Population Density and Distribution
advertisement

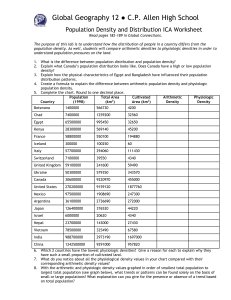
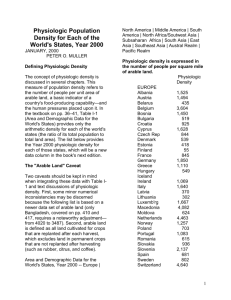
Population Density and Distribution Name:_____________________ Lab: The purpose of this lab is to understand how the distribution of people in a country differs from the population density. As well, students will compare arithmetic densities to physiologic densities in order to understand population pressures on the land. What is the difference between population distribution and population density? arithmetic population distribution physiologic population distribution 1) Complete the chart. (10 marks) Country Population (2006) Total Area Cultivated Area (km2) (km2) Botswana Chad Egypt Kenya Yemen Iceland Italy Switzerland Ukraine Canada United States Mexico 1 639 833 9,944,201 78,887,007 34,707,817 21,456,188 299,388 58,133,509 7,523,934 46,710,816 33,098,932 298,444,215 566 730 1 259 200 995 450 4 200 32 560 32 650 569 140 45 200 527,970 5,500 100 250 294 060 60 111 430 39 550 579 350 4 340 343 570 9 220 970 9 159 120 455 000 1 877 760 107,449,525 1 908 690 247 300 Arithmetic Density Physiologic Density 2) Which 3 countries have the lowest percentage of total area cultivated? Give one good reason why they have such a small proportion of cultivated land. (3 marks) 3) What do you notice about all the physiological density values in your chart compared with their corresponding arithmetic density values? (1 mark) 4) Explain why countries such as Egypt, Iceland, Switzerland, Japan, Israel and China have a special challenge in trying to provide sufficient amounts of food for their populations. Suggest two strategies that these countries might use to keep their populations well fed. (3 marks) 5) When we think of countries where there is chronic hunger, African countries such as Chad and Botswana come to mind, yet the number of people depending on each square kilometer of cultivated land in these countries is not nearly as high as in question 6. What does this say about the quality of land in the African countries? (1 mark 6) Based on the physiologic densities suggest at least 3 countries in the world that might be food exporters. (3 marks) 7) a) Find an example of a country with a high population but a relatively low physiologic population density. (1 mark) b) Find an example of a country with a low population but a relatively high physiologic population density. (1 mark) c) Does a high population necessarily lead to a high physiologic density? What relationship determines the physiologic density? (1 marks) 8) Explain one problem in only using arithmetic population density to determine how dense the population of a country is. (1 mark) Total = 25 marks