weather voc - bunn`s class website

5 th grade Weather Science Vocabulary & Key Facts
1.
condensation: water vapor in the air become liquid
2.
evaporation: liquid water escapes into the air as water vapor
3.
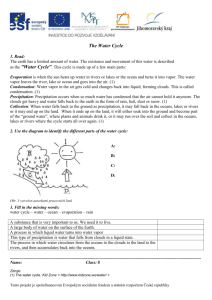
water cycle: the movement of water between the atmosphere and the earth’s surface
The water cycle is through the stages of precipitation – surface runoffevaporation-condensation. (be able to identify on picture)
4.
solid: something with definite shape and size
5.
liquid: able to be poured or it takes the shape of its container
6.
gas: vapor
7.
solar energy: energy provided by the sun, can change water from liquid to gas
8.
precipitation: any form of water that falls from the clouds and reaches the earth’s surface
9.
Types or forms of precipitation include: rain, sleet, freezing rain, hail
(lumps of ice), snow
10.
The two main factors that effect precipitation are winds and the presence of mountains.
11.
Air pressure: A force that is a result of the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area.
12.
Air Mass: large bodies of air that have the same temperature, moisture, and pressures, cause most of the weather
13.
latitude: distance from the equator, runs horizontally
14.
longitude: shows distance from the prime medidian, runs vertically
15.
Wind: The horizontal movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of lower pressure.
16.
meteorologist: a person who studies the weather
17.
wind speed: the speed the wind is moving, measured by an anemometer
18.
wind direction: the direction the wind is blowing, measured by a wind vane
19.
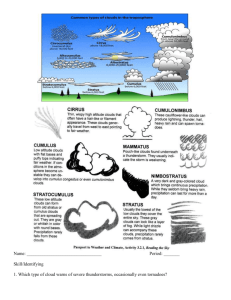
3 types of clouds: cumulus, stratus, cirrus
20.
All clouds form when water vapor in the air becomes liquid water or ice crystals.
21.
cumulus cloud: clouds that form less than 2 kilometers above the ground and look like fluffy, rounded piles of cotton
22.
stratus clouds: clouds that form in flat layers
23.
cirrus clouds: wispy, feathery clouds made mostly of ice crystals that form at high levels, above about 6 kilometers
24.
thunderheads or cumulonimbus clouds: the type of clouds that thunderstorms form from,
25.
temperature: average amount of energy of motion in the molecules of a substance, measured in degrees by a thermometer
26.
The two main factors that effect temperature are latitude, altitude, distance from large bodies of water, and ocean currents. The closer you are to the equator the warmer the climate and the farther you are the cooler the climate.
27.
The higher the altitude the colder the temperature.
28.
Water heats up slower than land.
29.
altitude: elevation above sea level
30.
atmosphere-layers of gases that surround the earth
31.
The atmosphere has four layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and the thermosphere.
32.
run off: water that flows off of a surface or through the ground and back into the ocean, lakes, and streams
33.
saturated: wet with water
34.
weather: the condition of the atmosphere
35.
water vapor: water in the form of a gas
36.
barometer: a tool to measure the changes in air pressure
37.
Front: The area where air masses meet and do not mix.
38.
Cold front: colder air replaces warmer air, usually moves from northwest to southeast
39.
Warm front: warmer air replaces cooler air, usually moves from southwest to northeast
40.
Climate: The average, year after year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds, and clouds in an area.
41.
equatorial zones: warmest areas on earth
42.
polar zones: the coldest areas on the earth
43.
land breeze: night time air flow from land to water
44.
sea (water) breeze: day time air flow from (water) sea to land
45.
trade winds: occurs between the equator and 30 degrees north and south, winds blow from east to west
46.
leeward: side of mountain where cooled air sinks and descends, faces away from wind
47.
rain shadow effect: lack of precipitation on the leeward side of the mountain
48.
windward: side of mountain where air goes up, faces toward the wind, more precipitation, vegetation growth is higher
49.
monsoon: large land-sea breeze, produces a very large amount of rain
50.
hurricanes: a tropical storm that has winds of 119 kilometers per hour or higher, 5 different levels of hurricanes, begins over warm water as a low pressure area or tropical disturbance, eye is the calmest part, draws energy from moist air so it slows down and weakens once it encounters land
51.
tornados: a rapidly whirling, funnel-shaped cloud that reaches down from a storm cloud to touch the earth’s surface, it is occurs over a lake or ocean it is known as a water spout, develop in low, heavy cumulonimbus clouds
52.
angle of incidence: angle that sunlight hi8ts the earth, more intensitywarmer
53.
convection: heat transfer through means of air
54.
Coriolis effect: explains why the air curves over the earth
55.
Density: amount of matter in an object, cold air is heavier than warm air so warm air rises since it is less dense
56.
Fog: cloud that touches the ground, can be thick
57.
Humidity: amount of water vapor in the air, higher humidity equals
“sticky” feeling and better chance for rain and storms, measured with a hygrometer
Water Cycle
The sun evaporates water from lakes and oceans. As the air rises, it cools. The water vapor condenses into tiny droplets of water. The droplets crowd together and form a cloud. Wind blows the cloud towards the land. The tiny droplets join together and fall as precipitation to the
ground. The water soaks into the ground and collects in rivers and lakes.
The cycle that never ends has started again!