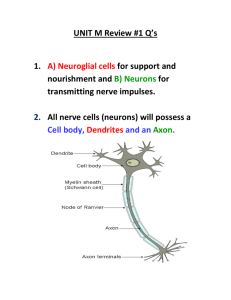
The Central Nervous System
advertisement

12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System • Master control and communication system • Has three overlapping functions • Sensory receptors monitor changes inside and outside the body • Change—a stimulus • Gathered information—sensory input Nervous System • Processes and interprets sensory input • Makes decisions—integration • Dictates a response by activating effector organs • Response—motor output Basic Divisions of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) • Brain and spinal cord • Integrating and command center • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) • Outside the CNS • Consists of nerves extending from brain and spinal cord • Cranial nerves • Spinal nerves • Peripheral nerves link all regions of the body to the CNS • Ganglia are clusters of neuronal cell bodies Sensory Input and Motor Output • Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors • Carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS • Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS • Innervate muscles and glands • Divided according to region they serve • Somatic body region • Visceral body region • Results in four main subdivisions • • • • Somatic sensory Visceral sensory Somatic motor Visceral motor (autonomic nervous system) Types of Sensory and Motor Information Basic Divisions of the Nervous System • Somatic sensory • General somatic senses—receptors are widely spread • Touch • Pain • Vibration • Pressure • Temperature (receptors discussed in Chapter 14) • Somatic sensory (continued) • Proprioceptive senses—detect stretch in tendons and muscle • Body sense—position and movement of body in space • Special somatic senses (Chapter 16) • Hearing • Balance • Vision • Smell • Visceral sensory • General visceral senses—stretch, pain, temperature, nausea, and hunger • Widely felt in digestive and urinary tracts, and reproductive organs • Special visceral senses • Taste • Somatic motor • General somatic motor—signals contraction of skeletal muscles • Under our voluntary control • Often called “voluntary nervous system” • Branchial motor • Typical skeletal muscle derived from somitomeres • • Visceral motor • • • • Regulates the contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle Makes up autonomic nervous system Controls function of visceral organs Often called “involuntary nervous system” • Autonomic nervous system (Chapter 15) Nervous Tissue • Cells are densely packed and intertwined • Two main cell types • Neurons—transmit electrical signals • Support cells (neuroglial cells in CNS) • Nonexcitable • Surround and wrap neurons The Neuron • The human body contains billions of neurons • Basic structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized cells conduct electrical impulses along the plasma membrane • Nerve impulse (action potential) The Neuron • Other special characteristics • Longevity—can live and function for a lifetime • Do not divide—fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate—require abundant oxygen and glucose • Neurons die after 5 minutes without oxygen The Cell Body • Cell body (soma) • Perikaryon—around the nucleus • Size of cell body varies from 5–140µm • Contains usual organelles plus other structures • Chromatophilic bodies (Nissl bodies) • Clusters of rough ER and free ribosomes • Stain darkly and renew membranes of the cell • • Neurofibrils—bundles of intermediate filaments • Form a network between chromatophilic bodies • • Most neuronal cell bodies are • Located within the CNS • Protected by bones of the skull and vertebral column • Ganglia—clusters of cell bodies • Lie along nerves in the PNS Structure of a Typical Large Neuron Neuron Processes • Dendrites • Extensively branching from the cell body • Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body • Chromatophilic bodies—only extend into the basal part of dendrites and to the base of the axon hillock • Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons Neuron Processes • Axons • • • • • • Neuron has only one Impulse generator and conductor Transmits impulses away from the cell body Chromatophilic bodies are absent No protein synthesis in axon Neurofilaments, actin microfilaments, and microtubules • Provide strength along length of axon • Aid in the transport of substances to and from the cell body • Axonal transport • Branches along length are infrequent • Axon collaterals • Multiple branches at end of axon • Terminal branches (telodendria) • End in knobs called axon terminals (also called end bulbs or boutons) • Nerve impulse • Generated at the initial segment of the axon • Conducted along the axon • Releases neurotransmitters at axon terminals • Neurotransmitters—excite or inhibit neurons • Neuron receives and sends signals Synapses • Site at which neurons communicate • Signals pass across synapse in one direction • Presynaptic neuron • Conducts signal toward a synapse • Postsynaptic neuron • Transmits electrical activity away from a synapse Types of Synapses • Axodendritic • Between axon terminals of one neuron and dendrites of another • Most common type of synapse • Axosomatic • Between axons and neuronal cell bodies Synapses • Elaborate cell junctions • Axodendritic synapses—representative type • Synaptic vesicles on presynaptic side • Membrane-bound sacs containing neurotransmitters • Mitochondria abundant in axon terminals • Synaptic cleft • Separates the plasma membrane of the two neurons 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Classification of Neurons • Structural classification • Multipolar—possess more than two processes • Numerous dendrites and one axon • Bipolar—possess two processes • Rare neurons • Found in some special sensory organs • Unipolar (pseudounipolar)—possess one short, single process • Start as bipolar neurons during development Functional Classification of Neurons • Functional classification is • According to the direction the nerve impulse travels relative to the CNS • Types of neurons • Sensory neurons • Motor Neurons • Interneurons Functional Classification of Neurons • Sensory neurons • Transmit impulses toward the CNS • Virtually all are unipolar neurons • Cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS • Short, single process divides into • The central process—runs centrally into the CNS • The peripheral process— extends peripherally to the receptors • Motor (efferent) neurons • • • • Carry impulses away from the CNS to effector organs Most motor neurons are multipolar Cell bodies are within the CNS Form junctions with effector cells • Interneurons (association neurons)—most are multipolar • Lie between motor and sensory neurons • Confined to the CNS Supporting Cells • Six types of supporting cells • Four in the CNS • Two in the PNS • Provide supportive functions for neurons • Cover nonsynaptic regions of the neurons Neuroglial in the CNS • Neuroglia • • • • Glial cells have branching processes and a central cell body Outnumber neurons 10 to 1 Make up half the mass of the brain Can divide throughout life • Astrocytes are the most abundant glial cell type • • • • • • Sense when neurons release glutamate Extract blood sugar from capillaries for energy Take up and release ions to control environment around neurons Involved in synapse formation in developing neural tissue Produce molecules necessary for neuronal growth (BDTF) Propagate calcium signals involved with memory • Microglia—smallest and least abundant glial cell • Phagocytes—the macrophages of the CNS • Engulf invading microorganisms and dead neurons • Derive from blood cells called monocytes • Ependymal cells • Line the central cavity of the spinal cord and brain • Bear cilia—help circulate the cerebrospinal fluid • Oligodendrocytes—have few branches • Wrap their cell processes around axons in CNS • Produce myelin sheaths Neuroglia in the PNS • Satellite cells—surround neuron cell bodies within ganglia • Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)—surround axons in the PNS • Form myelin sheath around axons of the PNS 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Myelin Sheaths • Segmented structures composed of the lipoprotein myelin • Surround thicker axons • Form an insulating layer • Prevent leakage of electrical current • Increase the speed of impulse conduction Myelin Sheaths in the PNS • Formed by Schwann cells • Develop during fetal period and in the first year of postnatal life • Schwann cells wrap in concentric layers around the axon • Cover the axon in a tightly packed coil of membranes • Neurilemma • Material external to myelin layers • Nodes of Ranvier—gaps along axon • Thick axons are myelinated • Thin axons are unmyelinated • Conduct impulses more slowly • Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheaths in the CNS • Have multiple processes • Coil around several different axons Nerves • Nerves—cablelike organs in the PNS • Consists of numerous axons wrapped in connective tissue • Axon is surrounded by Schwann cells • You see many nerves in lab • Nerves of brachial plexus • Radial, axillary, median, musculocutaneous, ulnar • Nerves of lumbosacral plexus Nerves • Endoneurium—layer of delicate connective tissue surrounding the axon • Perineurium—connective tissue wrapping surrounding a nerve fascicle • Nerve fascicles—groups of axons bound into bundles • Epineurium—whole nerve is surrounded by tough fibrous sheath Gray and White Matter in the CNS • Gray matter • Is gray-colored and surrounds hollow central cavities of the CNS • Forms H-shaped region in the spinal cord • Dorsal half contains cell bodies of interneurons • Ventral half contains cell bodies of motor neurons • Primarily composed of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons • Surrounds white matter of CNS in cerebral cortex and cerebellum • White matter • • • • Lies external to the gray matter of the CNS Composed of myelinated axons Consists of axons passing between specific regions of the CNS Tracts are bundles of axons traveling to similar destinations Integration Between the PNS and CNS • The CNS and PNS are functionally interrelated • Nerves of the PNS • Information pathways to and from body periphery • Afferent PNS fibers respond to sensory stimuli • Efferent PNS fibers transmit motor stimuli from CNS to muscles and glands Integration Between the PNS and CNS • Nerves of the CNS • Composed on interneurons that • Process and receive sensory information • Direct information to specific CNS regions • Initiate appropriate motor responses • Transport information from one area of the CNS to another Reflex Arcs • Reflex arcs—simple chains of neurons • Explain reflex behaviors • Determine structural plan of the nervous system • Responsible for reflexes • Rapid, autonomic motor responses • Can be visceral or somatic Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc • Receptor—site where stimulus acts • Sensory neuron—transmits afferent impulses to the CNS • Integration center—consists of one or more synapses in the CNS • Motor neuron—conducts efferent impulses from integration center to an effector • Effector—muscle or gland cell • Responds to efferent impulses • Contracting or secreting Types of Reflexes • Monosynaptic reflex • Simplest of all reflexes • Just one synapse • The fastest of all reflexes • Knee-jerk reflex • Polysynaptic reflex • More common type of reflex • Most have a single interneuron between the sensory and motor neuron • Withdrawal reflexes Neuronal Circuits • Diverging circuit—one presynaptic neuron synapses with several other neurons (divergence) • Converging circuit—many neurons synapse on a single postsynaptic neuron (convergence) • Reverberating circuit—circuit that receives feedback via a collateral axon from a neuron in the circuit • Serial processing • Neurons pass a signal to a specific destination along a single pathway from one to another • Parallel processing • Input is delivered along many pathways; a single sensory stimulus results in multiple perceptions Simplified Design of the Nervous System • Three-neuron reflex arcs • Basis of the structural plan of the nervous system • Similar reflexes are associated with the brain • Sensory neurons—located dorsally • Cell bodies outside the CNS in sensory ganglia • Central processes enter dorsal aspect of the spinal cord • Motor neurons—located ventrally • Axons exit the ventral aspect of the spinal cord • Interneurons—located centrally • Synapse with sensory neurons • Interneurons are neurons confined to CNS • Long chains of interneurons between sensory and motor neurons Disorders of the Nervous System • Multiple sclerosis • Common cause of neural disability • An autoimmune disease • Immune system attacks the myelin around axons in the CNS • Varies widely in intensity among those affected • More women than men are affected • When men are affected, disease develops quicker and is more devastating • Cause is incompletely understood Neuronal Regeneration • Neural injuries may cause permanent dysfunction • If axons alone are destroyed, cells bodies often survive and the axons may regenerate • PNS—macrophages invade and destroy axon distal to the injury • Axon filaments grow peripherally from injured site • Partial recovery is sometimes possible Neuronal Regeneration • CNS—neuroglia never form bands to guide re-growing axons and may hinder axon growth with growth-inhibiting chemicals • No effective regeneration after injury to the spinal cord and brain Nervous Tissue Throughout Life • Nervous system develops from the dorsal ectoderm • Invaginates to form the neural tube and neural crest • Neural tube walls begin as neuroepithelial cells • These cells divide and become neuroblasts Nervous Tissue Throughout Life 13 The Central Nervous System The Central Nervous System • Central nervous system • The brain and spinal cord • Directional terms unique to the CNS • Rostral—toward the nose • Caudal—toward the tail The Spinal Cord • Functions of the spinal cord • Spinal nerves attach to it • Provides two-way conduction pathway • Major center for reflexes • Location of the spinal cord • Runs through the vertebral canal • Extends from the foramen magnum to the level of the vertebra L1 or L2 • Conus medullaris • The inferior end of the spinal cord • Filum terminale • Long filament of connective tissue • Attaches to the coccyx inferiorly • Cervical and lumbar enlargements • Where nerves for upper and lower limbs arise • Cauda equina • Collection of spinal nerve roots • Spinal cord segments • Indicate the region of the spinal cord from which spinal nerves emerge • Designated by the spinal nerve that issues from it • T1 is the region where the first thoracic nerve emerges The Spinal Cord • Two deep grooves run the length of the cord • Posterior median sulcus • Anterior median fissure White Matter of the Spinal Cord • White matter • Outer region of the spinal cord • Composed of myelinated and unmyelinated axons • Allow communication between spinal cord and brain • Fibers classified by type • Ascending fibers • Descending fibers • Commisural fibers Gray Matter of the Spinal Cord and Spinal Roots • Shaped like the letter “H” • Gray commissure—contains the central canal • Dorsal horns • Consist of interneurons • Ventral and lateral horns • Contain cell bodies of motor neurons Organization of the Gray Matter of the Spinal Cord • Gray matter • Divided according to somatic and visceral regions • SS—somatic sensory • VS—visceral sensory • VM—visceral motor • SM—somatic motor Protection of the Spinal Cord • Protected by vertebrae, meninges, and CSF • Meninges • Dura mater—a single layer surrounding spinal cord • Arachnoid mater—lies deep to the dura mater • Pia mater—innermost layer • Delicate layer of connective tissue • Extends to the coccyx • Denticulate ligaments—lateral extensions of pia mater Cerebrospinal Fluid • Fills the hollow cavities of the brain and spinal cord • Provides a liquid cushion for the spinal cord and brain • Other functions: • Nourishes brain and spinal cord • Removes wastes • Carries chemical signals between parts of the CNS 13 The Central Nervous System The Brain • Performs the most complex neural functions • • • • • Intelligence Consciousness Memory Sensory-motor integration Involved in innervation of the head • Brain also controls: • Heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure • Autonomic nervous system • Endocrine system Embryonic Development of the Brain • Brain arises from rostral part of the neural tube • Three primary brain vesicles in 4-week-old embryo • Prosencephalon—the forebrain • Mesencephalon—the midbrain • Rhombencephalon—the hindbrain • Secondary brain vesicles • Prosencephalon • Divides into telencephalon and diencephalon • Mesencephalon—remains undivided • Rhombencephalon • Divides into metencephalon and myelencephalon • Structures of the adult brain • Develop from secondary brain vesicles • Telencephalon the cerebral hemispheres • Diencephalon thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus • Metencephalon pons and cerebellum • Myelencephalon medulla oblongata Embryonic Development of the Brain • Brain stem includes • The midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata • Ventricles • Central cavity of the neural tube enlarges Embryonic Development of the Brain • Brain grows rapidly • Changes occur in the relative position of its parts • Cerebral hemispheres envelop the diencephalon and midbrain • Wrinkling of the cerebral hemispheres • More neurons fit within limited space Basic Parts and Organization of the Brain • Divided into four regions • Cerebral hemispheres • Diencephalon • Brain stem • Midbrain, pons, and medulla • Cerebellum • Organization • Centrally located gray matter • Externally located white matter • Additional layer of gray matter external to white matter • Due to groups of neurons migrating externally • Cortex—outer layer of gray matter • Formed from neuronal cell bodies • Located in cerebrum and cerebellum Ventricles of the Brain • Expansions of the brain’s central cavity • Filled with cerebrospinal fluid • Lined with ependymal cells • Continuous with each other • Continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord • Lateral ventricles—located in cerebral hemispheres • Horseshoe-shaped from bending of the cerebral hemispheres • Third ventricle—lies in diencephalon • Connected with lateral ventricles by interventricular foramen Ventricles of the Brain • Cerebral aqueduct—connects 3rd and 4th ventricles • Fourth ventricle—lies in hindbrain • Connects to the central canal of the spinal cord The Brain Stem • Includes the • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla oblongata The Brain Stem • Several general functions • Produces automatic behaviors necessary for survival • Passageway for all fiber tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord • Heavily involved with the innervation of the face and head • 10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves attach to it The Brain Stem—The Medulla Oblongata • Most of the caudal level of the brain stem • Is continuous with the spinal cord • Choroid plexus lies in the roof of the fourth ventricle • External landmarks of medulla • Pyramids of the medulla • Lie on its ventral surface • Decussation of the pyramids • Crossing over of motor tracts • Inferior cerebellar peduncles • Fiber tracts connecting medulla and cerebellum • Olive (olive of the medulla) • Contains inferior olivary nucleus The Brain Stem—The Medulla Oblongata • Cranial nerves VIII–XII attach to the medulla • • • • VIII—vestibulocochlear IX—glossopharyngeal nerve X—vagus nerve XI—accessory • (spinal accessory—a branch of the vagus nerve) • XII—hypoglossal nerve The Brain Stem—The Medulla Oblongata • The core of the medulla contains • Much of the reticular formation • Nuclei influence autonomic functions • Visceral centers of the reticular formation include • Cardiac center • Vasomotor center • The medullary respiratory center • Centers for hiccupping, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing The Brain Stem—The Pons • A “bridge” between the midbrain and medulla oblongata • Pons contains the nuclei of cranial nerves • V—trigeminal nerve • VI—abducens nerve • VII—facial nerve • The pons contains • Motor tracts coming from the cerebral cortex • Pontine nuclei • Connect portions of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum • Send axons to cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncles The Brain Stem—The Midbrain • Lies between the diencephalon and the pons • Cerebral aqueduct • The central cavity of the midbrain • Cerebral peduncles located on the ventral surface of the brain • Contain pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts • Superior cerebellar peduncles • Connect midbrain to the cerebellum The Brain Stem—The Midbrain • Periaqueductal gray matter surrounds the cerebral aqueduct • Involved in two related functions • Fright-and-flight reaction • Mediates response to visceral pain • Corpora quadrigemina • The largest nuclei • Divided into the superior and inferior colliculi • Superior colliculi—nuclei that act in visual reflexes • Inferior colliculi—nuclei that act in reflexive response to sound The Brain Stem—The Midbrain • Imbedded in the white matter of the midbrain • Two pigmented nuclei • Substantia nigra—neuronal cell bodies contain melanin • Functionally linked to the basal nuclei • Red nucleus—lies deep to the substantia nigra • Largest nucleus of the reticular formation The Cerebellum • Located dorsal to the pons and medulla • Smoothes and coordinates body movements • Helps maintain equilibrium • Consists of two cerebellar hemispheres • Surface folded into ridges called folia • Separated by fissures • Hemispheres each subdivided into • Anterior lobe • Posterior lobe • Flocculonodular lobe (tiny) • Composed of three regions • Cortex—gray matter • Arbor vitae • Internal white matter • Deep cerebellar nuclei—deeply situated gray matter The Cerebellum • To coordinate body movements, the cerebellar cortex receives three types of information • Information on equilibrium • Information on current movements of the limbs, neck, and trunk • Information from the cerebral cortex The Cerebellum • Coordinating movement 1. The Cerebellum receives information on movement from the motor cortex of the cerebrum 2. The cerebellum compares intended movement with body position 3. The cerebellum sends instructions back to the cerebral cortex to continuously adjust and fine tune motor commands The Cerebellum • Higher cognitive functions of the cerebellum • Learning a new motor skill • Participates in cognition • Language, problem-solving, task planning The Cerebellum—Cerebellar Peduncles • Thick tracts connecting the cerebellum to the brain stem are • Superior cerebellar peduncles • Middle cerebellar peduncles • Inferior cerebellar peduncles • Fibers to and from the cerebellum are ipsilateral 13 The Central Nervous System The Diencephalon • Forms the center core of the forebrain • Surrounded by the cerebral hemispheres • Composed of three paired structures • Thalamus • Hypothalamus • Epithalamus • Border the third ventricle • Primarily composed of gray matter The Diencephalon—The Thalamus • Makes up 80% of the diencephalon • Contains approximately a dozen major nuclei • Act as relay stations for incoming sensory message • Every part of brain communicating with cerbral cortex relays signals through thalamic nuclei! • Send axons to regions of the cerebral cortex The Diencephalon—The Thalamus • Afferent impulses converge on the thalamus • Synapse in at least one of its nuclei • Is the “gateway” to the cerebral cortex • Nuclei organize and amplify or tone down signals The Diencephalon—The Hypothalamus • Lies between the optic chiasm and the mammillary bodies • Pituitary gland projects inferiorly • Contains approximately a dozen nuclei • Main visceral control center of the body • The master gland’s master!! The Diencephalon—The Hypothalamus • Functions include the following • • • • • • • • Control of the ANS Control of emotional responses Regulation of body temperature Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations Control of behavior Regulation of sleep-wake cycles Control of the endocrine system Formation of memory The Diencephalon—The Epithalamus • Forms part of the “roof” (top) of the third ventricle • Consists of a tiny group of nuclei • Includes the pineal gland (pineal body) • Secretes the hormone melatonin • Under influence of the hypothalamus • Aids in control of circadian rhythm The Cerebral Hemispheres • Account for 83% of brain mass • Fissures—deep grooves, which separate major regions of the brain • Transverse fissure—separates cerebrum and cerebellum • Longitudinal fissure—separates cerebral hemispheres The Cerebral Hemispheres • Sulci • Grooves on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres • Gyri • Twisted ridges between sulci • Prominent gyri and sulci are similar in all people The Cerebral Hemispheres • Deeper sulci divide cerebrum into lobes • Lobes are named for the skull bones overlying them • Central sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobes • Bordered by two gyri • Precentral gyrus • Postcentral gyrus The Cerebral Hemispheres • Parieto-occipital sulcus • Separates the occipital from the parietal lobe • Lateral sulcus • Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes • Insula—deep within the lateral sulcus The Cerebral Hemispheres • Frontal section through forebrain • Cerebral cortex • Cerebral white matter • Deep gray matter of the cerebrum (basal ganglia) The Cerebral Cortex • Home of our conscious mind • Enables us to • Be aware of ourselves and our sensations • Initiate and control voluntary movements • Communicate, remember, and understand The Cerebral Cortex • Composed of gray matter • Neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and short axons • Folds in cortex—triples its size • Approximately 40% of brain’s mass • Brodmann areas • 47 structurally distinct areas • Functional regions • Traditionally studied brain-injured people and animals • New discoveries—PET and fMRI • Regions of the cerebral cortex • Perform distinct motor and sensory functions • Memory and language spread over wide area 13 The Central Nervous System The Cerebral Cortex • Three general kinds of functional areas • Sensory areas • Association areas • Motor areas The Cerebral Cortex • There is a sensory area for each of the major senses • A “primary sensory cortex” • Each primary sensory cortex • Has an association area that processes sensory information • Sensory association areas • Multimodal association areas • Receive and integrate input from multiple regions of the cerebral cortex • Motor cortex • Plans and initiates voluntary motor functions The Cerebral Cortex-Information Processing • Sensory information received by primary sensory cortex • Information relayed to sensory association area • Multimodal association areas receive input in parallel from sensory areas • Motor plan enacted Sensory Areas • Cortical areas involved in conscious awareness of sensation • Located in • Parietal lobes • Temporal lobes • Occipital lobes • Distinct regions of each lobe interpret each of the major senses Sensory Areas—Primary Somatosensory Cortex • Located along the postcentral gyrus • Involved with conscious awareness of general somatic senses • Spatial discrimination • Precisely locates a stimulus • Certain regions are more adept at distinguishing precise stimili • Projection is contralateral • Cerebral hemispheres • Receive sensory input from the opposite side of the body • Sensory homunculus • A body map of the sensory cortex Sensory Areas—Somatosensory Association Cortex • Lies posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex • Integrates different sensory inputs • Touch • Pressure • Draws upon stored memories of past sensory experiences • You are able to recognize keys or coins in your pocket without looking at them Sensory Areas—Visual Areas • Primary visual cortex • Location is deep within the calcarine sulcus • On medial part of the occipital lobe • Largest of all sensory areas • Receives visual information that originates on the retina • Exhibits contralateral function • First of a series of areas processing visual input • Visual association area • Surrounds the primary visual area • Continues the processing of visual information • Analyzes color, form, and movement • Complex visual processing extends into • Temporal and parietal lobes Sensory Areas—Visual Areas • Visual association area • Approximately 30 cortical areas have been identified • Visual information proceeds in two streams • Ventral stream • Passes information into inferior part of the temporal lobe • Responsible for recognizing objects, words, and faces • Dorsal stream • Extends to the post-central gyrus • Perceives information about spatial relationships • Ventral and dorsal streams • The “what” and “where” pathways for vision Sensory Areas—Auditory Areas • Primary auditory cortex • Function • Conscious awareness of sound • Sound waves excite receptors in the inner ear • Impulses transmitted to primary auditory cortex • Location • Superior edge of the temporal lobe Sensory Areas—Auditory Areas • Auditory association area • Lies posterior to the primary auditory cortex • Permits evaluation of different sounds • Processes auditory stimuli serially and in parallel • Posterolateral—”where” pathway • Anterolateral—”what” pathway • Lies in the center of Wernicke’s area • Involved in recognizing and understanding speech Sensory Areas—Vestibular Cortex • Responsible for • Conscious awareness of sense of balance • Located in the posterior part of the insula • Deep to the lateral sulcus Sensory Areas—Gustatory Cortex • Function • Involved in the conscious awareness of taste stimuli • Location • On the “roof” of the lateral sulcus Sensory Areas—Olfactory Cortex • Lies on the medial aspect of the cerebrum • Located in the piriform lobe • Olfactory nerves transmit impulses to the olfactory cortex • Provides conscious awareness of smells Sensory Areas—Olfactory Cortex • Part of the rhinencephalon—“nose brain” • Includes • The piriform lobe, olfactory tracts, and olfactory bulbs • Connects the brain to the limbic system • Explains why smells trigger emotions • Involved with consciously identifying and recalling specific smells Visceral Sensory Areas • Location • Within the lateral sulcus • On the insula lobe • Receives general sensory input • Pain • Pressure • Hunger Multimodal Association Areas • Large areas of the cerebral cortex • Receive sensory input from • Multiple sensory modalities • Sensory association areas • Make associations between kinds of sensory information Multimodal Association Areas • Three multimodal association areas • Posterior association area • Anterior association area • Limbic association area Posterior Association Area • Located at interface of visual, auditory, and somatosensory association areas • Integrates sensory information into unified perception • Allows awareness of spatial location of body • “Body sense” • Related to language comprehension and speech Posterior Association Area • Multiple language areas in left cerebral cortex • Wernicke’s area functions in • Speech comprehension • Coordination of auditory and visual aspects of language • Initiation of word articulation • Recognition of sound sequences Posterior Association Area • Areas in right cerebral hemisphere act in • Creative interpretation of words • Emotional overtones of speech Anterior Association Area • A large region of the frontal lobe • The prefrontal cortex • • • • Receives information from posterior association area Integrates information with past experience Initiates and plans motor movements Has links to the limbic system Anterior Association Areas • More complex functions include all aspects of • • • • Thinking, perceiving, intentionally remembering Processing abstract ideas, reasoning, judgment Impulse control, mental flexibility, social skills Humor, empathy, conscience Anterior Association Area • Functional neuroimaging techniques • Reveal functions of specific parts of the prefrontal cortex • Anterior pole of frontal cortex • Active in solving the most complex problems • More complex problems, emotions, cognition at anterior part of frontal lobe. Anterior Association Area • Additional functions • Stores information for less than 30 seconds • Three working memory areas • Visual working memory • Auditory working memory • Executive area Limbic Association Areas • Located on medial side of frontal lobe • Involved with memory and emotions • Integrates sensory and motor behaviors • Aids in the formation of memory • Processes emotions Motor Areas • Cortical areas controlling motor function • • • • Premotor cortex Primary motor cortex Frontal eye field Broca’s area • All localized in posterior frontal lobe Motor Areas—Premotor Cortex • Located anterior to the precentral gyrus • Controls more complex movements • Receives processed sensory information • Visual, auditory, and general somatic sensory • Controls voluntary actions dependent on sensory feedback • Involved in planning movements Motor Areas—Primary Motor Cortex • Controls motor functions • Primary motor cortex (somatic motor area) • Located in precentral gyrus • Pyramidal cells • Large neurons of primary motor cortex Motor Areas—Primary Motor Cortex • Corticospinal tracts descend through brain stem and spinal cord • Axons signal motor neurons to control skilled movements • Contralateral • Pyramidal axons cross over to opposite side of the brain Motor Areas • Specific pyramidal cells control specific areas of the body • Face and hand muscles are controlled by many pyramidal cells • Somatotopy • Body is represented spatially in the primary motor cortex Motor Areas Motor Areas—Frontal Eye Field • Lies anterior to the premotor cortex • Controls voluntary movement of the eyes • Especially when moving eyes to follow a moving target Motor Areas—Broca’s Area • Located in left cerebral hemisphere • Manages speech production • Connected to language comprehension areas in posterior association area • A corresponding region in the right cerebral hemisphere controls emotional overtones to spoken words Lateralization of Cortical Functioning • The two hemispheres control opposite sides of the body • Contralateral = opposite side • Hemispheres are specialized for different cognitive functions Lateralization of Cortical Functioning • Left cerebral hemisphere—control over: • Language abilities, math, and logic • Right cerebral hemisphere—involved with • Visual-spatial skills • Reading facial expressions • Intuition, emotion, artistic, and musical skills 13 The Central Nervous System Cerebral White Matter • Different areas of the cerebral cortex • Communicate with each other • Communicate with the brain stem and spinal cord • Fibers communicating are • Usually myelinated and bundled into tracts Cerebral White Matter • Types of tracts • Commissures—composed of commissural fibers • Allows communication between cerebral hemispheres • Corpus callosum—the largest commissure • Association fibers • Connect different parts of the same hemisphere • Parts of Wernike’s and Broca’s areas are connected by association fibers Cerebral White Matter Cerebral White Matter • Types of tracts (continued) • Projection fibers—run vertically • Descend from the cerebral cortex • Ascend to the cortex from lower regions • Corticospinal tracts begin with pyramidal cells Cerebral White Matter Projection Tracts • Internal capsule—projection fibers form a compact bundle • Passes between the thalamus and basal nuclei • Corona radiata—superior to the internal capsule • Fibers run to and from the cerebral cortex 13 The Central Nervous System Deep Gray Matter of the Cerebrum • Consists of • Basal ganglia • Involved in motor control • Basal forebrain nuclei • Associated with memory • Claustrum • A nucleus of unknown function • Amygdala • Located in cerebrum but is considered part of the of the limbic system Basal Ganglia • A group of nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter • Formed from • Caudate nucleus—arches over thalamus • Putamen • Globus pallidus Basal Ganglia • Complex neural calculators • Cooperate with the cerebral cortex in controlling movement • Receive input from many cortical areas • Substantia nigra also influences basal ganglia Basal Ganglia • Evidence shows that they • Start, stop, and regulate intensity of voluntary movements • Select appropriate muscles for a task and inhibit others • In some way estimate the passage of time Basal Forebrain Nuclei • Structures composing basal forebrain nuclei • • • • Septum Diagonal band of Broca Horizontal band of Broca Basal nucleus of Meynert Basal Forebrain Nuclei • Part of cholinergic system • That is, they synthesize and release acetylcholine • Location • Anterior and dorsal to hypothalamus • Functions related to • • • • Arousal Learning Memory Motor control • Degeneration of basal forebrain in nuclei • Associated with Alzheimer’s disease 13 The Central Nervous System Functional Brain Systems • Networks of neurons functioning together • Limbic system • Spread widely in the forebrain • The reticular formation • Spans the brain stem Functional Brain Systems—The Limbic System • Location • Medial aspect of cerebral hemispheres • Also within the diencephalon • Composed of • Septal nuclei, cingulate gyrus, and hippocampal formation • Part of the amygdala • The fornix and other tracts link the limbic system together Functional Brain Systems—The Limbic System • The “emotional brain” • Cingulate gyrus • Allows us to shift between thoughts • Interprets pain as unpleasant • Hippocampal formation • Hippocampus and the parahippocampal gyrus Functional Brain Systems—The Reticular Formation • Runs through the central core of the medulla, pons, and midbrain • Forms three columns • Midline raphe nuclei • Medial nuclear group • Lateral nuclear group Functional Brain Systems—The Reticular Formation • Widespread connections • Ideal for arousal of the brain as a whole • Reticular activating system (RAS) • Maintains consciousness and alertness • Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep • Malfunctions in those with narcolepsy Protection of the Brain • The brain is protected from injury by • • • • The skull Meninges Cerebrospinal fluid Blood-brain barrier Protection of the Brain—Meninges • Functions of meninges • Cover and protect the CNS • Enclose and protect the vessels that supply the CNS • Contain the cerebrospinal fluid • Between pia and arachnoid maters The Dura Mater • Strongest of the meninges • Composed of two layers • Periosteal layer • Meningeal layer • Two layers are fused except to enclose the dural sinuses The Dura Mater The Dura Mater • Largest sinus—the superior sagittal sinus • Dura mater extends inward to subdivide the cranial cavity The Dura Mater The Arachnoid Mater • Located beneath the dura mater • Arachnoid villi • Project through the dura mater • Allow CSF to pass into the dural blood sinuses The Pia Mater • Delicate connective tissue • Clings tightly to the surface of the brain • Follows all convolutions of the cortex 13 The Central Nervous System Protection of the Brain—Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • Formed in choroid plexuses in the brain ventricles • Choroid plexus is • Located in all four ventricles • Composed of ependymal cells and capillaries • Arises from blood • 500 ml/day • Prevents most blood-borne toxins from entering the brain • Impermeable capillaries • Not an absolute barrier • Nutrients such as oxygen pass through • Allows alcohol, nicotine, and anesthetics through Sensory and Motor Pathways in the CNS • Multineuron pathways connect brain and body periphery • Pathways are composed of tracts • Ascending pathways—carry information to more rostral areas of the CNS • Descending pathways—carry information to more caudal regions of the CNS Ascending Pathways • Conduct general somatic sensory impulses • Chains of neurons composed of • First-, second-, and third-order neurons • Four main ascending pathways • • • • Dorsal column pathway Spinothalamic pathway Posterior spinocerebellar pathway Anterior spinocerebellar pathway Descending Pathways • Most motor pathways • Decussate at some point along their course • Consist of a chain of two or three neurons • Exhibit somatotopy • Tracts arranged according to the body region they supply • All pathways are paired • One of each on each side of the body Descending Pathways • Deliver motor instructions from the brain to the spinal cord • Divided into two groups • Pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts • Other motor pathways • Tectospinal tracts • Vestibulospinal tract • Rubrospinal tract • Reticulospinal tract Disorders of the Central Nervous System • Spinal cord damage • Paralysis—loss of motor function • Parasthesia—loss of sensation • Paraplegia—injury to the spinal cord is between T1 and L2 • Paralysis of the lower limbs • Quadriplegia—injury to the spinal cord in the cervical region • Paralysis of all four limbs Disorders of the Central Nervous System • Brain dysfunction • Degenerative brain diseases • Cerebrovascular accident (stroke) • Blockage or interruption of blood flow to a brain region • Alzheimer’s disease • Progressive degenerative disease leading to dementias Disorders of the Central Nervous System • Congenital malformations • Hydrocephalus • Neural tube defects • Anencephaly—cerebrum and cerebellum are absent • Spina bifida—absence of vertebral lamina • Cerebral palsy—voluntary muscles are poorly controlled • Results from damage to the motor cortex Postnatal Changes in the Brain • Brain structures complete development at different times • Critical periods in learning • Language • Some development occurs into early 20s • Decline with age attributed to changes • In neural circuitry • Amount of neurotransmitters being released 14 The Peripheral Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System • The PNS • Is the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord • Provides vital links to the body and outside world • Nerves allow the CNS to receive information and initiate action The Peripheral Nervous System • Sensory inputs and motor outputs • Categorized as • Somatic or visceral • General or special The Peripheral Nervous System • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • General visceral motor part of the PNS • ANS has two divisions • Parasympathetic • Sympathetic Basic Structural Components of the PNS • Sensory receptors—pick up stimuli from inside or outside the body • Nerves and ganglia • Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons • Ganglia—clusters of peripheral neuronal cell bodies • Motor endings—axon terminals of motor neurons • Innervate effectors (muscle fibers and glands) Peripheral Sensory Receptors • Structures that pick up sensory stimuli • Initiate signals in sensory axons Peripheral Sensory Receptors • Two main categories of sensory receptors • Free nerve endings of sensory neurons • Monitor general sensory information • Complete receptor cells—specialized epithelial cells or small neurons • Monitor most types of special sensory information Peripheral Sensory Receptors • Sensory receptors also classified according to • Location • Type of stimulus detected • Structure Classification by Location • Exteroceptors—sensitive to stimuli arising from outside the body • Located at or near body surfaces • Include receptors for touch, pressure, pain, and temperature Classification by Location • Interoceptors—receive stimuli from internal viscera • Located in digestive tube, bladder, and lungs • Monitor a variety of stimuli • Changes in chemical concentration • Taste stimuli • Stretching of tissues • Temperature Classification by Location • Proprioceptors • Located in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, and ligaments • Monitor degree of stretch • Send inputs on body movement to the CNS Classification by Stimulus Detected • Mechanoreceptors—respond to mechanical forces • Touch, pressure, stretch, vibration, and itch • Baroreceptors monitor blood pressure • Thermoreceptors—respond to temperature changes Classification by Stimulus Detected • Chemoreceptors • Respond to chemicals in solution • Photoreceptors—respond to light • Located in the eye • Nociceptors • Respond to harmful stimuli that result in pain Classification by Structure • General sensory receptors • Widely distributed • Nerve endings of sensory neurons monitor: • Touch • Pressure • Vibration • Stretch • Pain • Temperature • Proprioception Classification by Structure • General sensory receptors are • Divided into two groups • Free nerve endings • Encapsulated nerve endings Free Nerve Endings • Abundant in epithelia and underlying connective tissue • Respond to pain and temperature • Monitor affective senses Free Nerve Endings • Two specialized types of free nerve endings • Epithelial tactile complexes (Merkel discs) • Consist of tactile epithelial cell innervated by sensory nerve ending • Slowly adapting receptors for light touch • Hair follicle receptors—wrap around hair follicles • Rapidly adapting receptors Encapsulated Nerve Endings • Consist of one or more end fibers of sensory neurons • Enclosed in connective tissue • Mechanoreceptors • Include four main types • Tactile (Meissner’s) corpuscles • Lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscles • Bulbous corpuscles (Ruffini endings) • Proprioceptors Encapsulated Nerve Endings • Tactile (Meissner’s) corpuscles • • • • Spiraling nerve ending surrounded by Schwann cells Occur in the dermal papillae Rapidly adapting receptors for discriminative touch Occur in sensitive, hairless areas of the skin Encapsulated Nerve Endings • Lamellar Corpuscles • Single nerve ending surrounded by layers of flattened Schwann cells • Occur in the hypodermis • Sensitive to deep pressure—rapidly adapting receptors Encapsulated Nerve Endings • Bulbous Corpuscles • Located in the dermis and respond to pressure • Monitor continuous pressure on the skin—adapt slowly Encapsulated Nerve Endings • Proprioceptors • Monitor stretch in locomotory organs • Three types of proprioceptors Three Types of Proprioceptors • Muscle spindles—measure the changing length of a muscle • Imbedded in the perimysium between muscle fascicles • Golgi tendon organs—located near the muscle-tendon junction • Monitor tension within tendons • Joint kinesthetic receptors • Sensory nerve endings within the joint capsules 14 The Peripheral Nervous System Cranial Nerves • Attach to the brain and pass through foramina of the skull • Numbered from I–XII • Cranial nerves I and II attach to the forebrain • All others attach to the brain stem • Primarily serve head and neck structures • The vagus nerve (X) is the only cranial nerve that extends into the abdomen Olfactory Nerves • Sensory nerves of smell II The Optic Nerves • Sensory nerve of vision III The Oculomotor Nerves • Innervates four of the extrinsic eye muscles IV The Trochlear Nerves • Innervates the superior oblique muscle (an extrinsic eye muscle) V The Trigeminal Nerves The Trigeminal Nerves • Largest of the cranial nerves • Has three divisions • Ophthalmic division (V1) • Maxillary division (V2) • Mandibular division (V3) • Cell bodies of sensory neurons located in the trigeminal ganglion • Mandibular division contains motor fibers that innervate the chewing muscles 14 The Peripheral Nervous System VI The Abducens Nerves • Abducts the eyeball—innervates lateral rectus muscle VII The Facial Nerves • Innervates muscles of facial expression VIII The Vestibulocochlear Nerves • Sensory nerve of hearing and balance IX The Glossopharyngeal Nerves • Innervates structures of the tongue and pharynx X The Vagus Nerves • A mixed sensory and motor nerve • “Wanders” into thorax and abdomen • Parasympathetic innervation of organs XI The Accessory Nerves • Unique among cranial nerves • Accessory nerves are formed from ventral rootlets of the spinal cord • Do not arise from the brainstem XII The Hypoglossal Nerves • Runs inferior to the tongue • Innervates the tongue muscles 14 The Peripheral Nervous System Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs—contain thousands of nerve fibers • Connect to the spinal cord • Named for point of issue from the spinal cord • • • • • 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C1–C8) 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T1–T12) 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L1–L5) 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S1–S5) 1 pair of coccygeal nerves (Co1) Spinal Nerves Posterior View Spinal Nerves • Connect to the spinal cord by the dorsal root and ventral root • Dorsal root—contains sensory fibers • Cell bodies—located in the dorsal root ganglion • Ventral root—contains motor fibers arising from anterior gray column Spinal Nerves • Branch into dorsal ramus and ventral ramus • Dorsal and ventral rami contain sensory and motor fibers • Rami communicantes connect to the base of the ventral ramus • Lead to the sympathetic chain ganglia Innervation of the Back • Dorsal rami • Innervate back muscles • Follow a neat, segmented pattern • Innervate a horizontal strip of muscle and skin • In line with emergence point from the vertebral column Innervation of the Anterior Thoracic and Abdominal Wall • Thoracic region • Ventral rami arranged in simple, segmented pattern • Intercostal nerves—supply intercostal muscles, skin, and abdominal wall • Each gives off lateral and anterior cutaneous branches Introduction to Nerve Plexuses • Nerve plexus—a network of nerves • Ventral rami (except T2–T12) • Branch and join with one another • Form nerve plexuses • In cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions • Primarily serve the limbs • Fibers from ventral rami crisscross The Cervical Plexus • Buried deep in the neck • Under the sternocleidomastoid muscle • • • • Formed by ventral rami of first four cervical nerves (cn 1–4) Most are cutaneous nerves Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck Phrenic nerve—the most important nerve of the cervical plexus The Brachial Plexus and Innervation of the Upper Limb • Brachial plexus lies in the neck and axilla • Formed by ventral rami of C5–C8 • Cords give rise to main nerves of the upper limb Nerves from the Lateral and Medial Cords • Musculocutaneous—main branch of the lateral cord • Innervates the biceps brachii and brachialis • Median—originates from both lateral and medial cords • Innervates anterior forearm muscles and lateral palm Nerves from the Lateral and Medial Cords • Ulnar—branches from the medial cord • Innervates intrinsic hand muscles and skin of the medial hand Nerves from the Posterior Cord • Radial—continuation of the posterior cord • Largest branch of the brachial plexus • Innervates muscles of the posterior upper limb • Axillary • Innervates the deltoid and teres minor 14 The Peripheral Nervous System The Lumbar Plexus and Innervation of the Lower Limb • Lumbar plexus • Arises from L1– L4 • Smaller branches innervate the posterior abdominal wall and psoas muscle • Main branches innervate the anterior thigh • Femoral nerve—innervates anterior thigh muscles • Obturator nerve—innervates adductor muscles The Sacral Plexus • Arises from spinal nerves L4–S4 • Caudal to the lumbar plexus • Often considered with the lumbar plexus • Lumbosacral plexus Innervation of the Lower Limb • Sciatic nerve—the largest nerve of the sacral plexus • Actually two nerves in one sheath • Tibial nerve—innervates most of the posterior lower limb • Common fibular (peroneal) nerve—innervates muscles of the anterolateral leg Innervation of the Lower Limb • Superior and inferior gluteal nerves • Innervate the gluteal muscles • Pudendal nerve • Innervates muscles of the perineum Innervation of the Skin: Dermatomes • Dermatome—an area of skin • Innervated by cutaneous branches of a single spinal nerve • Upper limb • Skin is supplied by nerves of the brachial plexus • Lower limb • Lumbar nerves—anterior surface • Sacral nerves—posterior surface Disorders of the PNS • Shingles (herpes zoster) • • • • Viral infection Stems from childhood chicken pox Often brought on by stress Mostly experienced by those over 50 Disorders of the PNS • Migraine headache • Relates to sensory innervation of cerebral arteries • Arteries dilate and compresses and irritate sensory nerve endings • Myasthenia gravis • Progressive weakening of the skeletal muscles • An autoimmune disorder • Antibodies destroy acetylcholine receptors The PNS Throughout Life • Spinal nerves form late in week 4 • Each of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves: • Sends motor fibers to an individual myotome • Sends sensory fibers to the overlying band of skin • During week 5, nerves reach the organs they innervate The PNS Throughout Life • Embryonic muscles migrate to new locations • Some skin dermatomes become displaced • Muscles and skin always retain their original nerve supply 15 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons • The ANS—a system of motor neurons • Innervates • Smooth muscle • Cardiac muscle • Glands • The ANS—a system of motor neurons • Regulates visceral functions • Heart rate • Blood pressure • Digestion • Urination • The ANS is the • General visceral motor division of the PNS The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons Comparison of Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems • Somatic motor system • One motor neuron extends from the CNS to skeletal muscle • Axons are well myelinated, conduct impulses rapidly Comparison of Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems • Autonomic nervous system • Chain of two motor neurons • Preganglionic neuron • Ganglionic neuron • Conduction is slower than somatic nervous system due to • Thinly myelinated or unmyelinated axons • Motor neuron synapses in a ganglion Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions • Chains of two motor neurons • Innervate mostly the same structures • Cause opposite effects • Sympathetic division mobilizes the body during extreme situations • Parasympathetic division controls routine maintenance functions Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic—“fight, flight, or fright” • Activated during EXTREME situations • Exercise • Excitement • Emergencies Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic responses help us respond to dangerous situations • • • • Increase heart rate and breathing rate Increases blood and oxygen to skeletal muscles Dilates pupils and airways Motility of the digestive tract and urinary tracts are inhibited Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System • Parasympathetic division • Active when the body is at rest • Concerned with conserving energy • Directs “housekeeping” activities • Heart rate and breathing are at low-normal levels • Gastrointestinal tract digests food • Pupils are constricted Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions • Issue from different regions of the CNS • Sympathetic—also called the thoracolumbar division • Parasympathetic—also called the craniosacral division Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions • Length of postganglionic fibers • Sympathetic—long postganglionic fibers • Parasympathetic—short postganglionic fibers • Branching of axons • Sympathetic axons—highly branched • Influences many organs • Parasympathetic axons—few branches • Localized effect Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions • Neurotransmitter released by postganglionic axons • Sympathetic • Most release norepinephrine (adrenergic) • Parasympathetic • Release acetylcholine (cholinergic) Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Divisions The Parasympathetic Division • Cranial outflow • Comes from the brain • Innervates • Organs of the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen • Sacral outflow • Innervation supplies • Remaining abdominal and pelvic organs The Parasympathetic Division Cranial Outflow (Parasympathetic) • Preganglionic fibers run via • • • • Oculomotor nerve (III) Facial nerve (VII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Vagus nerve (X) • Cell bodies of CNs located in cranial nerve nuclei in the brain stem Outflow via the Oculomotor Nerve (III) • Parasympathetic fibers innervate smooth muscles in the eye • Cause pupil constriction • Preganglionic cell bodies • Located in the oculomotor nucleus in the midbrain • Ganglionic cell bodies • Lie in the ciliary ganglion Outflow via the Facial Nerve (VII) • Parasympathetic fibers stimulate secretion of glands in the head • Lacrimal nucleus • Located in the pons • Synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion • Superior salivatory nucleus • Located in the pons • Synapse in the submandibular ganglion Outflow via the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) • Parasympathetic fibers • Stimulate secretion of glands in the head • Lacrimal nucleus—located in the pons • Synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion • Superior salivatory nucleus—located in the pons • Synapse in the submandibular ganglion Outflow via the Vagus Nerve (X) • Fibers innervate visceral organs of the thorax and most of the abdomen • Stimulates: • Digestion, reduction in heart rate, and reduction in blood pressure • Preganglionic cell bodies • Located in dorsal motor nucleus in the medulla • Postganglionic neurons • Confined within the walls of organs being innervated • Cell bodies form intramural ganglia Path of the Vagus Nerve • Sends branches through • Autonomic nerve plexuses • Cardiac plexus • Pulmonary plexus • Esophageal plexus • Celiac plexus • Superior mesenteric plexus Autonomic nerves, plexuses and ganglia 15 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons Sacral Outflow • Emerges from S2–S4 • Innervates organs of the pelvis and lower abdomen • Preganglionic cell bodies • Located in visceral motor region of spinal gray matter Sacral Outflow • Axons run in ventral roots to ventral rami • Form pelvic splanchnic nerves • Run through the inferior hypogastric plexus The Sympathetic Division • Basic organization • Issues from T1–L2 • Preganglionic fibers form the lateral gray horn • Supplies visceral organs and structures of superficial body regions • Contains more ganglia than the parasympathetic division Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia • Located on both sides of the vertebral column • Linked by short nerves into sympathetic trunks • Sympathetic trunk ganglia are also called • Chain ganglia • Paravertebral ganglia Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia • Joined to ventral rami by white and gray rami communicantes • Fusion of ganglia fewer ganglia than spinal nerves • Fusion of ganglia most apparent in the cervical region • Superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia Collateral Ganglia • Differ from sympathetic trunk ganglia in three ways • Unpaired, not segmentally arranged • Occur only in abdomen and pelvis • Lie anterior to the vertebral column • Main ganglia • Celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, and inferior hypogastric ganglia Sympathetic Pathways • Preganglionic neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord send motor axons through: • Adjacent ventral root into • Spinal nerve, then the • White ramus communicans • And to the associated sympathetic trunk ganglion Sympathetic Pathways • Preganglionic axons follow one of three pathways 1. Synapes with a postganglionic neuron at the same level and exit on a spinal nerve at that level Sympathetic Pathways 2. Axon ascends or descends in the sympathetic trunk to synapse in another ganglion 3. Axon passes through the sympathetic trunk and exits on a splanchnic nerve Sympathetic Pathways to the Body Periphery • Innervate • Sweat glands • Arrector pili muscles • Peripheral blood vessels Pathways to the Body Periphery • Preganglionic fibers enter the sympathetic trunk ganglia and synapse there • Some preganglionic fibers travel superiorly or inferiorly on the sympathetic trunk • Postganglionic axons travel in gray rami communicantes Pathways to the Body Periphery • Gray and white rami communicantes • Gray rami—contain only postganglionic fibers traveling to peripheral structures • Fibers are unmyelinated • White rami—contain preganglionic fibers traveling to sympathetic trunk ganglia • Fibers are myelinated Sympathetic Pathways to the Head • Preganglionic fibers originate in spinal cord at T1–T4 • Fibers ascend in the sympathetic trunk • Synapse in superior cervical ganglion Sympathetic Pathways to the Head • Postganglionic fibers associate with large arteries • Carried by these structures to • Glands • Smooth muscle • Vessels throughout the head Sympathetic Pathways to Thoracic Organs • Preganglionic fibers originate at spinal levels T1–T6 • Some fibers synapse in nearest sympathetic trunk ganglion • Postganglionic fibers run directly to the organ supplied Sympathetic Pathways to Thoracic Organs • Sympathetic fibers to heart have a less direct route • Functions • • • • Increase heart rate Dilate bronchioles Dilate blood vessels to the heart wall Inhibit muscles and glands in the esophagus and digestive system Sympathetic Pathways to Abdominal Organs • Preganglionic fibers originate in spinal cord (T5–L2) • Pass through adjacent sympathetic trunk ganglia • Then travel in thoracic splanchnic nerves • Synapse in prevertebral ganglia on the abdominal aorta • Celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia • Inhibit activity of muscles and glands in visceral organs Pathways to the Pelvic Organs • Preganglionic fibers originate in the spinal cord from T10–L2 • Fibers descend in the sympathetic trunk to lumbar and sacral ganglia • Some postganglionic fibers run in lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves to plexuses • Inferior mesenteric plexus, aortic plexus, or hypogastric plexus Pathways to the Pelvic Organs (continued) • Other preganglionic fibers pass directly to autonomic plexuses and synapse in collateral ganglia • Inferior mesenteric ganglia or inferior hypogastric ganglia • Postganglionic fibers go from these plexuses to the • Bladder, reproductive organs, and distal large intestine The Role of the Adrenal Medulla in the Sympathetic Division • Major organ of the sympathetic nervous system • Constitutes largest sympathetic ganglia • Secretes great quantities of norepinephrine and adrenaline • Stimulated to secrete by preganglionic sympathetic fibers Visceral Sensory Neurons • General visceral sensory neurons monitor • Stretch, temperature, chemical changes, and irritation • Cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion • Visceral pain • No pain results when visceral organs are cut • Visceral pain results from chemical irritation or inflammation • Visceral pain often perceived to be of somatic origin • Phenomenon of referred pain Visceral Reflexes • Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons • Participate in visceral reflex arcs • Defecation reflex • Micturition reflex • Some are simple spinal reflexes • Others do not involve the CNS • Strictly peripheral reflexes Central Control of the ANS • Control by the brain stem and spinal cord • Reticular formation exerts most direct influence • Medulla oblongata • Periaqueductal gray matter • Control by the hypothalamus and amygdala • Hypothalamus—the main integration center of the ANS • Amygdala—main limbic region for emotions • Control by the cerebral cortex Disorders of the Autonomic Nervous System • Raynaud’s disease—characterized by constriction of blood vessels • Provoked by exposure to cold or by emotional stress • Hypertension—high blood pressure • Can result from overactive sympathetic vasoconstriction Disorders of the Autonomic Nervous System • Mass reflex reaction • Uncontrolled activation of autonomic and somatic motor neurons • Affects quadriplegics and paraplegics • Achalasia of the cardia • Defect in the autonomic innervation of the esophagus The ANS Throughout Life • Preganglionic neurons of the ANS develop from the neural tube • Ganglionic neurons develop from the neural crest • Development of the sympathetic division • Some cells migrate ventrally • Form the sympathetic trunk ganglia • Other cells migrate • Form the prevertebral ganglia The ANS Throughout Life • Efficiency of the ANS declines with advancing age • Constipation due to reduced mobility of gastrointestinal (GI) tract • Dry eyes due to reduced tear formation 16 The Special Senses The Special Senses • Taste, smell, sight, hearing, and balance • Touch—a large group of general senses • Special sensory receptors • Localized—confined to the head region • Receptors are not free endings of sensory neurons • Special receptor cells • Are neuronlike epithelial cells or small peripheral neurons • Transfer sensory information to other neurons in afferent pathways The Chemical Senses: Taste and Smell • Taste—gustation • Smell—olfaction • Receptors—classified as chemoreceptors • Respond to chemicals • Food dissolved in saliva • Airborne chemicals that dissolve in fluids of the nasal mucosa Taste—Gustation • Taste receptors • Occur in taste buds • Most are found on the surface of the tongue • Located within tongue papillae • Two types of papillae (with taste buds) • Fungiform papillae • Vallate papillae Taste Buds • Collection of 50–100 epithelial cells • Contain two major cell types • Gustatory epithelial cells supporting cells • Basal epithelial cells gustatory cells • Contain long microvilli—extend through a taste pore to the surface of the epithelium • Cells in tastebuds replaced every 7–10 days Taste Sensation and the Gustatory Pathway • Five basic qualities of taste • Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami • “Umami” is elicited by glutamate • The “taste map” is a myth • All taste modalities can be elicited from all areas containing taste buds Gustatory Pathway • Taste information reaches the cerebral cortex • Primarily through the facial (VII) and glossopharyngeal (IX) nerves • Some taste information through the vagus nerve (X) • Sensory neurons synapse in the medulla • Located in the solitary nucleus • Impulses are transmitted to the thalamus and ultimately to the gustatory area of the cerebral cortex in the insula Smell (Olfaction) • Olfactory receptors are part of the olfactory epithelium • Olfactory epithelium is pseudostratified columnar and contains three main cell types • Olfactory sensory neurons • Supporting epithelial cells • Basal epithelial cells Smell (Olfaction) • Cell bodies of olfactory sensory neurons • Located in olfactory epithelium • Have an apical dendrite that projects to the epithelial surface • Ends in a knob from which olfactory cilia radiate Smell (Olfaction) • Olfactory cilia act as receptive structures for smell • Mucus captures and dissolves odor molecules Smell (Olfaction) • Axons of olfactory epithelium • • • • Gather into bundles—filaments of the olfactory nerve Pass through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone Attach to the olfactory bulbs and synapse with mitral cells Mitral cells transmit impulses along the olfactory tract to 1.Limbic system 2.Piriform lobe of the cerebral cortex Disorders of the Chemical Senses • Anosmia—absence of the sense of smell • Due to injury, colds, allergies, or zinc deficiency • Uncinate fits—distortion of smells or olfactory hallucinations • Often result from irritation of olfactory pathways • After brain surgery or head trauma Embryonic Development of the Chemical Senses • Development of olfactory epithelium and taste buds • Olfactory epithelium—derives from olfactory placodes • Taste buds develop upon stimulation by gustatory nerves The Eye and Vision • Visual organ—the eye • 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eyes • 40% of the cerebral cortex is involved in processing visual information • Anterior one-sixth of the eye’s surface is visible Accessory Structures of the Eye • Eyebrows—coarse hairs on the superciliary arches • Eyelids (palpebrae)—separated by the palpebral fissure • • • • Meet at the medial and lateral angles (canthi) Lacrimal caruncle—reddish elevation at the medial canthus Tarsal plates—connective tissue within the eyelids Tarsal glands—modified sebaceous glands Accessory Structures of the Eye • Conjunctiva—transparent mucous membrane • Palpebral conjunctiva • Bulbar conjunctiva • Conjunctival sac Accessory Structures of the Eye • Lacrimal apparatus—keeps the surface of the eye moist • Lacrimal gland—produces lacrimal fluid • Lacrimal sac—fluid empties into nasal cavity Extrinsic Eye Muscles • Six muscles that control movement of the eye • Originate in the walls of the orbit • Insert on outer surface of the eyeball • Annular ring—origin of the four rectus muscles • The six extrinsic eye muscles are • Lateral rectus and medial rectus • Superior rectus and inferior rectus • Superior oblique and inferior oblique 16 The Special Senses Anatomy of the Eyeball • Components of the eye • Protect and support the photoreceptors • Gather, focus, and process light into precise images • • • • Anterior pole—most anterior part of the eye Posterior pole—most posterior part of the eye External walls—composed of three tunics Internal cavity—contains fluids (humors) The Fibrous Layer • Most external layer of the eyeball • Composed of two regions of connective tissue • Sclera—posterior five-sixths of the tunic • White, opaque region • Provides shape and an anchor for eye muscles • Cornea—anterior one-sixth of the fibrous tunic • Limbus—junction between sclera and cornea • Scleral venous sinus—allows aqueous humor to drain The Vascular Layer • The middle coat of the eyeball • Composed of choroid, ciliary body, and iris • Choroid—vascular, darkly pigmented membrane • Forms posterior five-sixths of the vascular tunic • Brown color—from melanocytes • Prevents scattering of light rays within the eye • Choroid corresponds to the arachnoid and pia maters The Vascular Layer • Ciliary body—thickened ring of tissue, which encircles the lens • Composed of ciliary muscle • Ciliary processes—posterior surface of the ciliary body • Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament) • Attached around entire circumference of the lens The Iris • Visible colored part of the eye • Attached to the ciliary body • Composed of smooth muscle • Pupil—the round, central opening • Sphincter pupillae muscle • Dilator pupillae muscle • Act to vary the size of the pupil • Pupillary light reflex • Protective response of pupil constriction when a bright light is flashed in the eye The Inner Layer (Retina) • Retina—the deepest tunic • Composed of two layers • Pigmented layer—single layer of melanocytes • Neural layer—sheet of nervous tissue • Contains three main types of neurons • Photoreceptor cells • Bipolar cells • Ganglion cells The Inner Layer • Photoreceptor cells signal bipolar cells • Bipolar cells signal ganglion cells to generate nerve impulses • Axons from ganglion cells run along internal surface of the retina • Converge posteriorly to form the optic nerve Photoreceptors • Two main types • Rod cells—more sensitive to light • Allow vision in dim light • Cone cells—operate best in bright light • Enable high-acuity, color vision • Considered neurons Photoreceptors • Rods and cones have an inner and outer segment • Outer segments are receptor regions • Light absorbing pigments are present • Light particles modify the visual pigment and generate a nerve impulse Photoreceptors • Photoreceptors • Vulnerable to damage by light or heat • Cannot regenerate if destroyed • Continuously renew and replace their outer segments Regional Specializations of the Retina • Ora serrata retinae • Neural layer ends at the posterior margin of the ciliary body • Pigmented layer covers ciliary body and posterior surface of the iris • Macula lutea—contains mostly cones • Fovea centralis—contains only cones • Region of highest visual acuity • Optic disc—blind spot Blood Supply of the Retina • Retina receives blood from two sources • Outer third of the retina—supplied by capillaries in the choroid • Inner two-thirds of the retina—supplied by central artery and vein of the retina Internal Chambers and Fluids • The lens and ciliary zonules divide the eye • Posterior segment (cavity) • Filled with vitreous humor • Clear, jelly-like substance • Transmits light • Supports the posterior surface of the lens • Helps maintain intraocular pressure Internal Chambers and Fluids • Anterior segment • Divided into anterior and posterior chambers • Anterior chamber—between the cornea and iris • Posterior chamber—between the iris and lens • Filled with aqueous humor • Renewed continuously • Formed as a blood filtrate • Supplies nutrients to the lens and cornea 16 The Special Senses The Lens • A thick, transparent, biconvex disc • Held in place by its ciliary zonule • Lens epithelium—covers anterior surface of the lens • Lens fibers form the bulk of the lens • New lens fibers are continuously added • Lens enlarges throughout life The Eye as an Optical Device • Structures in the eye bend light rays • Light rays converge on the retina at a single focal point • Light bending structures (refractory media) are • The lens, cornea, and humors • Accommodation—curvature of the lens is adjustable • Allows for focusing on nearby objects Visual Pathways • Most visual information travels to the cerebral cortex • Responsible for conscious “seeing” • Other pathways travel to nuclei in the midbrain and diencephalon Visual Pathways to the Cerebral Cortex • Pathway begins at the retina • • • • Light activates photoreceptors Photoreceptors signal bipolar cells Bipolar cells signal ganglion cells Axons of ganglion cells exit eye as the optic nerve Visual Pathways to the Cerebral Cortex • Optic tracts send axons to • Lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus • Synapse with thalamic neurons • Fibers of the optic radiation reach the primary visual cortex Visual Pathways to Other Parts of the Brain • Some axons from the optic tracts • Branch to midbrain • Superior colliculi • Pretectal nuclei • Other branches from the optic tracts • Branch to the suprachiasmatic nucleus Disorders of the Eye and Vision • Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) • Involves the buildup of visual pigments in the retina • Retinopathy of prematurity • Blood vessels grow within the eyes of premature infants • Vessels have weak walls—causes hemorrhaging and blindness • Trachoma—contagious infection of the conjunctiva Embryonic Development of the Eye • Eyes develop as outpocketings of the brain • By week 4, optic vesicles protrude from the diencephalon Embryonic Development of the Eye • Ectoderm thickens and forms a lens placodes • By week 5, a lens vesicle forms • Internal layer of the optic cup becomes • Neural retina • External layer becomes • Pigmented retina • Optic fissure—pathway for blood vessels The Ear: Hearing and Equilibrium • The ear—receptor organ for hearing and equilibrium • Composed of three main regions • Outer ear—functions in hearing • Middle ear—functions in hearing • Internal ear—functions in both hearing and equilibrium The Outer (External) Ear • Composed of • The auricle (pinna) • Helps direct sounds • External acoustic meatus • Lined with skin • Contains hairs, sebaceous glands, and ceruminous glands • Tympanic membrane • Forms the boundary between the external and middle ear Structure of the Ear The Middle Ear • Composed of • The tympanic cavity • A small, air-filled space • Located within the petrous portion of the temporal bone • Medial wall is penetrated by • Oval window • Round window • Pharyngotympanic tube (auditory or eustachian tube) • Links the middle ear and pharynx Structures of the Middle Ear The Middle Ear • Ear ossicles—smallest bones in the body • Malleus—attaches to the eardrum • Incus—between the malleus and stapes • Stapes—vibrates against the oval window • Tensor tympani and stapedius • Two tiny skeletal muscles in the middle ear cavity The Internal Ear • Internal ear—also called the labyrinth • Lies within the petrous portion of the temporal bone • Bony labyrinth—a cavity consisting of three parts • Semicircular canals • Vestibule • Cochlea The Internal Ear The Internal Ear • Membranous labyrinth • Series of membrane-walled sacs and ducts • Fit within the bony labyrinth • Consists of three main parts • Semicircular ducts • Utricle and saccule • Cochlear duct The Internal Ear • Membranous labyrinth (continued) • Filled with a clear fluid—endolymph • Confined to the membranous labyrinth • Bony labyrinth is filled with perilymph • Continuous with cerebrospinal fluid The Internal Ear The Cochlea • A spiraling chamber in the bony labyrinth • Coils around a pillar of bone—the modiolus • Spiral lamina—a spiral of bone in the modiolus • The cochlear nerve runs through the core of the modiolus The Cochlea • The cochlear duct (scala media)—contains receptors for hearing • Lies between two chambers • The scala vestibuli • The scala tympani • The vestibular membrane—the roof of the cochlear duct • The basilar membrane—the floor of the cochlear duct The Cochlea • The cochlear duct (scala media)—contains receptors for hearing • Spiral organ (of Corti)—the receptor epithelium for hearing • Consists of • Supporting cells • Inner and outer hair cells (receptor cells) • Inner hair cells are the receptors that transmit vibrations of the basilar membrane • Outer hair cells actively tune the cochlea and amplify the signal The Anatomy of the Cochlea The Role of the Cochlea in Hearing The Vestibule • The central part of the bony labyrinth • Lies medial to the middle ear • Utricle and saccule—suspended in perilymph • Two egg-shaped parts of the membranous labyrinth • House the macula—a spot of sensory epithelium The Vestibule • Macula—contains receptor cells • Monitor the position of the head when the head is still • Contains columnar supporting cells • Receptor cells—called hair cells • Synapse with the vestibular nerve • Tips of hair cells are embedded in otolithic membrane • Contains crystals of calcium carbonate called otoliths 16 The Special Senses The Semicircular Canals • Lie posterior and lateral to the vestibule • Anterior and posterior semicircular canals • Lie in the vertical plane at right angles • Lateral semicircular canal • Lies in the horizontal plane The Semicircular Canals • Semicircular duct—snakes through each semicircular canal • Membranous ampulla—located within bony ampulla • Houses a structure called a crista ampullaris • Cristae contain receptor cells of rotational acceleration • Epithelium contains supporting cells and receptor hair cells Equilibrium and Auditory Pathways • The equilibrium pathway • Transmits information on the position and movement of the head • Most information goes to lower brain centers (reflex centers) • The ascending auditory pathway • Transmits information from cochlear receptors to the cerebral cortex Disorders of Equilibrium and Hearing • Motion sickness—carsickness, seasickness • Popular theory for a cause—a mismatch of sensory inputs • Meniere’s syndrome—equilibrium is greatly disturbed • Excessive amounts of endolymph in the membranous labyrinth Disorders of Equilibrium and Hearing • Deafness • Conduction deafness • Sound vibrations cannot be conducted to the inner ear • Ruptured tympanic membrane, otitis media, otosclerosis • Sensorineural deafness • Results from damage to any part of the auditory pathway Embryonic Development of the Ear • Begins in the fourth week of development • The inner ear forms from ectoderm • The middle ear forms from the first pharyngeal pouches • Ear ossicles develop from cartilage • The external ear differentiates from the first branchial groove The Special Senses Throughout Life • Smell and taste • Sharp in newborns • In the fourth decade of life • Ability to taste and smell declines The Special Senses Throughout Life • Photoreceptors—fully formed by 25 weeks • All newborns are hyperopic • By 3 months—image can be focused on the retina • By 6 months—depth perception is present The Special Senses Throughout Life • With increased age • The lens loses its clarity • The dilator muscles of the iris become inefficient • Visual acuity is dramatically lower in people over 70 The Special Senses Throughout Life • In the newborn • Responses to sounds are reflexive • Low-pitched and middle-pitched sounds can be heard • In the elderly • Hair cells are gradually lost • Ability to hear high-pitched sounds fades • Presbycusis—gradual loss of hearing with age 18 Blood Blood Circulation • Powered by the pumping action of the heart • Functions of blood • Carries respiratory gases, nutrients, and hormones • Helps body regulate temperature • Blood volume • Males: 5–6 liters • Females: 4–5 liters Composition of Blood • Contains cellular and liquid components • A specialized connective tissue • Blood cells—formed elements • Plasma—fluid portion and fibrinogen • Hematocrit—measure of % RBC • Males: 47% ± 5% • Females: 42% ± 5% Major Components of Whole Blood Blood Plasma • Straw-colored, sticky fluid portion of blood • Approximately 90% water • Contains over 100 kinds of molecules • Ions—Na+ and Cl– • Nutrients—Sugars, amino acids, lipids, wastes, and proteins • Three main proteins • Albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen Formed Elements • Blood cells • Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets • Staining of blood cells • Acidic dye—eosin; stains pink • Basic dye—methylene blue; stains blue and purple Erythrocytes • Oxygen-transporting cells—7.5 µm in diameter (diameter of capillary 8—10mm) • Most numerous of the formed elements • Females: 4.3–5.2 million cells/cubic millimeter • Males: 5.2–5.8 million cells/cubic millimeter • Have no organelles or nuclei • Are the ideal measuring tool for estimating sizes of nearby structures Erythrocytes • Are packed with oxygen-carrying hemoglobin • Hemoglobin molecule bears four oxygen molecules • Each O2 molecule bears an iron molecule • Oxidation of iron atoms of hemoglobin molecules • Gives blood its red color Erythrocytes • Pick up O2 at lung capillaries • Release O2 across other tissue capillaries • Structural characteristics contribute to respiratory function • Biconcave shape 30 more surface area • 97% hemoglobin • Lack mitochondria • Do not consume O2 they pick up An Erythrocyte Leukocytes—White Blood Cells (WBCs) • 4800–11,000/cubic millimeter • Protect the body from infectious microorganisms • Function outside the bloodstream in loose connective tissue • Diapedesis—circulating leukocytes leave the capillaries • Originate in bone marrow Leukocytes—White Blood Cells (WBCs) • Two types of leukocytes • Granulocytes • Agranulocytes • Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas Relative Percentages of the Different Types of Leukocytes Granulocytes • Neutrophils—most numerous WBC • Phagocytize and destroy bacteria • Nucleus—has two to six lobes • Granules pick up acidic and basic stains • Eosinophils—compose 1–4% of all WBCs • Play roles in • Ending allergic reactions, parasitic infections Granulocytes • Basophils—about 0.5% of all leukocytes • Nucleus—usually two lobes • Granules secrete histamines • Function in inflammation mediation • Similar in function to mast cells Agranulocytes • Lymphocytes—compose 20–45% of WBCs • • • • The most important cells of the immune system Nucleus—stains dark purple Effective in fighting infectious organisms Act against a specific foreign molecule (antigen) Agranulocytes • Two main classes of lymphocyte • T cells—attack foreign cells directly • B cells—multiply to become plasma cells • Secrete antibodies Agranulocytes • Monocytes—compose 4–8% of WBCs • The largest leukocytes • Nucleus—kidney shaped • Transform into macrophages • Phagocytic cells Platelets • Cell fragments • Break off from megakaryocytes • Function in clotting of blood Summary of Formed Elements Blood Cell Formation • Hematopoiesis—process by which blood cells are formed in red marrow • 100 billion new blood cells formed each day Bone Marrow as the Site of Hematopoiesis • Bone marrow—located within all bones • Red marrow—actively generates new blood cells • Contains immature erythrocytes • In adults, red marrow is located • Between trabeculae of spongy bone of axial skeleton • Girdles • Proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur Bone Marrow as the Site of Hematopoiesis • Tissue framework of bone marrow • Reticular connective tissue • Fibroblasts covering and secreting the fiber network are reticular cells • Blood sinusoids run throughout the reticular tissue • Mature blood cells enter the blood stream through endothelial cells of sinusoids Bone Marrow as the Site of Hematopoiesis • Reticular tissue of bone marrow • Contains macrophages that extend pseudopods to capture antigens • Some cells of the reticular network are mesenchymal stem cells • Can give rise to • Fat cells, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, fibroblasts, and muscle cells Red Bone Marrow Bone Marrow as the Site of Hematopoiesis • Yellow marrow—dormant • Contains many fat cells • Located in the long bones of adults Cell Lines in Blood Cell Formation • All blood cells originate in bone marrow • All originate from one cell type • Blood stem cell (pluripotential hematopoeitic stem cell) • Lymphoid stem cells • Give rise to lymphocytes • Myeloid stem cells • Give rise to all other blood cells Cell Lines in Blood Cell Formation • Genesis of erythrocytes • Committed cells are proerythroblasts • Remain in the reticulocyte stage for 1–2 days in circulation • Make up about 1–2% of all erythrocytes Cell Lines in Blood Cell Formation • Formation of leukocytes • Granulocytes form from myeloblasts • Monoblasts enlarge and form monocytes • Platelet-forming cells from megakaryoblasts • Break apart into platelets Stages of Differentiation of Blood Cells Disorders of the Blood • Disorders of erythrocytes • Polycythemia • Abnormal excess of erythrocytes • Anemia • Erythrocyte levels or hemoglobin concentrations are low Disorders of the Blood • Disorders of erythrocytes (continued) • Sickle cell disease • Inherited condition • Results from a defective hemoglobin molecule • Erythrocytes distort into a sickle shape • Hemachromatosis • Inherited • Abnormal excess of iron Disorders of the Blood • Disorders of leukocytes • Leukemia—a form of cancer • Classified as lymphoblastic or myeloblastic • Disorders of platelets • Thrombocytopenia • Abnormally low concentration of platelets The Blood Throughout Life • First blood cells develop with the earliest blood vessels • Mesenchyme cells cluster into blood islands • Late in the second month: • Liver and spleen take over blood formation • Bone marrow becomes major hematopoietic organ at Month 7 19 The Heart The Heart • A muscular double pump • Pulmonary circuit—takes blood to and from the lungs • Systemic circuit—vessels transport blood to and from body tissues • Atria—receive blood from the pulmonary and systemic circuits • Ventricles—the pumping chambers of the heart The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Location and Orientation within the Thorax • Heart—typically weighs 250–350 grams (healthy heart) • Largest organ of the mediastinum • Located between the lungs • Apex lies to the left of the midline • Base is the broad posterior surface Location of the Heart in the Thorax Four “Corners” of the Heart • Superior right • At costal cartilage of third rib and sternum • Inferior right • At costal cartilage of sixth rib lateral to the sternum • Superior left • At costal cartilage of second rib lateral to the sternum • Inferior left • Lies in the fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line Structure of the Heart—Coverings • Pericardium—two primary layers • Fibrous pericardium • Strong layer of dense connective tissue • Serous pericardium • Formed from two layers • Parietal layer of the serous pericardium • Visceral layer of the serous pericardium Layers of the Pericardium and of the Heart Wall Structure of the Heart—Layers of the Heart Wall • Epicardium • Visceral layer of the serous pericardium • Myocardium • Consists of cardiac muscle • Muscle arranged in circular and spiral patterns • Endocardium • Endothelium resting on a layer of connective tissue • Lines the internal walls of the heart Circular and Spiral Arrangements of Cardiac Muscle Bundles Heart Chambers • Right and left atria • Superior chambers • Right and left ventricles • Inferior chambers • Internal divisions • Interventricular septa • Interatrial septa • External markings • Coronary sulcus • Anterior interventricular sulcus • Posterior interventricular sulcus Gross Anatomy of the Heart Right Atrium • Forms right border of heart • Receives blood from systemic circuit • Pectinate muscles • Ridges inside anterior of right atrium • Crista terminalis • Landmark used to locate veins entering right atrium • Fossa ovalis • Depression in interatrial septum • Remnant of foramen ovale Right Ventricle • Receives blood from right atrium through the tricuspid valve • Pumps blood into pulmonary circuit via • Pulmonary trunk • Internal walls of right ventricle • Trabeculae carneae • Papillary muscles • Chordae tendineae • Pulmonary semilunar valve • Located at opening of right ventricle and pulmonary trunk Left Atrium • Makes up heart’s posterior surface • Receives oxygen-rich blood from lungs through pulmonary veins • Opens into the left ventricle through • Mitral valve (left atrioventricular valve) Left Ventricle • Forms apex of the heart • Internal walls of left ventricle • Trabeculae carneae • Papillary muscles • Chordae tendineae • Pumps blood through systemic circuit via • Aortic semilunar valve (aortic valve) Heart Chambers Inferior View of the Heart Heart Valves—Valve Structure • Each valve composed of • Endocardium with connective tissue core • Atrioventricular (AV) valves • Between atria and ventricles • Aortic and pulmonary valves • At junction of ventricles and great arteries Fibrous Skeleton • Surrounds all four valves • Composed of dense connective tissue • Functions • • • • Anchors valve cusps Prevents overdilation of valve openings Main point of insertion for cardiac muscle Blocks direct spread of electrical impulses Heart Valves—Valve Structure Heart Sounds • “Lub-dup”—sound of valves closing • First sound “lub” • The AV valves closing • Second sound “dup” • The semilunar valves closing Heart Sounds • Each valve sound is best heard near a different heart corner • • • • Pulmonary valve—superior left corner Aortic valve—superior right corner Mitral (bicuspid) valve—at the apex Tricuspid valve—inferior right corner Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • Beginning with oxygen-poor blood in the superior and inferior venae cavae • Go through pulmonary and systemic circuits • A blood drop passes through all structures sequentially • Atria contract together • Ventricles contract together Heartbeat • 70–80 beats per minute at rest • Systole—contraction of a heart chamber • Diastole—expansion of a heart chamber • Systole and diastole also refer to • Stage of heartbeat when ventricles contract and expand Structure of Heart Wall • Walls differ in thickness • Atria—thin walls • Ventricles—thick walls • Systemic circuit • Longer than pulmonary circuit • Offers greater resistance to blood flow Structure of Heart Wall • Left ventricle— three times thicker than right • Exerts more pumping force • Flattens right ventricle into a crescent shape Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Forms a thick layer called myocardium • Striated like skeletal muscle • Contractions pump blood through the heart and into blood vessels • Contracts by sliding filament mechanism Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Cardiac muscle cells • • • • Short Branching Have one or two nuclei Not fused colonies like skeletal muscle Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Cells join at intercalated discs • Complex junctions • Form cellular networks • Cells are separated by delicate endomysium • Binds adjacent cardiac fibers • Contains blood vessels and nerves Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Intercalated discs—complex junctions • Adjacent sarcolemmas interlock • Possess three types of cell junctions • Desmosomes • Fasciae adherans—long desmosome-like junctions • Gap junctions Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Triggered to contract by Ca2+ entering the sarcoplasm • Signals sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca2+ ions • Ions diffuse into sarcomeres • Trigger sliding filament mechanism Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Not all cardiac cells are innervated • Will contract in rhythmic manner without innervation • Inherent rhythmicity • Is the basis for rhythmic heartbeat Conducting System • Cardiac muscle tissue has intrinsic ability to • Generate and conduct impulses • Signal these cells to contract rhythmically • Conducting system • A series of specialized cardiac muscle cells • Sinoatrial (SA) node sets the inherent rate of contraction Innervation • Heart rate is altered by external controls • Nerves to the heart include • Visceral sensory fibers • • Parasympathetic branches of the vagus nerve Sympathetic fibers—from cervical and upper thoracic chain ganglia 19 The Heart Blood Supply to the Heart • Functional blood supply • Coronary arteries • Arise from the aorta • Located in the coronary sulcus • Main branches • Left and right coronary arteries Disorders of the Heart • Coronary artery disease • Atherosclerosis—fatty deposits • Angina pectoris—chest pain • Myocardial infarction—blocked coronary artery • Heart attack • Silent ischemia—no pain or warning Disorders of the Heart • Heart failure • Progressive weakening of the heart • Cannot meet the body’s demands for oxygenated blood • Congestive heart failure (CHF) • Heart enlarges • Pumping efficiency declines • Pulmonary arterial hypertension • Enlargement and potential failure of right ventricle Disorders of the Conduction System • Arrythmias—variation from normal heart rhythm • Ventricular fibrillation • Rapid, random firing of electrical impulses in the ventricles • Results from crippled conducting system • Common cause of cardiac arrest Disorders of the Conductory System • Arrythmias (continued) • Atrial fibrillation • Impulses circle within atrial myocardium, stimulating AV node • Promotes formation of clots • Leads to strokes • Occur in episodes characterized by • Anxiety, fatigue, shortness of breath, palpitations Development of the Heart • Heart folds into thorax region about Day 20–21 • Heart starts pumping about Day 22 • Earliest heart chambers are unpaired • From “tail to head,” the chambers are • • • • Sinus venosus Atrium Ventricle Bulbus cordis Development of the Heart • Sinus venosus—will become • Smooth-walled part of right atrium, coronary sinus, and SA node • Also contributes to back wall of left atrium • Atrium—will become • Ridged parts of right and left atria Development of the Heart • Ventricle—is the strongest pumping chamber • Gives rise to the left ventricle • Bulbus cordis • Bulbus cordis and truncus arteriosus give rise to the pulmonary trunk and first part of aorta • Bulbus cordis gives rise to the left ventricle Congenital Heart Defects • Can be traced to month 2 of development • Most common defect is ventricular septal defect • Two basic categories of defect • Inadequately oxygenated blood reaches body tissues • Ventricles labor under increased workload The Heart in Old Age • Heart usually functions well throughout life • Regular exercise increases the strength of the heart • Aerobic exercise can help clear fatty deposits in coronary arteries The Heart in Old Age • Age-related changes 1. Hardening and thickening of heart valve cusps 2. Decline in cardiac reserve 3. Fibrosis of cardiac muscle 20 Blood Vessels Types of Blood Vessels • Arteries—carry blood away from the heart • Capillaries—smallest blood vessels • The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid • Veins—carry blood toward the heart Structure of Blood Vessels • Composed of three layers (tunics) • Tunica intima—composed of simple squamous epithelium • Tunica media—sheets of smooth muscle • Contraction—vasoconstriction • Relaxation—vasodilation • Tunica externa—composed of connective tissue • Lumen • Central blood-filled space of a vessel Structure of Blood Vessels Structure of Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries Types of Arteries • Elastic arteries—the largest arteries • • • • Diameters range from 2.5 cm to 1 cm Includes the aorta and its major branches Sometimes called conducting arteries High elastin content dampens surge of blood pressure Types of Arteries • Muscular (distributing) arteries • Lie distal to elastic arteries • Diameters range from 1 cm to 0.3 mm • Includes most named arteries • Tunica media is thick • Unique feature • Internal and external elastic laminae Types of Arteries • Arterioles • • • • Smallest arteries Diameters range from 0.3 mm to 10 µm Larger arterioles possess all three tunics Diameter of arterioles controlled by • Local factors in the tissues • Sympathetic nervous system Capillaries • Smallest blood vessels • Diameter from 8–10 µm • Red blood cells pass through single file • Site-specific functions of capillaries • Lungs—oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves • Small intestines—receive digested nutrients • Endocrine glands—pick up hormones • Kidneys—remove of nitrogenous wastes RBCs in a Capillary Capillary Beds • Network of capillaries running through tissues • Precapillary sphincters • Regulate the flow of blood to tissues • Tendons and ligaments—poorly vascularized • Epithelia and cartilage—avascular • Receive nutrients from nearby CT Capillary Permeability • Endothelial cells—held together by tight junctions and desmosomes • Intercellular clefts—gaps of unjoined membrane • Small molecules can enter and exit • Two types of capillary • Continuous—most common • Fenestrated—have pores Routes of Capillary Permeability • Four routes into and out of capillaries • • • • Direct diffusion Through intercellular clefts Through cytoplasmic vesicles Through fenestrations Low Permeability Capillaries • Blood-brain barrier • Capillaries have complete tight junctions • No intercellular clefts are present • Vital molecules pass through • Highly selective transport mechanisms • Not a barrier against: • Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some anesthetics Sinusoids • Wide, leaky capillaries found in some organs • Usually fenestrated • Intercellular clefts are wide open • Occur in bone marrow and spleen • Sinusoids have a large diameter and twisted course Veins • Conduct blood from capillaries toward the heart • Blood pressure is much lower than in arteries • Smallest veins—called venules • Diameters from 8–100 m • Smallest venules—called postcapillary venules • Venules join to form veins • Tunica externa is the thickest tunic in veins Mechanisms to Counteract Low Venous Pressure • Valves in some veins • Particularly in limbs • Skeletal muscle pump • Muscles press against thin-walled veins Vascular Anastomoses • Vessels interconnect to form vascular anastomoses • Organs receive blood from more than one arterial source • Neighboring arteries form arterial anastomoses • Provide collateral channels • Veins anastomose more frequently than arteries Vasa Vasorum • Tunica externa of large vessels have • Tiny arteries, capillaries, and veins • Vasa vasorum—vessels of vessels • Nourish outer region of large vessels • Inner half of large vessels receive nutrients from luminal blood Pulmonary Circulation • Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle • Divides into right and left pulmonary arteries • Superior and inferior pulmonary veins • Carry oxygenated blood into the left atrium Systemic Circulation • Systemic arteries • Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart • Aorta—largest artery in the body The Aorta • Ascending aorta—arises from the left ventricle • Branches—coronary arteries • Aortic arch—lies posterior to the manubrium • Branches • Brachiocephalic trunk • Left common carotid • Left subclavian arteries The Aorta • Descending aorta—continues from the aortic arch • Thoracic aorta—in the region of T5–T12 • Abdominal aorta—ends at L4 • Divides into right and left common iliac arteries 20 Blood Vessels Arteries of the Head and Neck Common Carotid Arteries • Located in the anterior triangle of the neck • Two branches of the common carotid artery • External carotid artery • Internal carotid artery Common Carotid Arteries • External carotid artery branches • • • • • • • Superior thyroid artery Lingual artery Facial artery Occipital artery Posterior auricular artery Superficial temporal artery Maxillary artery Common Carotid Arteries • Internal carotid artery branches • Optithalmic artery • Anterior cerebral artery • Anterior communicating artery • Forms part of the cerebral arterial circle • Middle cerebral artery Vertebral Arteries • Supply the posterior brain • Join to form the basilar artery • Basilar artery divides into two posterior cerebral arteries • Posterior cerebral arteries connect to the posterior communicating arteries Cerebral Arterial Circle • Two posterior communicating arteries join the anterior communicating artery Arteries of the Upper Limb • Subclavian artery enters the axilla as the axillary artery • Axillary artery becomes the brachial artery at the inferior border of teres major • Brachial artery divides into • Radial artery and ulnar artery Arteries of the Upper Limb and Thorax Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta • Inferior phrenic arteries • Celiac trunk • Superior mesenteric artery • Suprarenal arteries • Renal arteries • Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) arteries • Inferior mesenteric artery • Common iliac arteries 20 Blood Vessels Distribution of the Superior and Inferior Mesenteric Arteries Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs • Internal iliac arteries • External iliac artery • Femoral artery • Popliteal artery • Anterior tibial artery • Posterior tibial artery Systemic Veins • Three major veins enter the right atrium • Superficial veins lie just beneath the skin • Multivein bundles—venous plexuses • Unusual patterns of venous drainage • Dural sinuses • Hepatic portal system Venae Cavae and Tributaries • Superior vena cava • Returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm • Inferior vena cava • Returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm • Superior and inferior vena cava • Join the right atrium Major Veins of the Systemic Circulation 20 Blood Vessels Veins of the Head and Neck • Venous drainage • Internal jugular veins • External jugular veins • Vertebral veins Veins of the Head and Neck • Dural sinuses • • • • Superior and inferior sagittal sinuses Straight sinus Transverse sinuses Sigmoid sinus Veins of the Upper Limbs • Deep veins • Follow the paths of companion arteries • Have the same names as the companion arteries • Superficial veins • Visible beneath the skin • Cephalic vein • Basilic vein • Median cubital vein • Median vein of the forearm Veins of the Thorax and Right Upper Limb Superficial Veins of the Right Upper Limb • Form anastomese frequently • Median cubital vein is used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids Veins of the Thorax • Azygos vein • Hemiazygos vein • Accessory hemiazygos vein Veins of the Abdomen • Lumbar veins • Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) veins • Renal veins • Suprarenal veins • Hepatic veins The Hepatic Portal System • A specialized part of the vascular circuit • Picks up digested nutrients • Delivers nutrients to the liver for processing The Basic Scheme of the Hepatic Portal System 20 Blood Vessels Veins of the Hepatic Portal System Veins of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs • Deep veins • Share the name of the accompanying artery • Superficial veins • Great saphenous vein empties into the femoral vein • Small saphenous vein empties into the popliteal vein Disorders of the Blood Vessels • Aneurysm • Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb • Venous disease • Microangiopathy of diabetes • Arteriovenous malformation Abdominal Aneurysm Blood Vessels Throughout Life • Fetal circulation • All major vessels in place by month three of development • Differences between fetal and postnatal circulation • Fetus must supply blood to the placenta • Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Vessels to and from the Placenta • Umbilical vessels run in the umbilical cord • Paired umbilical arteries • Unpaired umbilical vein • Fetal vessels and structures • Ductus venosus • Ligamentum teres • Ligamentum venosum • Medial umbilical ligaments Shunts Away from the Pulmonary Circuit • Foramen ovale • Ductus arteriosus Fetal and Newborn Circulation Compared Blood Vessels in Adulthood • Atherosclerosis begins in youth • Consequences evident in middle to old age • Males • More atherosclerosis than females between ages 45–65 • Females • Experience heart disease and atherosclerosis later in life 21 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems • Lymphatic system • Main function is to return excess tissue fluid to blood vascular system • Lymphatic vessels collect tissue fluid The Lymphatic and Immune Systems • Immune system • Protects our bodies from foreign organisms • Confers immunity to disease • Main components • Lymphocytes, lymphoid tissue, and lymphoid organs The Lymphatic System • Lymphatic vessels collect tissue fluid from loose connective tissue • Carry fluid to great veins in the neck • Fluid flows only toward the heart • Once tissue fluid is within lymphatic vessels it is termed lymph Functions of Lymphatic Vessels • Collect excess tissue fluid and blood proteins • Return tissue fluid and blood proteins to bloodstream Orders of Lymphatic Vessels • Lymph capillaries • Smallest lymph vessels • First to receive lymph • Lymphatic collecting vessels • Collect from lymph capillaries • Lymph nodes are scattered along collection vessels Orders of Lymphatic Vessels • Lymph trunks • Collect lymph from collecting vessels • Lymph ducts • Empty into veins of the neck Lymphatic Capillaries • Located near blood capillaries • Receive tissue fluid from CT • Increased volume of tissue fluid • Minivalve flaps open and allow fluid to enter • High permeability allows entrance of • Tissue fluid and protein molecules • Bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells Lymphatic Capillaries • Lacteals—specialized lymphatic capillaries • Located in the villi of the small intestines • Receive digested fats • Fatty lymph—chyle Lymphatic Collecting Vessels • Accompany blood vessels • Composed of the same three tunics as blood vessels • Contain more valves than veins do • Helps direct the flow of blood • Lymph propelled by • Skeletal muscles bulging • Nearby arteries pulsing • Tunica media of the lymph vessels • Lymph flow is unaided by heartbeat Lymph Nodes • Cleanse the lymph of pathogens • Human body contains around 500 • Superficial lymph nodes located in • Cervical, axillary, and inguinal regions • Deep nodes are • Tracheobronchial, aortic, and iliac lymph nodes Microscopic Anatomy of a Lymph Node • Fibrous capsule—surrounds lymph nodes • Trabeculae—connective tissue strands • Lymph vessels • Afferent lymphatic vessels • Efferent lymphatic vessels Lymph Trunks • Lymphatic collecting vessels converge • Five major lymph trunks • Lumbar trunks • Receives lymph from lower limbs • Intestinal trunk • Receives chyle from digestive organs • Bronchomediastinal trunks • Collects lymph from thoracic viscera Lymph Trunks • Five major lymph trunks (continued) • Subclavian trunks • Receive lymph from upper limbs and thoracic wall • Jugular trunks • Drain lymph from the head and neck Lymph Ducts • Cisterna chyli • Located at the union of lumbar and intestinal trunks • Thoracic duct • Ascends along vertebral bodies • Empties into venous circulation • Junction of left internal jugular and left subclavian veins • Drains three quarters of the body Lymph Ducts • Right lymphatic duct • Empties into right internal jugular and subclavian veins 21 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Immune System • Recognizes specific foreign molecules • Destroys pathogens effectively • Key cells—lymphocytes • Also includes lymphoid tissue and lymphoid organs • Lymphoid organs • Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, aggregated lymphoid nodules, and appendix Lymphocytes • Infectious organisms attacked by inflammatory response • Macrophages, then lymphocytes • Are effective fighters of infectious organisms • Each lymphocyte recognizes a specific foreign molecule • Antigens are any molecules inducing a response from a lymphocyte Lymphocytes • B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes are the two main classes of lymphocytes • Cytotoxic T lymphocytes • Attack foreign cells directly • Binds to antigen-bearing cells • Perforates cell membrane • Signals cell to undergo apoptosis • Destroy virus infected cells and some cancer cells Lymphocytes • B lymphocytes • Become plasma cells • Secrete antibodies • Mark cells for destruction by macrophages • Respond primarily to bacteria and bacterial toxins Lymphocyte Activation • Lymphocytes originate in bone marrow • Some travel to the thymus gland • T lymphocytes • Some stay in bone marrow • B lymphocytes • Able to recognize a unique antigen • Gain immunocompetence • Travels through blood stream • Meets and binds to a specific antigen Lymphocyte Activation • During activation • Lymphocyte is presented its antigen by • A macrophage • Or a dendritic cell Lymphocyte Activation • Both T and B lymphocytes produce clones of • Effector lymphocytes • Respond immediately, then die • Memory cells • Wait until the body encounters the antigen again • Basis of acquired immunity • Prevent subsequent infections of the same illness Lymphoid Tissue • Most important tissue of the immune system • Two general locations • Mucous membranes of • Digestive, urinary, respiratory, and reproductive tracts • Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) • Lymphoid organs (except thymus) Lymphoid Organs • Primary lymphoid organs • Bone marrow • Thymus • Secondary lymphoid organs • Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils • Aggregated lymphoid nodules • Appendix Lymphoid Organs • Designed to gather and destroy infectious microorganisms and to store lymphocytes Thymus • Immature lymphocytes develop into T lymphocytes • Secretes thymic hormones • Most active in childhood • Functional tissue atrophies with age • Composed of cortex and medulla • Medulla contains Hassall’s corpuscles (thymic corpuseles) • Differs from other lymphoid organs • Functions strictly in lymphocyte maturation • Arises from epithelial tissue Thymus Lymph Nodes • Function • Lymph percolates through lymph sinuses • Most antigenic challenges occur in lymph nodes • Antigens destroyed and activate B and T lymphocytes Spleen • Largest lymphoid organ • Two main blood-cleansing functions • Removal of blood-borne antigens • Removal and destruction of old or defective blood cells • Site of hematopoiesis in the fetus Spleen • Destruction of antigens • Site of B cell maturation into plasma cells • Phagocytosis of bacteria and worn-out RBCs, WBCs and platelets • Storage of platelets Spleen • White pulp • Thick sleeves of lymphoid tissue • Blood-borne antigens are destroyed as they activate the immune response • Provides the immune function of the spleen • Red pulp • Surrounds white pulp • Composed of • Venous sinuses • Splenic cords • Responsible for disposing of worn out RBCs Tonsils • Simplest lymphoid organs • Four groups of tonsils • Palatine, lingual, pharyngeal, and tubal tonsils • Arranged in a ring to gather and remove pathogens • Underlying lamina propria consists of MALT Aggregated Lymphoid Nodules and Appendix • MALT—abundant in walls of intestines • Fight invading bacteria • Generate a wide variety of memory lymphocytes • Aggregated lymphoid nodules (Peyer’s patches) • Located in the distal part of the small intestine • Appendix—tubular offshoot of the cecum Aggregated Lymphoid Nodule Disorders of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems • Chylothorax • Leakage of fatty lymph into the thorax • Lymphangitis • Inflammation of a lymph vessel • Mononucleosis • Viral disease caused by Epstein-Barr virus • Attacks B lymphocytes Disorders of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems • Hodgkin’s disease • Malignancy of lymph nodes • Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma • Uncontrolled multiplication and metastasis of undifferentiated lymphocytes The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Throughout Life • Lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes • Develop from lymphatic sacs • Thymus originates as an outgrowth of the endoderm • Spleen, lymph nodes, and MALT • Arise from mesodermal mesenchyme