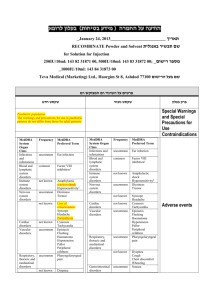
הודעה על החמרה ( מידע בטיחות) בעלון לצרכן
advertisement
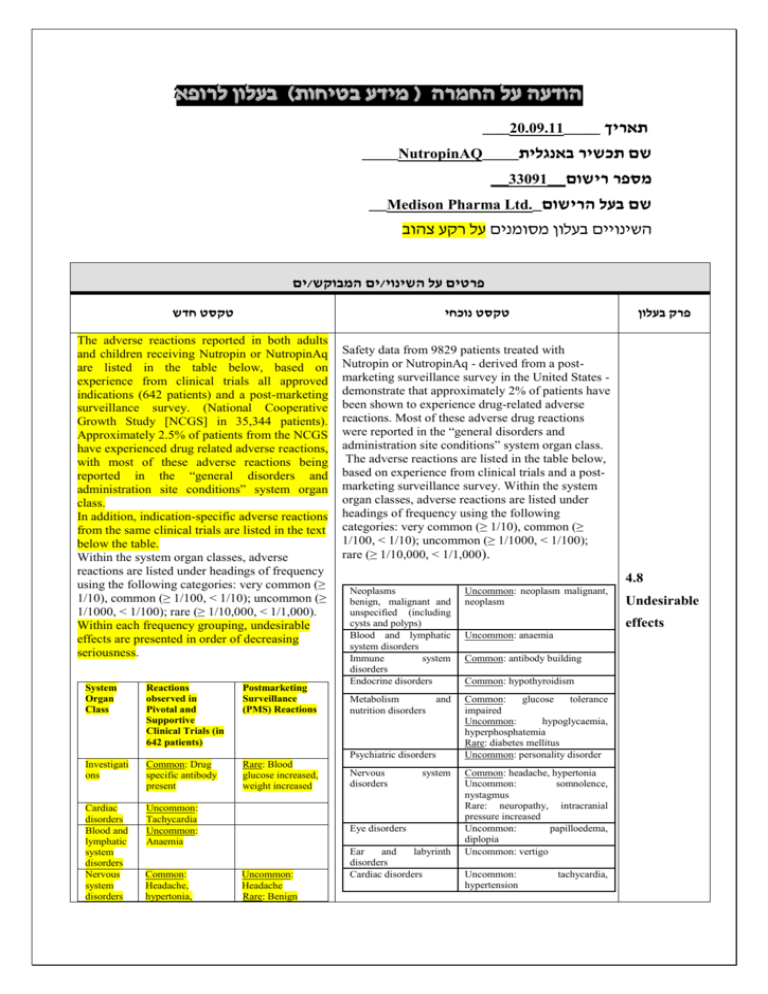
רופא בעלון ללרופא בטיחות) בעלון )מידע בטיחות החמרה (( מידע על החמרה הודעה על הודעה ___0010.1..____ תאריך ____NutropinAQ____שם תכשיר באנגלית __990..__מספר רישום __Medison Pharma Ltd._שם בעל הרישום השינויים בעלון מסומנים על רקע צהוב ים/ים המבוקש/פרטים על השינוי טקסט חדש טקסט נוכחי The adverse reactions reported in both adults and children receiving Nutropin or NutropinAq are listed in the table below, based on experience from clinical trials all approved indications (642 patients) and a post-marketing surveillance survey. (National Cooperative Growth Study [NCGS] in 35,344 patients). Approximately 2.5% of patients from the NCGS have experienced drug related adverse reactions, with most of these adverse reactions being reported in the “general disorders and administration site conditions” system organ class. In addition, indication-specific adverse reactions from the same clinical trials are listed in the text below the table. Within the system organ classes, adverse reactions are listed under headings of frequency using the following categories: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100, < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000, < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000, < 1/1,000). Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. System Organ Class Reactions observed in Pivotal and Supportive Clinical Trials (in 642 patients) Postmarketing Surveillance (PMS) Reactions Investigati ons Common: Drug specific antibody present Rare: Blood glucose increased, weight increased Cardiac disorders Blood and lymphatic system disorders Nervous system disorders Uncommon: Tachycardia Uncommon: Anaemia Safety data from 9829 patients treated with Nutropin or NutropinAq - derived from a postmarketing surveillance survey in the United States demonstrate that approximately 2% of patients have been shown to experience drug-related adverse reactions. Most of these adverse drug reactions were reported in the “general disorders and administration site conditions” system organ class. The adverse reactions are listed in the table below, based on experience from clinical trials and a postmarketing surveillance survey. Within the system organ classes, adverse reactions are listed under headings of frequency using the following categories: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100, < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000, < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000, < 1/1,000). 4.8 Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) Blood and lymphatic system disorders Immune system disorders Endocrine disorders Uncommon: neoplasm malignant, neoplasm Metabolism and nutrition disorders Common: glucose tolerance impaired Uncommon: hypoglycaemia, hyperphosphatemia Rare: diabetes mellitus Uncommon: personality disorder Psychiatric disorders Common: Headache, hypertonia, Nervous disorders system Eye disorders Uncommon: Headache Rare: Benign פרק בעלון Ear and labyrinth disorders Cardiac disorders Undesirable effects Uncommon: anaemia Common: antibody building Common: hypothyroidism Common: headache, hypertonia Uncommon: somnolence, nystagmus Rare: neuropathy, intracranial pressure increased Uncommon: papilloedema, diplopia Uncommon: vertigo Uncommon: hypertension tachycardia, Uncommon: Carpal tunnel syndrome, somnolence, nystagmus Eye disorders Ear and labyrinth disorders Respirator y disorders Gastrointe stinal disorders Renal and urinary disorders Skin and subcutane ous tissue disorders Musculosk eletal and connective tissue disorders Uncommon: Papilloedema, diplopia Uncommon: Vertigo Uncommon: Abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, flatulence Uncommon: Urinary incontinence, pollakiuria, polyuria, urine abnormality Uncommon: Exfoliative dermatitis, skin atrophy, skin hypertrophy, hirsutism, lipodystrophy, urticaria Very common in adults, common in children: Arthralgia, myalgia Uncommon: Muscle atrophy, bone pain Endocrine disorders Metabolis m and nutrition disorders Common: Hypothyroidism Common: Glucose tolerance impaired Uncommon: Hypoglycaemia, hyperphosphatemia Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecifie d (including cysts and polyps) Vascular disorders General disorders and administra tion site conditions Uncommon: Neoplasm malignant, neoplasm benign Uncommon: Hypertension Very common in adults, common in children: Peripheral oedema, oedema Common: Asthenia, injection site reaction Uncommon: intracranial hypertension, intracranial pressure increased, migraine, carpal tunnel syndrome, paraesthesia, dizziness Rare: Papilloedema, vision blurred Rare: Tonsillar hypertrophy Rare: Abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting Gastrointestinal disorders Uncommon: vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, nausea Rare: diarrhoea Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Uncommon: lipodystrophy, skin atrophy, dermatitis exfoliative, urticaria, hirsutism, skin hypertrophy Very common in adults, common in children: arthralgia, myalgia Uncommon: muscle atrophy, bone pain, carpal tunnel syndrome Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Renal and disorders Reproductive system and breast disorders General disorders and administration site conditions Rare: Generalised pruritus, urinary Investigations Uncommon: urinary incontinence, haematuria, polyuria, urine frequency/pollakiuria, urine abnormality Uncommon: genital discharge Very common in adults, common in children: oedema, peripheral oedema Common: injection site reactions, asthenia Uncommon: injection site atrophy, injection site haemorrhage, injection site mass, hypertrophy Rare: renal function test abnormal urticaria,rash Uncommon: Epiphysiolysis, scoliosis progression, arthralgia Rare: Bone development abnormal, osteochondrosis, muscular weakness, pain in extremity Rare: Hypothyroidism Rare: Diabetes mellitus, hyperglycaemia, hypoglycaemia, glucose tolerance impaired Rare: Neoplasm malignant recurrence, melanocytic naevus Rare: Hypertension Uncommon: Peripheral oedema, oedema, injection site reaction (irritation, pain) Rare: Asthenia, As with all medicinal products, a small percentage of patients may develop antibodies to the protein somatropin. The binding capacity of growth hormone antibodies was lower than 2 mg/l in NutropinAq subjects tested, which has not been associated with adversely affected growth rate. Leukaemia has been reported in a small number of growth hormone deficient patients treated with growth hormone. A causal relationship to somatropin therapy is unlikely. Patients with endocrinological disorders are more prone to develop an epiphysiolysis. Indication-specific adverse drug reactions from clinical trials Paediatric patients: Patients with growth failure due to inadequate growth hormone secretion Common: central nervous system neoplasm. Patients with growth failure associated with Turner syndrome Common: menorrhagia. Patients with growth failure associated with chronic renal insufficiency Common: renal failure, peritonitis, osteonecrosis, blood creatinine increase. Children with chronic renal insufficiency receiving NutropinAq are more likely to develop intracranial hypertension. The greatest risk is at the beginning of treatment. Adult patients: Adults with growth hormone deficiency Very common: paraesthesia. Common: hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidaemia, Reproducti ve system and breast disorders Psychiatric disorders Injection site haemorrhage, injection site atrophy, injection site mass, hypertrophy face oedema, fatigue, irritability, pain, pyrexia, injection site reaction (haemorrhage, haematoma, atrophy, urticaria, pruritus, swelling, erythema) Uncommon: Uterine haemorrhage, genital discharge Uncommon: Personality disorder Rare: Gynaecomastia Rare: Abnormal behaviour, depression, insomnia As with all recombinant proteins, a small percentage of patients may develop antibodies to the protein somatropin. The binding capacity of growth hormone antibodies was lower than 2 mg/l in NutropinAq subjects tested, which has not been associated with adversely affected growth rate. Patients with endocrinological disorders are more prone to develop an epiphysiolysis. Indication-specific adverse drug reactions from clinical trials Paediatric patients: Patients with growth failure due to inadequate growth hormone secretion (n=236) Common: central nervous system neoplasm. (2 patients experienced a recurrent medulloblastoma, 1 patient experienced a histiocytoma). See also section 4.4. Patients with growth failure associated with Turner syndrome (n=108) Common: menorrhagia. Patients with growth failure associated with chronic renal insufficiency (n=171) Common: renal failure, peritonitis, osteonecrosis, blood creatinine increase. Children with chronic renal insufficiency receiving NutropinAq are more likely to develop intracranial hypertension although children with organic GHD and Turner syndrome also have an increased incidence.. The greatest risk is at the beginning of treatment. Adult patients: Adults with growth hormone deficiency (n=127) Very common: paraesthesia. Common: hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidaemia, insomnia, synovial disorder, arthrosis, muscular weakness, back pain, breast pain, gynaecomastia. insomnia, synovial disorder, arthrosis, muscular weakness, back pain, breast pain, gynaecomastia.