Floriculture Crop Nutrients: NPK, pH, Fertilizers
advertisement

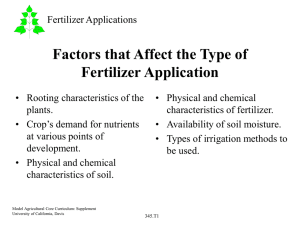
Supplying Nutrients to Floriculture Crops Interest Approach • • • • • What do vitamins do for you? What do you feel like when your sick? What are essential elements in fertilizer? What do they do for the plant? What does a plant look like when it’s deficient in this nutrient? Interest Approach – Vitamins: • • • • • C – health D – strength A – eyesight Calcium-bones Iron-blood – Elements • • • • N – growth P – blossoms Ca – cell strength K - roots Student Objectives After this lesson you CAN 1. Name the nutrients needed for plant growth. 2. Describe pH and how it is modified. 3. Describe the components of a fertilizer. 4. Explain the methods of applying fertilizers to floriculture crops. Macronutrients - elements that are needed by the plant in the largest amount. • • • • Primary macros nitrogen (N) phosphorus (P) potassium (K) • • • • Secondary macros calcium (Ca) magnesium (Mg) sulfur (S). Micronutrients -Needed in Smaller Amounts by the Plants, but Are Still Essential • • • • Boron (B) Copper(Cu) Chlorine (Cl) Iron (Fe) • Manganese (Mn) • Molybdenum (Mo) • Zinc (Zn) Soil Tests • can be performed on the soil to determine which nutrients are present or deficient (absent or lacking). • Are only as accurate as the test – you get what you pay for • Can confirm nutrient deficiency shown by plant leaves. Chlorosis Generally begins in older leaves Symptoms include poor plant growth, and leaves that are pale green or yellow because they are unable to make sufficient chlorophyll. Nitrogen Undersides of tomato plant leaves, and the veins and stems, may turn purple often overlooked or misdiagnosed as a nitrogen deficiency weak thin stalks may cause the plant to stop producing blooms Phosphorous brown scorching and curling of leaf tips as well as chlorosis(yellowing) between leaf veins Purple spots may also appear on the leaf undersides Potassium Fertilizer • Material provided to supply nutrients needed for plant growth. – 2 types of fertilizer • Complete – contains the 3 Primary Macros • Incomplete – missing 1 or more Primaries • Fertilizer analysis states the percentage of primary nutrients. 16 – 4 – 8 • • • • 16 % N 4 % P2O5 8 % K2O Equals 28%??? Where is the rest?!? • Salts and other fillers make up the remaining 72% Fertilizer • Available in three phases – Liquid, solid, gas (rarely used in floriculture) • • • • • Applied by several methods Premixed into soil. Sprayed onto foliage. Injected into irrigation water. Slow release – dissolves over extended period of time. Organic vs. Inorganic • First off, what does this mean?? – Organic is naturally occurring – Inorganic is man made or produced – CLIP Review What are the nutrients needed for plant growth? • • • • • • • • Name the 3 primary macronutrients. NPK Name the 3 secondary macronutrients. Ca S Mg The micronutrients? Fe., Cu B, Zn, Cl, Mo, MN What is pH and how is it modified? • Define pH. • Measure of acidity / alkalinity – potential of Hydrogen • Add limestone to _________ pH? • Add sulfur to ___________pH? What are the components of a fertilizer? • • • • Incomplete vs. complete? Complete has the 3 primary macros Incomplete is missing some primaries What is fertilizer analysis? How are fertilizers applied to floriculture crops? • • • • • • • List the 3 phases of fertilizers. Liquid, solid, gas List the application methods. Irrigation injection Slow release Premix into soil Spray onto foliage