PLAN
advertisement

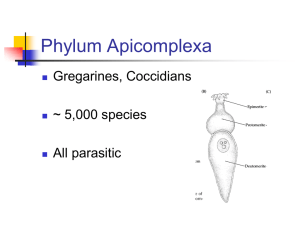
№ 1. 2 GENERAL MEDICINE Themes of practical classes 1st semester Content Themes Light microscope. A plant and an animal cell. Molecular basis of heredity. Nucleic acids. 3. Molecular basis of heredity DNA replication. DNA recombinaton. 4. Molecular basis of heredity Storage and Expression of Genetic information. 5. Molecular basis of heredity Storage and Expression of Genetic information. 6. 7. 8. 1. Cells of onion peel. 2. Chloroplasts in Elodea cells 3. Infusoria Paramaecium caudatum cell. 4. Cells of frog skin epithelium. 5. Amoeba sp. 6. Euglena viridis. 7. Volvox globator. 1. Characteristics of the genetic material. 2. Evidence favoring DNA as the genetic material. 3. Nucleic acid chemistry. 4. The structure of DNA. 5. Classes of DNA. Organization of genes. 6. The structure of RNA. 7. Problem-solving tasks. 1. The mode of DNA replication 2. Origins, forks and units of DNA replication. 3. Scheme of basic molecular events at the replication fork. 4. Repair of DNA. 5. DNA recombination. 6. Problem-solving tasks. 1. The genetic Code. 2. Transcription: RNA synthesis. 5. Transcription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. 6. Regulation of transcription. 7. Problem-solving tasks. 1. Translation: Components those are necessary for protein synthesis. 2. Translation in Eukaryotes. 3. Regulation of Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. 4. Problem-solving tasks. Test-control on the topic: “Molecular basis of heredity”. The Cell Cycle. Mitosis. Gametogenesis and Meiosis. 1. The Structure of Eukaryotic chromosomes. Chromosome Number. Homologous Chromosomes. Haploidy and Diploidy. Karyotype. 2. The Cell Cycle. Phases of the cell cycle. 3. Mitosis. Phases of Mitosis. 4. Cell Cycle Control. 1. Gametogenesis. Drawing the scheme of gametogenesis. 2. Meiosis. Phases of Meiosis. 3. Writing down the description of prophase stage of first meiotic division. 4. Examining the cross section through rat testis under microscope 5. Focusing on the behavior of chromosomes during cell division and gamete formation. 6. Comparison between Mitosis and Meiosis. 9. Mendelian Genetics. Mono- and dihybrid cross. 10. Linkage. Crossing Over. 11. Sex Determination. Sex Linkage. 12. Interaction of genes. Multiple alleles. 13. 14 15. Human Genetics. Methods of investigation of Human Heredity. Human Genetics. Methods of investigation of Human Heredity. Human Genetics. Methods of investigation of Human Heredity. 1. The Monohybrid Cross. Three Mendel’s postulates. Mendel’s analytical approach. 2. Independent assortment and genetic variation. 3. Probability and genetic events. The Product Law and Sum Law. 4. Evaluating Genetic Data. Chi-square Analysis. 5. Problem- solving tasks. 1. Linkage. The Chromosomal theory of inheritance. 2. Incomplete linkage. Crossing Over. 3. Chromosome mapping. 4. The Human Genome Project. 5. Problem-solving tasks. 1. X-linked inheritance. 2. The XX/XY sex-determination system. 3. The ZW sex-determination system. 4. Examples of X-linked diseases: red-green color blindness and hemophilia A. 5. Problem-solving tasks. 1. Complete and incomplete dominance. 2. Codominance. 3. Complementary genes. 4. Epistasis. 5. Supplementary genes. 6. Duplicate genes. 7. Problem-solving tasks. 1. Pedigree Analysis. Learning the rules of making up a human pedigree. 2. Application of twin - study method to evaluate a role of heredity and environment. 3. Using of the Holzinger formula for calculation of the coefficient of heritability. 1. Dermatoglyphic method 2. Biochemical methods 3. Population statistical method 4. Investigation of Human Karyotype. 5. Using cytogenetic method to make the ideogram of human karyotype. 6. Filling in the table on sex-chromosome abnormalities 16. Test - control on the topic: “Classic Genetics” 17. Credit Зав.каф.биологии, проф., д.б.н. Щербатюк Т.Г. GENERAL MEDICINE Themes of practical classes 2nd semester № Themes Content 1. Entamoeba histolytica - slide 2. Lamblia intestinalis - slide Kingdom Protista 3. Balantidium coli - slide 1. Phylum Sarcomastigophora 4. Leshmania sp. - slide Phylum Ciliophora 5. Trypanosoma sp. - slide 6. Trichomonas vaginalis - slide 1. Toxoplasma gondii - slide Kingdom Protista 2 2. Plazmodium species - slide Phylum Apicomplexa 3. The seminar on the topic “MEDICAL PROTOZOOLOGY” 1. Fasciola hepatica - slide 2. Opistorchis felineus - slide 3. Dicrocoelium dendriticum - slide Kingdom Animalia 4. Phylum Platyhelminthes 4. Paragonimus westermani - tables 5. Schistosoma sp. – tables Class Trematoda (flukes) 6. Eggs of Trematoda – slide 7. Formaldehyde preserved worms 1. Diphyllobothrium latum - slide 2. Taenia saginata - slide Kingdom Animalia 5. Phylum Platyhelminthes 3. Taenia solium – slide 4. Eggs of Cestoda – slide Class Cestoda (Tapeworms) I 5. Formaldehyde preserved worms 1. Hymenolepis nana - slide Kingdom Animalia 2. Echinococcus granulosus - slide 6. Phylum Platyhelminthes 3. Echinococcus multilocularis – slide Class Cestoda (Tapeworms) II 4. Eggs of Cestoda – slide 1. Ascaris lumbricoides - slide 2. Enterobius vermicularis - slide Kingdom Animalia 3. Trichuris trichiura – tables 7. Phylum Nemathelminthes 4. Trichinella spiralis - slide Class Nematoda I 5. Eggs of Nematoda – slide 6. Formaldehyde preserved worms 1. Strongyloides stercoralis – tables 2. Ancylostoma duodenale – tables 3. Necator americanus – tables 4. Wuchereria bancrofti – tables Kingdom Animalia 8. Phylum Nemathelminthes 5. Brugia malayi – tables 6. Loa loa – tables Class Nematoda II 7. Onchocerca volvulus – tables 8. Dracunculus medinensis – tables 9. Eggs of Nematoda - slide 9. The seminar on the topic “MEDICAL HELMINTHOLOGY” 1. Ixodes persulcatus - slide 2. Ornithodorus papillipe- slide Arachnids and human diseases: 3. Sarcoptes scabie - slide Kingdom Animalia 10. 4. Poisonous Chelicerate: scorpions, spiders Phylum Arthropoda 5. Ethanol – preserved ticks and poisonous Subphylum Chelicerate Chelicerate 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 1. Pediculus humanus capitis - slide 2. Pediculus humanus humanus - slide Insects and human diseases I: 3. Phthirus pubis - slide Subphylum Tracheata 4. Xenopsylla cheopis - slide (Uniramian) 5. Musca domestica - slide 6. Blatta orientalis (Blatta germanica) - slide 1. Mosquitoes Anopheles - slide Insects and human diseases II: 2. Mosquitoes Culex - slide Subphylum Tracheata 3. Mosquitoes Aedes - tables (Uniramian) 4. Phlebotomus mosquito - slide The seminar on the topic “ARTHROPODA AND HUMAN DISEASE” 1. Types of ontogenesis 2. Stages of ontogenesis 3. Pre-embryonic development 4. Embryonic development: fertilization, Ontogenesis cleavage, gastrulation, histo- and organogenesis 5. Post-embryonic development 6. Mechanisms of development 1. Phylogenesis of respiratory systems (lancelet, fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, human) Phylogenesis of organs and 2. Phylogenesis of digestive systems (lancelet, systems of phylum Chordata I fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, human) 1. Phylogenesis of circulatory systems (lancelet, fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, human) Phylogenesis of organs and 2. Phylogenesis of excretory systems (lancelet, systems of phylum Chordata II fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, human) The seminar on the topic “ONTOGENESIS. EVOLUTION. PHYLOGENESIS OF SYSTEMS OF PHYLUM CHORDATA” Credit Зав.каф.биологии, проф., д.б.н. Щербатюк Т.Г.