Review of Types of Weathering
advertisement

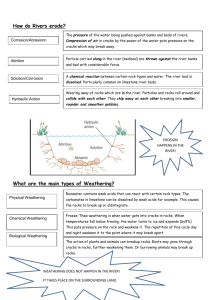
Name: ___________________________ Block: ______________ Review of Types of Weathering Use the words in the box to fill in the blanks of the paragraphs below. Plants Freezing Climate Sediments Chemical Dissolves Tropical Moisture Oxidation Desert Frost wedging Temperatures Mechanical Acids Air Minerals Cracks Carbonic acid Weathering is the breaking of rocks into _______________________. There are two main types of weathering. ____________________________ weathering involves breaking rocks without changing their chemical composition. For example, rocks may collide with other rocks and break apart. In _____________________, water trapped in rock cracks freezes and expands, forcing the rocks apart. ________________________ can also cause mechanical weathering. As their roots grow and put pressure on rocks, _______________ widen and rock fragments may fall off. ______________ weathering involves water, air, and other substances reacting with the minerals in the rocks. Water _____________ the minerals in rocks or combines with compounds in the __________. When metal is exposed to water and oxygen, ____________ occurs and rust forms. ____________ in plant roots and mosses can also dissolve the ____________ in rocks. Water and carbon dioxide combine to form ________________, which dissolves minerals such as calcite in limestone. How rapidly weathering occurs in an area depends on the ______________. In ______________ regions, chemical weathering is more rapid. Chemical weathering happens more slowly in _____________ areas and polar regions due to a lack of ____________ and/or low ______________. Whenever ___________ and thawing alternate, mechanical weathering becomes an important form of weathering. Weathering includes mechanical weathering and chemical weathering. Mechanical weathering is any process that breaks up a rock without changing its chemical composition. Chemical weathering is any process in which water, air, or other substances react with the minerals in the rock and change the chemical composition of the rock. Decide if the following descriptions are examples of mechanical weathering or chemical weathering. Write the word “mechanical” or “chemical” in the blank at the left. Then in the second blank, determine what specific type of mechanical or chemical weathering it is. _____________ 1. Mosses growing on the surface of rocks, producing pits in the rocks. _____________ _____________ 2. The wedging of tree roots along natural joints in granite outcrops. _____________ _____________ 3. Limestone dissolved by carbonic acid. _____________ _____________ 4. The oxidation of minerals that contain iron. _____________ _____________ 5. Animal burrows dug in rock that let in water and air. _____________ _____________ 6. Repeated freezing and thawing of water that cracks rock. _____________ _____________ 7. The action of water, salt, and air on car fenders and panels. _____________ _____________ 8. Acids from plant roots, which break up rocks. _____________ _____________ 9. Formation of potholes in streets during severe winters. _____________ _____________ 10. Lifted sections of sidewalk along tree-lined streets. _____________ _____________ 11. A large rock falling from a cliff and then breaking. _____________ _____________ 12. Feldspar mixed with water, producing clay materials. _____________ _____________ 13. Rocks that have been carried by streams and have become smaller and _____________ and more rounded _____________ 14. Decaying plants dissolving some of the minerals in rocks. _____________ _____________ 15. Tree roots cracking the concrete foundation of a house. _____________