Sure-Vue Select Staph ID
advertisement

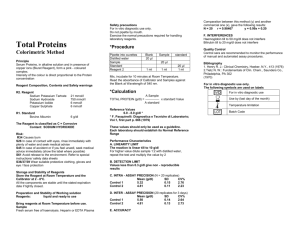
Russell County Hospital 1610 Dowell Road Russell Springs, KY 42642 270-866-4141 DEPARTMENT: Laboratory POLICY/PROCEDURE TITLE Sure-Vue Select Staph ID POLICY/PROCEDURE NUMBER: 400-PE-MIC-101A Issued: 5/10/06 Revised: Supercedes: 400-PE-MIC-101 Prepared by: R. Johnson Approved: Reviewed: Medical Director Approved: Reviewed: Laboratory Director _________________________________________________________________________________________________ I. PRINCIPLE. The Sure-Vue Select Staph ID latex slide agglutination test is a rapid test for the detection of both clumping factor and protein A that are used in the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. II. SPECIMEN. A. Use staphylococcal isolates freshly grown (18-36 hr incubation) on nonselective media, such as blood agar (BAP). B. HANDLE ALL BACTERIAL SPECIMENS AS POTENTIALLY BIOHAZARDOUS AND USE STANDARD PRECAUTIONS IN ACCORDANCE WITH HOSPITAL AND LABORATORY SAFETY AND INFECTION CONTROL POLICIES. III. REAGENTS/SUPPLIES/EQUIPMENT. A. Protective gloves and other appropriate PPE. B. Timer. C. Microbiological loop or wooden mixing sticks. D. Quality control organisms. E. Test kit containing: 1. Two vials of Sure-Vue Select Staph ID reagent (plasma-coated latex particles suspended in buffered saline). 2. Applicator sticks. 3. Disposable test slides. F. Storage and handling. 1. HANDLE ALL REAGENTS, CONTROLS, AND CONTAMINATED MATERIALS AS POTENTIALLY BIOHAZARDOUS AND USE STANDARD PRECAUTIONS IN ACCORDANCE WITH HOSPITAL AND LABORATORY SAFETY AND INFECTION CONTROL POLICIES. Page 1 of 3 Russell County Hospital Policy/procedure name: Sure-Vue Select Staph ID Policy/procedure number: 400-PE-MIC-101A Issued: 2/1/06 Revised: NA _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Store reagents at 2-8C. Stable until expiration date on label if store properly. Return to refrigerator after use. 3. Do not use reagent test kit if auto-agglutination is evident or if the expiration date has been exceeded. IV. CALIBRATION. NA. V. QUALITY CONTROL. A. Quality control must be performed at least once each day of patient testing, and when a new lot number or shipment is put into use, using the following organisms,: 1. Positive control - S. aureus strain such as ATCC 29213. 2. Negative control - S. epidermidis strain such as ATCC 12228 B. QC organisms must be tested in the same manner as unknown test organisms. Do not accept test results without valid QC results. Should the reagents fail to perform to standard, discard and use a new kit. Document all QC results in the LIS. C. HANDLE ALL CONTROL ORGANISMS AND CONTAMINATED MATERIALS AS POTENTIALLY BIOHAZARDOUS AND USE STANDARD PRECAUTIONS IN ACCORDANCE WITH HOSPITAL AND LABORATORY SAFETY AND INFECTION CONTROL POLICIES. D. To perform QC: 1. Add one drop of reagent to a slide to check for auto-agglutination. None should occur. 2. Use the positive control organism to obtain agglutination. 3. Use the negative control organism to obtain no agglutination VI. PROCEDURE. A. Use only fresh control and test organisms (18-24 hours old). B. Prior to each use, suspend the reagent by gentle inversion for a few seconds. Place a drop in each of the test circles to be used. C. Using a separate applicator stick for each test well, pick up 2-5 colonies of identical morphology (pick up fewer colonies if they are large and more colonies if they are small). D. Deposit and spread the colony material onto a dry portion of the well, next to the droplet of reagent. Mix the bacteria into the reagent droplet to obtain a homogenous suspension covering the entire well. E. Rotate the slide for 25 seconds observing for red clumps. Positive reaction will usually take 5-20 seconds. F. Repeat for additional test organisms. VII. CALCULATIONS. NA. Page 2 of 3 Russell County Hospital Policy/procedure name: Sure-Vue Select Staph ID Policy/procedure number: 400-PE-MIC-101A Issued: 2/1/06 Revised: NA _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VIII. REPORTING RESULTS. A. Interpretation: 1. Positive – red clumps of agglutination, accompanied by clearing of the opaque background visible to the unaided eye. 2. Negative – little or no agglutination occurs. 3. Rough or stringy reactions appear as red specks or string aggregates and should be interpreted as positive when accompanied by a clearing of the background or negative when accompanied by an opaque pink (no clearing) background. 4. Auto-agglutination is indicative of contamination or deterioration. The test is considered invalid if either stock control gives an unexpected result or the expiration date of the reagent has been exceeded. B. Record each test result as positive or negative in the LIS. IX. PROCEDURE NOTES. X. LIMITATIONS. A. Some streptocci possess plasma protein binding factors, and several species, such as Enterbacteriaceae, non-specifically agglutinate latex particles. Gram stains should be performed to insure that only organisms with staphylococcal morphology are tested to eliminate potential interference by these organisms. B. Media containing high salt concentrations inhibit protein A production and can cause false negative reactions. Cultures older than 48 hours will frequently yield rough, stringy reactions that may be non-interpretable or false. Stock cultures should be subcultured to sheep blood agar overnight before use. C. Rough strains of staphylococci and yeasts frequently cause non-specific reactions and should be screen before testing with this method. Gram stain a representative colony to confirm morphology and Gram stain characteristics. D. Perform other tests such as catalase to rule out non-staphylococci species. XI. REFERENCE. Product insert Sure Vue Select Staph ID Screening/Identification System, Fisher Health Care, Inc. Houston, TX 77038, 1-800-640-0640, 1-877-500-2049, Rev. 02N0326. Page 3 of 3