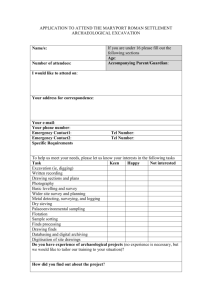
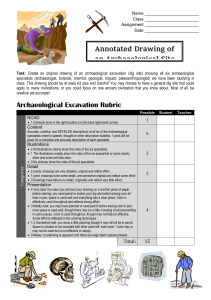
The midterm exam covers all class lectures, activities, and text
advertisement

Study Guide ANTH 13 Midterm The midterm exam covers all class lectures, activities, and text readings through chapter 7 You should be able to identify, define or appropriately use these terms and concepts. This is a general study guide and you should review your notes and readings for material not covered here. Epistemology Paradigms Theoretical positions (chp 3) Culture Historic Processual Approach Post processual Post modern Taphonomy Typology Stratigraphy (chapter 4) Low level theory. Mid range theory High theory antiquarianism cultural anthropology scientific archaeology inductive reasoning deductive reasoning ethnoarchaeology organic artifact artifact ecofact geofact Secondary deposit Principle of Superposition Principle of Association site feature Methodology Survey Sample size Screening / wet screens Arbitrary levels/natural levels seriation Dating techniques (chp 7) Dendrochronology Radiometrics C14 K/Ar Thermoluminessence AMS Obsidian hydration sampling theory/ sample universe statistical sample living floor sample fraction kill site stratified random sample absolute and relative dating Remote sensing technologies Magnetometer GPR Sonar Electrical resistivity Infrared detection Metal detectors Geophysical survey Laws and Regulations NAGPRA Section 106 CEQA NHPA seriation Typology Type Functional type Morphological type Attributes Phase Period Cyrus Thomas Thomas Jefferson Heinreich Schliemann GIS GPS trench shovel test use wear analogy human ecology flintknapping Misc. terms mano and metate rock shelter pedestrian survey / “gumshoe survey” faunal remains plow zone index collection / reference collection excavation unit Clovis shovel test, augering, coring provenience, provenience control in situ bioturbation floraturbation unit profile archaeological site site component assemblage, sub assemblage site plan “Battleship curves” flake, core, blade, projectile point Harris matrix kiva Gatecliff shelter space/time : phases Mesa Verde surface clearing Taphonomic processes Study Guide ANTH 13 Midterm Sample questions from previous exams. 10. An annoying natural process wherein animals cause damage to archaeological deposits is called A. bioturbation. B. floraturbation. C. morphological typing. D. the Frison effect. 18. Most CRM projects are carried out in order to help companies or agencies comply with the regulations set forth in the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA). This is commonly referred to as A. NAGPRA qualified. B. C14 testing. C. section 106 assessment. D. ethnoarchaeology. 22. Archaeologists have generally settled on ¼ inch mesh in screening dirt from excavations because A. it is the easiest screen size to find at hardware stores. B. the size allows the capture of most botanical and faunal remains. C. it can be used to collect large artifacts while wet screening. D. the size of the mesh catches most identifiable artifacts while still allowing most soil to pass through easily. 11. The excavation of a site generally relies on a statistical sample. The standard sample size attempted at most excavations is A. 10% of the site. B. 20% of the site C. 50% of the site D. variable based on the size of the site. 19. All artifacts found at a site from a single excavation are referred to together as A. components. B. an assemblage. C. a phase. D. a sample fraction. 4. An archaeologist digging an excavation unit in regular 10 cm levels is said to using A. arbitrary levels. B. natural stratigraphy. C. dendrochronology D. a statistical sample. Sample short constructed answer questions from previous exams.. The best answers generally are three or more paragraphs in length and provide examples. These should be detailed, not general in scope. D. Compare and contrast the Culture Historical Approach to the Processual Approach in archaeological research. A. Describe the principle of Superposition and explain why it is fundamental to archaeological reconstruction of the past. How is this principle applied in interpretation of site histories? B. What is NAGPRA? Why was this law enacted? Describe how is has affected archaeological research. E. Identify and describe three different remote sensing techniques used in archaeological investigations. Provide an example of each in a situation for which it is best suited. Study Guide ANTH 13 Midterm