Earthquake Epicenter Triangulation Worksheet
advertisement

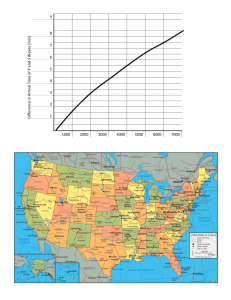
“Locating the Epicenter of an Earthquake” In order to practice triangulation we will use data from three separate earthquakes and locate three epicenters. Table 1 shows the distance of three separate earthquakes from each of the recording stations provided on the data map. Each earthquake is labeled by the date on which it occurred (October 9, October 16, and March 17). Section I : (In complete sentences!) 1. In your own words, describe what is meant by the process of “triangulation.” ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ _______________________________ 2. What is the difference between the “focus” of an earthquake and the “epicenter” of an earthquake? ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ 3. What is the “radius” of a circle? ____________________________________ ____________________________________ 4. Draw and label a the radius on the circle to the right: Procedure: 1. Start by locating the epicenter for the October 9th Earthquake. 2. Notice that the map key shows us that 1 cm = 1 mile (mi.) 3. Using your ESRT ruler set your compass to the width of 7.5mi to represent the distance Van Nuys is the to epicenter. 4. Place the center of your drawing compass on the point of the map that says Van Nuys. 5. Draw the circle (epicenter distance) accordingly. 6. Repeat this procedure for the two remaining recording station measurements. 7. Locate the city nearest the epicenter. (Recall that the epicenter is located where the three circles intersect!) 8. Repeat steps 1-9 for the data from the other 2 earthquakes (October 16th, & March 17th) DATA TABLE 1: * 5. What is the radius of this circle in centimeters? (Round to the nearest tenth) __________ cm 6. If the center of the circle was a seismic station and 1cm = 1mi what would be the distance this seismic station is from the epicenter? ____________mi 7. When the three circles are drawn, what occurs at the location where they all intersect? ____________________________________ ____________________ (Hint: This Table is also found on your Map Worksheet) Recording Station Van Nuys Westwood Simi Valley City Nearest to Epicenter October 9th Quake October 16th Quake March 17th Quake 7.5 mi 8.5 mi 8.5 mi 4.0 mi 4.5 mi 8.0 mi 4.0 mi 8.0 mi 11.0 mi Section III: Analysis and Conclusion 1. Which station was closest to the epicenter of the March 17th Earthquake?___________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Which city probably felt October 16th Earthquake last? Why did you choose this answer? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Which earthquake occurred directly along a fault line?_________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. Why must we use data from at least three recording stations to locate an epicenter? ___ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Thinking: Besides proximity (how close something is) to an epicenter, what other factors might contribute to the amount of destruction at a certain location? Give at least 2 examples. __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ October 9th Quake Section II: 2. Explain why S-waves from this earthquake were not directly received on the opposite side of Earth. 1. Which part of this seismogram is used to find the distance to the epicenter of the earthquake? (1) P-wave arrival time, only (2) S-wave arrival time, only (3) difference in the arrival time of the Pwave and S-wave (4) difference in the height of the P-wave and S-wave __________________________________________ __________________________________________ _________________________ 3. The first S-wave arrived at a seismograph station 11 minutes after an earthquake occurred. How long after the arrival of the first P-wave did this first Swave arrive? (1) 3 min 15 s (3) 6 min 05 s (2) 4 min 55 s (4) 9 min 00 s October 16th Quake Section III: 1. In the United States, most of the major damage expected from a future earthquake is predicted to occur near a (1) divergent plate boundary, only (2) convergent plate boundary, only (3) mid-ocean ridge and a divergent plate boundary (4) transform plate boundary and a hot spot 2. Which New York State location has the greatest risk of earthquake damage? (1) Binghamton (2) Plattsburgh (3) Buffalo (4) Elmira