AP Biology Vocabulary & Roots: Ch
advertisement

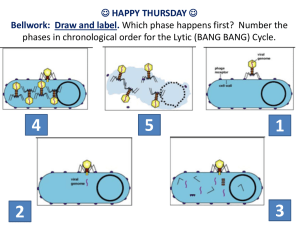
AP Biology Vocabulary & Roots: Ch. 19 1. AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)-The symptoms and signs present during the late stages of HIV infection, defined by a specified reduction in the number of T cells and the appearance of characteristic secondary infections. 2. bacteriophage-A virus that infects bacteria; also called a phage. 3. capsid The protein shell that encloses a viral genome. It may be rod-shaped, polyhedral, or more complex in shape. 4. HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)-The infectious agent that causes AIDS. HIV is a retrovirus. 5. host range-The limited range of host cells that each type of virus can infect. 6. lysogenic cycle-A type of phage reproductive cycle in which the viral genome becomes incorporated into the bacterial host chromosome as a prophage and does not kill the host. 7. lytic cycle-A type of phage reproductive cycle resulting in the release of new phages by lysis (and death) of the host cell. 8. pandemic-A global epidemic. 9. phage-A virus that infects bacteria; also called a bacteriophage. 10. prion-An infectious agent that is a misfolded version of a normal cellular protein. Prions appear to increase in number by converting correctly folded versions of the protein to more prions. 11. prophage-A phage genome that has been inserted into a specific site on a bacterial chromosome. 12. provirus-A viral genome that is permanently inserted into a host genome. 13. restriction enzyme-An endonuclease (type of enzyme) that recognizes and cuts DNA molecules foreign to a bacterium (such as phage genomes). The enzyme cuts at specific nucleotide sequences (restriction sites). 14. retrovirus- An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome; an important class of cancer-causing viruses. 15. reverse transcriptase- An enzyme encoded by certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis. 16. temperate phage-A phage that is capable of reproducing by either a lytic or lysogenic cycle. 17. vaccination- an immunization 18. vaccine-A harmless variant or derivative of a pathogen that stimulates a host’s immune system to mount defenses against the pathogen. 19. viral envelope-A membrane that cloaks the capsid that in turn encloses a viral genome. 20. viroid-A plant pathogen consisting of a molecule of naked, circular RNA a few hundred nucleotides long. 21. virulent phage-A phage that reproduces only by a lytic cycle. Word Roots capsa- = a box (capsid: the protein shell that encloses the viral genome) lyto- = loosen (lytic cycle: a type of viral replication cycle resulting in the release of new phages by death or lysis of the host cell) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) 1 pro- = before (provirus: viral DNA that inserts into a host genome) retro- = backward (retrovirus: an RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome) virul- = poisonous (virulent virus: a virus that reproduces only by a lytic cycle) 2