Define: Fault, Focus, Epicenter
advertisement

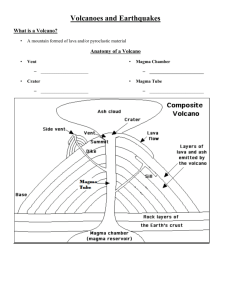
Earthquake and Volcano Review! (Test is Friday 12/13) 1) Define: Fault Focus Epicenter Elastic Rebound Magnitude Intensity Body Wave Surface Wave 2) True or False and why if it is false: Earth quakes can only occur along faults 3) True or False and why if it is false: Earthquakes can only occur along the tectonic plate boundaries Indicate relative speed (fastest, slowest…) and how they move. 4) Primary waves – 5) Secondary waves – 6) What are the two types of Surface waves and two types of body waves? Volcano Review 1) What are the 3 types of volcanoes? 2) How does water and silica-rich magma affect a volcanic eruption? 3) What are the four types of pyroclastic material? 4) What are the four types of lava? 5) Define: Viscosity Active Dormant Extinct 6) What are the three types of volcanic landforms? 7) What is the difference between magma and lava? 8) What is the difference between an explosive and nonexplosive eruption? Earthquake and Volcano Review! (Test is Friday 12/13) 1) Define: Fault Focus Epicenter Elastic Rebound Magnitude Intensity Body Wave Surface Wave 2) True or False and why if it is false: Earth quakes can only occur along faults 3) True or False and why if it is false: Earthquakes can only occur along the tectonic plate boundaries Indicate relative speed (fastest, slowest…) and how they move. 4) Primary waves – 5) Secondary waves – 6) What are the two types of Surface waves and two types of body waves? Volcano Review 1) What are the 3 types of volcanoes? 2) How does water and silica-rich magma affect a volcanic eruption? 3) What are the four types of pyroclastic material? 4) What are the four types of lava? 5) Define: Viscosity Active Dormant Extinct 6) What are the three types of volcanic landforms? 7) What is the difference between magma and lava? 8) What is the difference between an explosive and nonexplosive eruption? Earthquake and Volcano Review! (Test is Friday 12/18) 1) Fault – a place where two bodies of rock slide against one another Focus – location along the fault where an earthquake begins Epicenter – location on the surface of the earth directly above the focus Elastic Rebound - When deformed rock snaps back to its original formation after an earthquake Magnitude – The measurement of ground movement by an earthquake Intensity – what is felt and the damage that is caused by an earthquake at different locations Body Wave – Siesmic waves that travel only on the surface of the earth Surface Wave - Siesmic waves that travel through the interior of the earth 2) Earth quakes can only occur along faults- True 3) Earthquakes can only occur along the tectonic plate boundaries - False – they can also occur inside the plates as well but they are more frequent along the plate boundaries Indicate relative speed (fastest, slowest…) and how they move. 4) Primary waves – Fastest, push pull (compression and expansion of rock) 5) Secondary waves – second fastest, side-to-side or shear Surface waves – slowest, Love waves move side-to-side (horizontal motion) and Rayleigh move up and down (vertical motion) 6) What are the two types of Surface waves? Love and Reyleigh Two Body waves: Primary and Secondary Waves Volcano Review 1) What are the 3 types of volcanoes? Composite – formed from explosive and nonexplosive eruptions, shield is formed from nonexplosive eruptions, cinder cone is formed from mild explosive eruptions 2) How does water and silica-rich magma affect a volcanic eruption? As you increase water or silica-rich magma you increase the likelihood of an explosive eruption 3) What are the four types of pyroclastic material? Ash, lapilli, bombs, blocks 4) What are the four types of lava? Aa, pahoehoe, pillow, blocky 5) Viscosity – how a liquid or lava flows, Active – a volcano that is currently erupting, Dormant a volcano that has erupted in modern history but is not erupting now, and Extinct - a volcano that has not erupted in modern history. 6) What are the three types of volcanic landforms? Volcanic plateau, lava dome, crater, caldera 7) What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock inside the Earth and lava is molten rock on the surface of the Earth. 8) What is the difference between an explosive and nonexplosive eruption? Explosive eruption is when pyroclastic material is shot into the air. A nonexplosive eruption is when lava oozes out of a volcano.