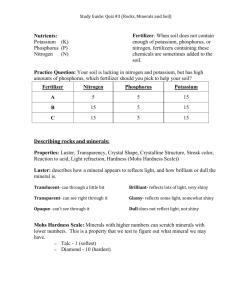
potassium nitrogen
advertisement

Soil Fertility and Plant Nutrition 1. (1) Define nitrification and denitrification. What are the factors affecting these reactions in soils? (2) Describe some land management practices that can help in minimizing nitrogen losses. 2. (1) What is the efficiency of fertilizer? (2) Why the efficiency of P fertilizer is so low in soil? (3) What are the practical ways of improving the agronomic effectiveness of P fertilizer? 3. What is the different between active absorption and passive absorption, and describe the mechanism for each of them. 4. (1) Define the term ” organic farming”. (2) Try to compare the advantages and disadvantages of organic farming to convenient farming. 5. What mechanisms are thought to account for (1) N fixation, (2) P fixation and (3) K fixation in soil? 6. (1) List the benefits of proper liming of strongly acidic soil on nutrient availability and plant growth. (2) What effects will the liming have on the retention of phosphorus and potassium in strongly acidic soil? 7. (1) What causes soil to have negative and positive charges ? (2) How does CEC affect nutrient availability? 8. Describe a set of conditions that are believed to result in serious denitrification losses. Are there practical ways of largely eliminating such losses? If so, identify them. 9. What is luxury consumption of potassium? Is it a serious problem under most soil and cropping conditions? How can it be minimized? 10. (1) What soil properties determine the pH buffer capacity of strongly acidic soil? (2) There are many lime materials sold in the market, how to select the best lime material to correct soil acidity of acid soil? 11. Name some advantages and disadvantages of deficiency symptoms, plant analysis, and soil testing for detecting plant-nutrient needs. 12. (1) What ways may nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium be lost other than by crop removed? (2) What are the practical ways of improving the agronomic effectiveness of N fertilizer? 13. How would you evaluate the quality of organic fertilizers to be used to improve soil quality and soil productivity? Explain the reasons. 14. Mixing straight fertilizer not only supplies several kinds of nutrients that crops need, but also improves the efficiency of fertilizer. However, but not all chemical fertilizers can be mixed. The mixing type of straight fertilizer can be divided into three categories, which are (1) Can be mixed; (2) Mix while using; (3) Can not be mixed. Please indicate which category each of the following fertilizer groups belongs to and explain why. (1) Superphosphate and lime (2) Calcium nitrate and fresh manure (3) Grounded apatite powder and ammonium sulfate 15. Generally speaking, the uptake percentage of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by crops in a seasonal are only about 40, 10 and 50%, respectively. Thus, how to raise efficiency of fertilizers has become a major subject of agricultural science. Answer the following questions. (1) If the fertilizer used is not absorbed and utilized by crop, what kind of type it will be? Where it would go? (2) Provide the concrete and feasible methods, which would enhance the efficiency of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in fertilizers. 16. The efficiency of fertilizer may be influenced by soil properties, climatic conditions, characteristics of crop, cultivating management and fertilizer nature. Please demonstrate individually their influences. 17. Define and explain the following terms. Then compare the difference each of the following groups. (1) Absorption and adsorption (2) Humic acid and fulvic acid (3) Infiltration and percolation (4) Active acidity and potential acidity 18. Define and explain the following terms. Then compare the difference each of the following groups. (1) Ammonification and ammoniation (2) Immobilization and mineralization (3) Denitrification and nitrification (4) Antagonism and synergism 19. The foliar fertilization has been widely used. Please answer the following questions. (1) What are the advantages of foliar fertilization? (2) While applying foliar fertilization what should be put into consideration in terms of the type, concentration, period and position of the foliar fertilizer? (3) Please discuss whether foliar fertilization can replace totally with soil fertilization. 20. You have disked in a large amount (may be 5 tons-dry basis/ha) of rice straw just about a week before planting fall cabbage. At planting time you applied chemical fertilizer which supplied 40 kg/ha of nitrogen (N), 60 kg/ha of phosphorus (P2O5) and 60 kg/ha of potassium (K2O). The cabbage germinates and shortly thereafter turns yellow of leaves. Tests show very low NO3- nitrogen in the tissue. What is wrong with the cabbage, and way? The farmer on whose field this is observed asks you, what to do. What is your answer? 21. Indicate the following statements to be true or false and give reasons. The persons who only answer the true or false are not scored. (1) It is unsuitable to use nitrate-nitrogen in the paddy field. (2) For rhizome crops such as potato, sweet potato, the application of potassium sulfate is superior to that of potassium chloride. (3) It is the better that the solubility of a fertilizer is higher. (4) The influences of exceeding nitrogen on plants growth are more serious than that of nitrogen deficiency. (5 )Grounded apatite powder and superphosphate are efficient using broadcast and band fertilization, respectively. 22. Under what soil conditions would the band placement of phosphorus result in its greatest utilization by the plant? If there were no such thing as phosphorus fixation, what method of fertilizer placement would probably result in the greatest utilization of this element by plants? Why? 23. Answer the following question. (1) In what forms are calcium and magnesium absorbed by plants? What is the primary transport mechanism of these forms to the root surface? (2) Describe the deficiency symptom of calcium and magnesium. (3) What conditions are conducive to shortages of calcium and magnesium in soils? 24.Ammonium sulfate (containing 20% N), superphosphate (containing 18% P2O5) and potassium chloride (containing 60% K2O) are commonly used as the straight fertilizers for the supplement of the three major nutrients. Answer the following questions. (1) Use the above-mentioned 3 straight fertilizers to formulate 1,000 kg 8-8-8 blended fertilizer. (2) Can we formulate a 20-20-20 blended fertilizer using the above-mentioned straight fertilizers? If the answer is no, what can be the substitute for any of them. Narrate the formulating processes. (3) What will be the major problems resulting from using self-made 8-8-8 blended fertilizer of long-term and high rate? Explain for your answer. 25. Assume that you addressing a group of farmers and business managers who are well versed in crop production but who are not so conversant with the technical aspects of plant nutrition, fertilizer, and soil fertility. Your mission is to explain to this group the nature of soil cation exchange capacity, base saturation, organic matter content and pH and why they are important to crop production. How would you proceed? 26. Although the following agro-farming measures are usually condemned by the agricultural expert, they are still adopted by some peasants. Why? What will you suggest and what are the advantages and disadvantages resulting from the changes suggested by you. (1) Remove all plant stubble and plow deeply prior to sowing maize. (2) Burn the rice straw. (3) The chicken excrement is used directly. (4) Ameliorate the soil acidity with grounded oyster shell or siliceous slag for a long time. (5) Inoculate p-solubilizing microorganism without adding phosphorus fertilizer. 27. The application of a large amount of chemical nitrogen often results in the leaching of nitrate, the nitrate with irrigating water or rainwater through soil profiles subsequently pollute groundwater, and high nitrate content of vegetables. To avoid these problems, organic fertilizers have been suggested to be the substitute for chemical fertilizers. In fact, the organic nitrogen will also cause the nitrogen pollution of groundwater and vegetables, what are the mechanisms? How to decrease down the risks of nitrate to the environment and human health while conducting organic or traditional agriculture? What kind of natural fertilizers (fertilizer without chemical processing) can be added to the supplement of P and K in composts when organic farming is carried out? 28. During composting, you may meet the problems listed below. Please give possible reasons for these problems and provide the strategies to solve them. (1)The temperature in the compost piles can not be raised. (2)The bad odor is emitted. 29. Describing effects of nitrogen overfertilization on plants. 30. Describing the interactions between mineral elements during plant uptake. 31. Describing the interactions between elements in plant metabolism. 32 Describing the function of boron in plant metabolism. 33 Describing the function of zinc in plant metabolism. 34 Describing the function of copper in plant metabolism. 35 Describing the function of iron in plant metabolism. 36 Describing the function of magnesium in plant metabolism. 37 Describing the function of manganese in plant metabolism. 38 Describing the function of phosphorus in plant metabolism. 39 Describing the function of potassium in plant metabolism. 40 Describing the function of calcium in plant metabolism.