Unit 2: Geography & Native Texans Vocabulary geography
advertisement

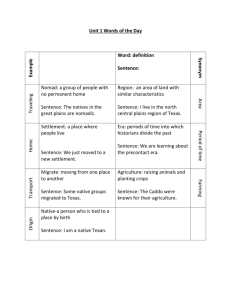
Unit 2: Geography & Native Texans Vocabulary geography - the study of the spatial aspects of the earth and the people that live on it. Simplified Definition: the study of the earth and people. Parts of a Map Compass Rose – a feature on a map that points to the four cardinal directions – north, south, east and west – and four intermediate directions – northeast, northwest, southeast, and southwest. Legend – a key that helps explains the symbols, colors, and other features on a map. Scale – a feature on a map that indicates the relationship between distance on a map and actual distance (example: 1 inch = 200 miles) Grid Map – a grid system that uses lines running east-west and north-south with corresponding numbers running across the body and top of the map and letters running along one or both sides. Latitude & Longitude Latitude is the measurement in degrees north or south of the equator Longitude is the measurement in degrees east or west of the prime meridian 5 Themes of Geography Location – how do I get there? Absolute Location - the exact position of a place on earth's surface. Relative Location - the location of a place in relation to other places. Places and Regions – what is the place like? Place – refers to those features and characteristics that give an area its own identity and personality. Regions – are areas that are united by one or more common characteristics. Human-Environment Interaction – how people who live there interact with their surroundings. Human Systems – how are those people in that place linked (or connected) with other people and places? Movement – continual movement of people, ideas, and goods. Cultural Diffusion – bringing ideas and cultures from other places and. Physical Systems – how hurricanes, tornadoes, glaciers, earthquakes and other natural occurrences shape the world around us. 4 Natural Regions of Texas Gulf Coastal Plains Size - Largest Location – next to the Gulf of Mexico, southeastern Texas Climate – hot, rainy, humid Landforms – plains, prairies, forests, and rivers Products – lumber, farming, ranching, and oil Major Cities – Dallas, Galveston, Houston, Corpus Christi, and San Antonio Central Plains Size – 3rd Largest Location – north central Texas Climate – hot summer, cold winter Landforms – plains, rivers, hills Products – farming, ranching, transportation center, manufacturing, and oil Major Cities – Fort Worth, Abilene, Wichita Falls, and Austin Great Plains Size – 2nd Largest Location – northwest Texas (Panhandle down to the Rio Grande) Climate – little rainfall, hot summer, cold winter Landforms – plains, hills, rivers, plateaus Major Cities – Midland, Odessa, Lubbock, and Amarillo Mountain and Basins Size – Smallest Location – western most part of Texas (west of Pecos River) Climate – dry, hot, desert Landforms – mountains, basins, plateaus Products – farming, ranching (sheep & goats), oil, sulphur, and silver Major Cities – El Paso Native American Cultures IMPORTANT TERMS TO REMEMBER: Nomad – wandered from place to place Sedentary – lived in permanent villages; stayed in one place Remember that early people came to America from Asia over 35,000 over a land bridge. Southeastern Culture Tribes – Caddo and Wichita Housing – domes homes made of poles, mud, & straw Food Sources – farming, hunting & gathering, and fishing Daily Life – men and women farmed together, painted their bodies Religions & Customs – Shaman leader of religious ceremonies, very religious society Gulf Culture Tribes – Karankawa and Coahuiltecan Housing – wigwams Food Sources – farming, hunting & gathering, and fishing Daily Life – nomads, women ran the villages, men hunted Religions & Customs – children have two names, feast/dance celebrations, shaman’s Puebloan Culture Tribes – Jumano Housing – very large adobe huts built into the side of cliffs Food Sources – hunting & gathering, limited farming, traded for food and other goods Daily Life – created pottery and other goods, traded goods with other tribes Religions & Customs – religious ceremonies to celebrate important events Plains Culture Tribes - Tonkawa, Apache, Wichita, and Comanche Housing - teepees Food Sources - hunting the buffalo Daily Life - painted their bodies, were skilled fighters, raided others for what they needed Religions & Customs - Comanche had two chiefs - war and peace chief