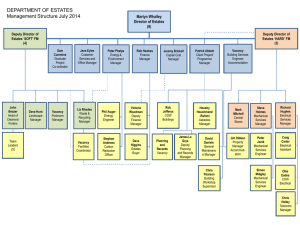
Building and Refurbishment Projects
advertisement

University of Leeds Guidelines on Investment Decision Making: Building and Refurbishment Projects Advice may be obtained from Clive Smith (Treasury Manager) E-mail: c.r.smith@adm.leeds.ac.uk Introduction Sound decision-making processes are a fundamental aspect of good governance and management in any organisation. This requires a clear identification of the need or problem to be solved. It also requires objective evaluation of the alternative options, if objectives are to be met and value for money secured. The outcome of such decisions may have a significant impact on the University, both in the short and long-term. Decisions should be justifiable: the reasons for them should be analysed and supported by evidence. To obtain maximum value from the evaluation process it is necessary to understand the assumptions on which the decisions are based, and also the circumstances that might lead to a different outcome. Consequently the assessment of risk and uncertainty will be as important as the base estimates for each option. The University must follow both Treasury and HEFCE guidelines1 and is ultimately accountable to the Committee of Public Accounts on the use of public monies. In addition, grant awarding bodies require that the University demonstrates good practice has been followed in respect of investment decision making. This is particularly so when resources are scarce and when the University has to establish value for money. The HE Sector was subject to major criticism in 1998, following the publication of the Committee of Public Accounts report on the management of building projects in English higher education institutions (“HEIs”). This report arose from a National Audit Office study into major capital projects. A key observation was that HEIs did not set out clearly the objectives for a project, which meant it was unlikely that an accurate assessment of the costs and benefits could be made. A crucial element in the decision making process is the identification of objectives and their link with higher level strategy. The following guidelines combine the University and external requirements on investment decision making. An illustrative case study is available on the Finance web site. 1 Hefce Good Practice Guidance: Investment Decision Making (April 2003/17) Investment Decision Making in the University of Leeds These guidelines relate to all University building and refurbishment projects except minor works projects. For building and refurbishment projects costing up to £250,000 Estates will complete a Project Detail Sheet. This should include as a minimum: identification of need, outline cost, funding and benefits. The completed Sheet should be signed by the Faculty Dean or Service Director, to evidence their agreement, and approval given by the Director of Estates. For building and refurbishment projects costing between £250,000 and £1 million, a Short Business Case should be prepared the Faculty / Service Area Finance Manager in conjunction with Estates. The Case should include the detailed academic case (including consideration against the ten key criteria derived from the University Strategy Map, which are shown at Appendix 1), an appraisal of the build options (including NPV) and identification of the impact on the University and School/Service area reserves. The completed Case should be signed by the Faculty Dean or Service Director as project sponsor, to evidence their agreement, prior to going to Capital Group. Capital Group2 approves all projects costing between £250,000 and £1 million, unless they consider that a particular project warrants a full evaluation, whereupon it is treated the same as those over £1 million (see below). For all building and refurbishment projects costing over £1 million, the University undertakes a six-stage evaluation process to ensure they are financially viable and fit both the Estates strategy and the longer-term academic direction of the University. The six stages, which are detailed below, are as follows:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identification of need Development of the prima facie case Development of the full business case Formal approval Delivery and implementation Post-project review The Vice-Chancellor’s Executive Group (“VCEG”) will consider all building and refurbishment projects over £1 million. VCEG can give formal approval for projects up to £3 million but projects over this must be approved by Council. VCEG, in scrutinising requests, are advised through decisions reached by Capital Group. The rationale for including all projects above the threshold, irrespective of funding source, is to cover areas where University funding maybe required, and more importantly, to enable a risk assessment to be carried out as to any potential effect on the University Accounts. In addition to the University’s guidelines, any additional requirements from HEFCE and/or other funding agencies must be met. 2 Capital Group is chaired by the Deputy Vice-Chancellor and reports to VCEG. Membership comprises the Director of Estates, the Finance and Commercial Director, the Treasury Manager, the Estate Planning and Information Manager and the Estate Services Finance Manager. Quarterly the Capital Group meeting is extended to include the Pro_Vice_Chancellors and the Deans of Faculty. Stage 1: Identification of Need The University determines that there is a need to be satisfied (or a problem to be solved) through strategic/ annual planning of Estates, Faculty or Service plans. This need must be clearly defined, since it will form the basis of the whole evaluation. As the evaluation develops it may call into question whether the need actually exists, and if it does, the University should ensure it cannot be met from re-allocating existing resources. Confirmation of need is decided by VCEG, Strategy Group or annual Faculty/ Service area reviews and it will be reflected in the annual 5-year capital expenditure forecast and Estate Strategy, prepared by Estates. Stage 2: Development of the Prima Facie Case The prima facie case comprises two essential elements: the academic case and the initial option appraisals. It is developed within the Faculty or Service area in conjunction with Estates and the Treasury Manager. The Faculty Dean or Service Director (or their nominee) is the person who “champions” the project, referred to as the “Project Sponsor”. Estates maintain a Target Dates schedule which flags the key dates in the approval process and highlights the required lead time. The project sponsor is responsible for the preparation of the academic case and issues to consider are attached at Appendix 2. Identification of the various build options should be led by Estates in conjunction with the project sponsor. It is important to consider as wide a range of options as possible, including a “do nothing” option as the “base case”. Where doing nothing is not an option, for instance due to statutory or regulatory changes, then a “do minimum” option should be included as the base case. Some options can be discarded at an early stage, if there are good grounds for doing so, but the reasons for rejection should be stated. The project sponsor, in conjunction with Estates, should then consider each option against the ten key criteria, derived from the University Strategy Map, which identify the strategic context and objectives. These objectives set out what is to be achieved and provide the criteria against which the various options will be judged, and against which the success of the project will be evaluated. The prima facie case is further developed by the project sponsor, with assistance from Estates, to include identification of the outline cost and funding, sustainability and recurrent business plan. Initial appraisal of the various build options is undertaken by Estates in conjunction with the Faculty/ Service Area Finance Manager. An evaluation should contain a list of the factors to be considered in each option, even when it is not possible to quantify them. It should assess, and where possible quantify and value, all benefits and costs (including ongoing service and maintenance costs). The values should be realistic and objectively assessed, as being over-optimistic (or overly pessimistic) about values or dates can lead to the wrong conclusion. Investment appraisals should be produced for each option, with a calculated net present value (“NPV”)3. At this stage the project sponsor, in conjunction with the Director of Estates, should agree the preferred option or options, which as well as meeting the criteria, must also be affordable and viable. The project sponsor, in conjunction with Estates, takes responsibility for the prima facie case, which must include clearly articulated financial assumptions and show the range of options open to the University, and the logic behind the selection of the preferred option(s). The project sponsor submits the prima facie case to Capital Group: it should be reviewed by them (including project scoring using the criteria matrix attached at Appendix 3) and VCEG advised accordingly. VCEG review the prima facie case and inform Council where they support the case and project cost exceeds £3 million. At this stage VCEG may authorise the commitment of fees associated with the project, as recommended by Estates. A flowchart, showing development of the prima facie case, is attached at Appendix 4. Stage 3: Development of the Full Business Case The project sponsor develops the full business case, for the preferred option(s) and the base case, with support from Estates and the Treasury Manager. The full business case should be forwarded to the Treasury Manager for their review at least two weeks prior to the Capital Group meeting.The amended case should then be forwarded to Capital Group,four working days before the meeting. If Capital Group approves the business case, it should be submitted to VCEG for their decision at least four weeks before Council. A flowchart showing development of the full business case is attached at Appendix 5. The following steps should be undertaken in preparing the full business case: 3 Ensure the original assumptions remain valid. Consider alternative procurement routes for the realistic options, each of which will have different costs, benefits and risks. Consider the alternative financing options and their associated costs. Is there third-part funding available, and if so are there any “strings attached” and/or any time constraints? How does the forecast funding pattern compare with the spending pattern? What is the internal funding requirement and how is it to be met? What is the impact on the University cashflow and would this require any short or long-term borrowing? Reassess the relative costs, benefits, timings, risks and uncertainties of each of the realistic project options, together with the base case, using investment appraisals and NPV calculations. The discount rate to be applied is that recommended by Hefce (currently 3.5%). This is a real rate and it reflects the “social time preference rate” of money- the fact that normally people would rather have cash now than later, and would prefer to pay bills later rather than sooner. It must not be confused with inflation. Consider the risks and uncertainties associated with the different combinations of project, procurement and funding options. Undertake sensitivity analysis of the key assumptions, identify those that are critical to success and confirm the preferred solution. Identify the impact of the preferred solution on the University’s financial forecasts. In particular on the School/Service area reserves and the University Income & Expenditure Account, reserves and cashflow. If the preferred solution appears unaffordable then the assumptions will need revisiting. Plan for monitoring during implementation and post-project review upon completion (where relevant), including putting in place mechanisms to enable monitoring and measurement of progress, and specification of the monitoring data which will be collected in the course of implementation. Capital Group should be involved in the preparation of this section and, both project sponsor and Capital Group should understand and agree the timing of such reviews and the criteria and indicators being used to assess project outcomes. The project sponsor forwards the full business case plus all appendices, to the Treasury Manager for review at least two weeks prior to the Capital Group meeting. The Treasury Manager passes any comments back to the project sponsor who then forwards the amended case plus all appendices, to Capital Group for their review. Once Capital Group is satisfied, the project sponsor will be asked to submit a paper, plus key appendices, to VCEG (if the project costs more than £3 million this will be a draft Council paper and an illustrative example is used in the case study on the Finance web site). If approved by VCEG, and the project costs more than £3 million, the project sponsor will need to submit a first version of the Council paper, plus key appendices, to the University Secretary at least 7 days ahead of the Council meeting. The approving committee, VCEG or Council, need to understand the logic behind the choice of preferred solution, and the risks and sensitivities associated with it, therefore the business case should be sufficiently detailed to enable this. It should show clearly the need or problem to be solved, which project option represents the best value and whether that option is affordable. If after approval any of the assumptions are invalidated, then the approving committee should be informed, as this may alter the decision reached. As a general rule the project sponsor should not bid for external funding until approval of the full business case. It is however recognised that in certain circumstances the timescales involved do not allow production of the business case in advance of the bid, and therefore, subject to reporting to Council, the ViceChancellor can approve such a bid. The business case must follow and be approved prior to announcement of funding, and in the event of a failed bid, there is no supposition that the University will fund the gap. Stage 4: Formal Approval VCEG are authorised to approve projects costing up to £3 million based on the paper plus key appendices. For projects costing more than £3 million, which are supported by VCEG, the project sponsor should submit the final paper plus key appendices to Council for their approval. An illustrative example is used in the case study on the Finance web site. Stage 5: Delivery and Implementation Estates delivery is ultimately the responsibility of the Director of Estates, but day to day implementation is undertaken by an Estates Project Manager. Business delivery is ultimately the responsibility of the Faculty Dean or Service Director, but responsibility for day to day implementation can be delegated. Every project over £1 million should have a steering group made up of interested parties which undertakes monitoring of the project and reports to Capital Group by exception. Any project under spends will automatically be released and cannot be used to improve the project specification without prior approval from Capital Group. Stage 6: Post-Project Review Post-project review (“PPR”) is an essential aid to improving project performance, achieving best value for money, improving decision making and learning lessons. PPR is mandatory for all projects costing more than £3 million4 and the project sponsor should understand both the timing of such reviews and the criteria and indicators being used to assess project outcomes. The PPR has three parts:The first part will be undertaken by Estates one year after completion and specifically cover the Estates delivery. The report should go to Capital Group. The second and third parts are interim and final reviews of the business delivery and should be undertaken by the Treasury Management section in conjunction with the Faculty/ Service Finance Manager two years and five years respectively after completion. They should test the assumptions set out in the business case and cover: the extent to which the objectives were met; any time and cost overruns; comparison of estimated and actual costs, benefits and risks, and any implications for future decisions. The report should be reviewed by Capital Group then submitted to the Faculty Management group (“FMG”) and Audit and Risk Management Committee. 4 The limit was £1 million until it was increased at Council on 16 th November 2006. Appendix 1: The Ten Key Criteria The ten key criteria, split by responsible party and showing the Strategy Map reference, are as follows:Project Sponsor 1. Academic development and performance (in research) Deliver international excellence in all areas of our research (T4) Develop selected peaks that deliver world-leading performance (T5) Aggressively grow research income (F1) Proactively attract and retain high quality staff (S3) 2. Student support and experience Provide an exceptional student experience (T8) 3. Academic development and performance (in learning and teaching) Deliver excellent and inspirational learning and teaching (T7) Provide an exceptional student experience (T8) 4. Internationality and enhance enterprise and knowledge transfer Develop, promote and publicise our international profile (T1) Increase recruitment and participation of international students (T2) Develop a strong international research culture (T3) Enhance performance and value derived from enterprise and knowledge transfer (T10) Contribute to the enrichment of society on a local to global scale (T11) 5. Financial sustainability – business plan and option appraisal Manage resources to deliver strategic priorities (F3) Ensure all faculties and schools are able to generate surpluses for reinvestment (F4) 6. Making it happen – logistics/ timing and leadership/ risk management Improve core systems and processes (E4) Manage organisational performance (E5) Estates 7. Existing business and fitness for purpose, backlog maintenance Provide first class facilities (E2) 8. Optimum space utilisation Provide first class facilities (E2) Manage resources to deliver strategic priorities (F3) 9. Campus vision, best location/ fit Provide first class facilities (E2) Capital Group 10. Source of capital funds Manage resources to deliver strategic priorities (F3) Grow additional sources of profitable income to invest in our future (F2) Ensure all faculties and schools are able to generate surpluses for reinvestment (F4) Appendix 2: Preparation of the Academic Case Suggested format / contents: 1. Short summary 2. Context setting: Faculty, School or Service Vision. Links to Strategy Map 3. Explanation of the need to be satisfied. This may include information on one or more of the following :a. Need for expansion e.g. student numbers, new programmes, increased research, staffing etc b. Quality of facilities Offensive or defensive move e.g. growing markets or protecting markets? Supporting market analysis? Quality as well as quantity of students. Relevant peer university comparatives. 4. Identification of the benefits of investment 5. Consequences of doing nothing – the base case. University of Leeds Project Name: Prepared by: Investment Decision Making Department: Key Criteria Scoring Matrix Faculty/ Service area: Date: Reviewed by Capital Group: Appendix 3 Option Scoring Assessment Criteria Option Scoring (Weighted) Weighting 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 Project Sponsor 1 Academic Development and Performance (Research) 10 0 0 0 0 0 2 Student Support and Experience 10 0 0 0 0 0 3 Academic Development and Performance (L&T) 10 0 0 0 0 0 4 Internationality and enhance Enterprise/ Knowledge Transfer 5 0 0 0 0 0 5 Financial Sustainability- Business Plan and Option Appraisal 10 0 0 0 0 0 6 Making it Happen- Logistics/ Timing/ Leadership/ Risk Mgmt 10 0 0 0 0 0 7 Existing Business and Fitness for Purpose, BLM 20 0 0 0 0 0 8 Optimum Space Utilisation 10 0 0 0 0 0 9 Campus Vision, best location/ fit 5 0 0 0 0 0 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Estates Capital Group 10 Source of Capital Funds 100 OPTION SCORES OPTION RANKINGS Appendix 4: Development of the Prima Facie Case Identify need or problem Need or problem reflected in annual 5-year Capital Expenditure Forecast and Estate Strategy Prepare timeline Prepare academic case Identify options Evaluate options against criteria matrix Discard options Prepare Initial option appraisals Identify preferred solution(s) Submit case to Capital Group Not supported Submit case to VCEG Not supported Proceed to full business case Appendix 5: Development of the Full Business Case Confirm assumptions of preferred option(s) plus base case Consider alternative procurement routes for the realistic options, and associated timescales Assess alternative financing options and their associated costs Select a preferred financing solution Prepare risk allocated option appraisal Undertake sensitivity analysis and confirm preferred solution Identify the impact of the preferred solution on the University's financial forecasts and assess sustainability Plan for monitoring during implementation and post project review Submit full business case plus all appendices to Treasury Manager Forward assessment and full business case plus all appendices to Capital Group Not supported Submit paper (draft Council paper) plus key appendices to VCEG Not Approved < £3m Submit paper plus key appendices to Council Not Approved Monitor implementation and keep assumptions under review Changed Circumstances Post Project Review (Estates Delivery) Post Project Review (Business Delivery) Appendix 6: Responsibilities in Investment Decision Making The project sponsor will: Review the Project Detail Sheet or Short Business Case, and sign as evidence of agreement, for projects costing less than £250,000 or £1 million respectively. Prepare the academic case for the faculty/ service area and liaise with Estates to identify the associated building and refurbishment needs. Prepare a timeline to project approval stage with agreement from Estates. Develop the prima-facie case with assistance from Estates and Finance, and submit to Capital Group. Develop the full business case with support from Estates and Finance, and submit to the Treasury Manager at least two weeks prior to Capital Group. Submit Paper (plus key appendices) to VCEG (and Council where required). Sit on the project steering group which receives reports from the Estates Project Manager. Assist Estates with the Estates delivery PPR. Assist with the business delivery PPR two years and five years after completion (if required). Estates will: Undertake meetings with faculties/ service areas to identify building and refurbishment needs and reflect in the annual 5-year capital expenditure forecast and Estate Strategy. Maintain the Target Dates schedule. Undertake any build option appraisals within the prima facie case in conjunction with the project sponsor. Recommend the fee commitment for projects going to the full business case. Provide advice to the project sponsor on the feasibility of the selected option in the full business case. Undertake the project management issues of construction. Undertake the Estates delivery PPR one year after completion. Treasury Manager will: Assist identification of funds and preparation of the prima facie and full business cases when requested. Review the full business case plus all appendices and advise the faculty/ service area of any proposed amendments. Undertake the business delivery PPR two and five years after completion, with assistance from the project sponsor. Capital Group will: Review the prima facie case and advise VCEG accordingly. Review the full business case plus all appendices and advise VCEG accordingly. Receive the Estates delivery PPR report. Review the Business delivery PPR report and forward to FMG. VCEG will: Review the 5-year capital expenditure forecast and Estate Strategy and, once agreed, forward to Council for approval. Review prima facie cases and, where supported, agree the fee commitment and, advise Council, where project cost exceeds £3 million. Receive paper (draft Council paper where cost exceeds £3m) plus key appendices for approval. Council will: Approve the 5-year capital expenditure forecast and Estate Strategy. Receive notification of prima facie cases where project cost exceeds £3 million. Receive Council paper plus key appendices for approval for projects over £3 million.