molecular characterisation methods
advertisement

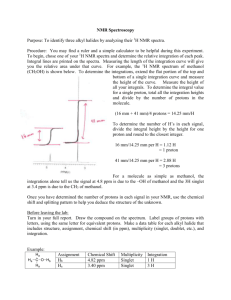
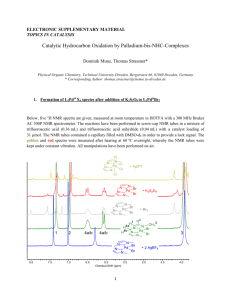
NGEE ANN POLYTECHNIC FEBRUARY 2009 EXAM School of Life Sciences and Chemical Technology (Certificate in Chemistry) Time Allowed: 2 Hours MOLECULAR CHARACTERISATION METHODS (008197) INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: 1. Please read instructions carefully. 2. Write ALL answers in the answer booklet provided. 3. This paper consists of 7 questions, and all questions should be attempted. 4. This paper consists of 7 pages including this cover page. Please check carefully to make sure your set is complete. 5. The following information may also be used: Atomic weights: C: 12; H: 1; O: 16; N: 14 Formula for number of rings and double bonds for a molecule CxHyOz: No of rings+double bonds = x+1- (y/2) MCM (CCI) 1 Feb 2009 Answer all questions Question 1 Identify the circled pair of protons (Fig 1) as unrelated, homotopic, enantiotopic or diastereotopic and give your reasons(s). (3 marks) OH H H3C CH3 H H H H Figure 1 Question 2 Predict and sketch the coupling pattern of the circled proton (Fig 2) in the proton NMR of the compound below and give your reasoning. (5 marks) Cl H H Figure 2 Question 3 Draw the predicted detectable fragments in the mass spectrum of the ketone below (Fig 3) if it undergoes (12 marks) (a) the McLafferty rearrangement (b) alpha cleavage Note: You do not need to calculate the molecular weights of the fragments. H CH3 O CH3 Figure 3 Question 4 You have a bottle labelled ‘benzene’ but you suspect it contains toluene (Fig 4) instead. How would you use IR, proton NMR and 13-C NMR to tell which chemical it is? Explain your answers fully. (15 marks) CH3 Benzene Toluene Figure 4 MCM (CCI) 2 Feb 2009 Question 5 Compound X has the empirical formula C4 H10 O Study the IR, 13-C, proton NMR and mass spectra of compound X (Fig 5a-c) Identify compound X. Explain your reasoning and assign as many peaks in the 13-C and proton NMR spectra as you can. (20 marks) Spectroscopic Information for compound X MS (Figure 5a): m/z 74 IR (Figure 5b): 3328 (br, s); 2958 (s); 1471 (m); 1387 (m); 1247 (w);1042 (s) cm-1 13C NMR (Figure 5c – on top): 69.2, 30.8, 18.9 ppm (NB – the triplet at about 75 ppm is the solvent CDCl3) Proton NMR (Figure 5c – below): 3.4 ppm (2H, doublet of doublet, J=4.9, 2 Hz); 2.4 ppm (1H, triplet, J=2 Hz); 1.75 ppm (1H, multiplet); 0.92 ppm (6H, doublet, J=5.5 Hz) Question 6 Compound Y has the empirical formula C8 H10 O Study the IR, 13-C, proton NMR and mass spectra of compound Y. (Fig. 6a-c) Identify compound Y and explain your reasoning. (20 marks) Spectroscopic Information for compound Y MS (Figure 6a): m/z 122 IR (Figure 6b): 3060 (w), 3047 (w), 2981 (m), 1602 (s), 1498 (s) cm-1 13C NMR (Figure 6c – on top): 158.9 (v weak), 129.4, 129.5, 114.5, 63.2, 14.8 ppm (NB – the triplet at about 75 ppm is the solvent CDCl3) Proton NMR (Figure 6c – below): 6.8-7.4 ppm (5H, multiplet); 4.0 ppm (2H, quartet, J=4 Hz); 1.4 ppm (3H, triplet, J=4 Hz) Question 7 Compound Z has the empirical formula C6 H12 O Study the IR, 13-C, proton NMR and mass spectra of compound X. (a) Identify compound Z. Explain your reasoning. (b) Assign the peaks in the mass spectrum at m/z 43, 58 and 85 (25 marks) Spectroscopic Information for compound Z MS (Figure 7a): m/z 100, 85, 58, 43 IR (Figure 7b): 2974 (m), 1714 (vs) cm-1 13C NMR (Figure 7c – on top): 208.5 (v weak), 52.8, 30.3, 24.7, 22.5 ppm (NB – the triplet at about 75 ppm is the solvent CDCl3) Proton NMR (Figure 7c – below): 2.32 ppm (2H, doublet, J=4 Hz); 2.15 ppm (1H, multiplet); 2.12 ppm (3H, singlet); 0.95 (6H, doublet, J=5 Hz) -END OF PAPER - MCM (CCI) 3 Feb 2009