Mineral notes with blanks
advertisement

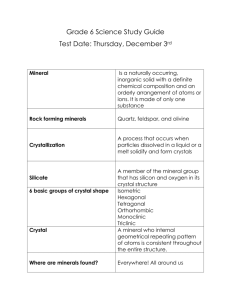
Ch 3 Minerals _________ (8 to 32 km) _________ (2900 km) Liquid Core(_________ km) Solid Core (_________ km) Core 1. Solid Inner Core: • Made of solid _________ and Iron • Under great pressure -resulting in a _________ form. • _________ causes the Earth to be magnetic • _________ degrees Celsius 2. Liquid Outer Core • Made of liquid Nickel and _________ • 2200 degrees _________ Mantle • Molten, liquid _________ (Magma) • Makes up about _________% of Earth’s volume • Ranges from _________ to 2200 degrees Celsius • Crust and Mantle divided by the Moho _________ Crust • Very thin, _________ layer of rock • Made of mostly _________ & Oxygen (75%) What are Minerals? • Naturally occurring – not _________-made, in the earth • _________ – doesn’t come from living things • Always a solid – has _________ and shape • Definite _________ composition – made of a single pure substance or element • Crystalline form – flat sides, sharp edges & _________ • Formation & Composition • As hot _________ cools, the minerals will _________. • If the magma cools very _________ it forms large crystals. If it cools very quickly it forms tiny to _________ crystals. • Some mineral crystals will form _________ dissolved in liquids. Minerals will be left behind when the liquid _________. • The eight most common elements in the crust form a large number of the known _________. • (O, Si, Al, _________, Ca, _________, K, & Mg) • The _________ formed by Silicon & Oxygen is known as Silicate. Mineral Identification • The identification of a mineral is based on its _________ properties • 1. Color • Some minerals have __________________ colors • Some minerals can come in several different color _________ EX: Quartz & _________ • Some of the colors can change due to temperature, _________, or radiation. • 2. Luster • The way a mineral _________ light off its surface. • 2 types • A. _________ – very shiny, looks like a metal • B. Non-metallic – • _________ – shiny, transparent, translucent • Earthy - clay-like, _________ • _________: pearl-like • 3. Hardness • The ability for a mineral to resist being __________________. • _________ Hardness Scale • A list of ten minerals _________ according to hardness. • • • • • • • 1= softest (_________) 10=hardest (diamond) A mineral that is higher on the scale will _________ the mineral that is lower. Other common items have been given ratings on the scale for identification _________. EX: Fingernail, _________, File, Glass 4. Streak The color of the _________ scraped off a mineral when rubbed against a rough surface (streak plate.) • Very useful property for showing the _________ color. • Same color _________, no matter what the variation • 5. Breakage • 2 types – • a. _________ - breaks in smooth, definite surfaces • Same every time • b. _________ - breaks in rough or _________ surfaces • 6. Crystal Form • Geometric crystals with flat surfaces and definite edges • _________ • Hexagonal • _________ • Orthorhombic • _________ • Triclinic • Different _________ cleavage • 7. Other Properties • 1. Reaction to _________ - some minerals will _________ in acid • 2. _________ - some special minerals will be magnetic • 3. Smell - some will have distinct _________ • 4. _________ - some have a distinct taste Mineral Groups • 1. _________ • Most common mineral _________ • Silicon-oxygen tetrahedron (SiO4) along with additional _________. • Joined together into _________, sheets, or 3-demensional networks. • EXAMPLES: Feldspars, _________, Micas • 2. _________ • Carbonates are used in _________ & lime. • Made of Carbonate (CO3) with other _________. • EXAMPLES: _________ & Dolomite • 3. _________ • Used in steel making, _________, & salt • EXAMPLES: Halite & Fluorite • 4. _________ • Used in plaster. • Made of Sulfate (_________) with other elements. • EXAMPLE: Gypsum • 5. _________ • Have Oxygen as a major _________. • EXAMPLES: Hematite, Magnetite, Corundum, & _________ • 6. _________ Elements • Minerals of great economic _________ that are pure elements. • EXAMPLES: _________, Silver, Diamond (C), Sulfur, _________ (C), Copper, Platinum Uses for Minerals • 1. _________ • Minerals or combinations of minerals from which _________ and nonmetals can be removed in usable amounts. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Examples: _________ (Mercury), Bauxite (Aluminum), Hematite (Iron) Smelting- when an ore is heated so that a _________ can be separated from it. _________- when pure metals are combined to form other metallic substances. (Steel & Brass) 2. _________ Minerals that are hard, _________, and durable. They are substances that can be cut & polished for _________ & decoration. a. Precious _________ The _________ & most valuable. Ex: Diamonds, Rubies, _________, Sapphires, & _________ b. __________________ Stones The other gemstones Ex: _________, Zircons, Garnets, Turquoises, _________, & more c. Non-Mineral _________ Come from _________ things Ex: _________, _________, & _________