Supplementary Table 1 - Word file (124 KB )
advertisement
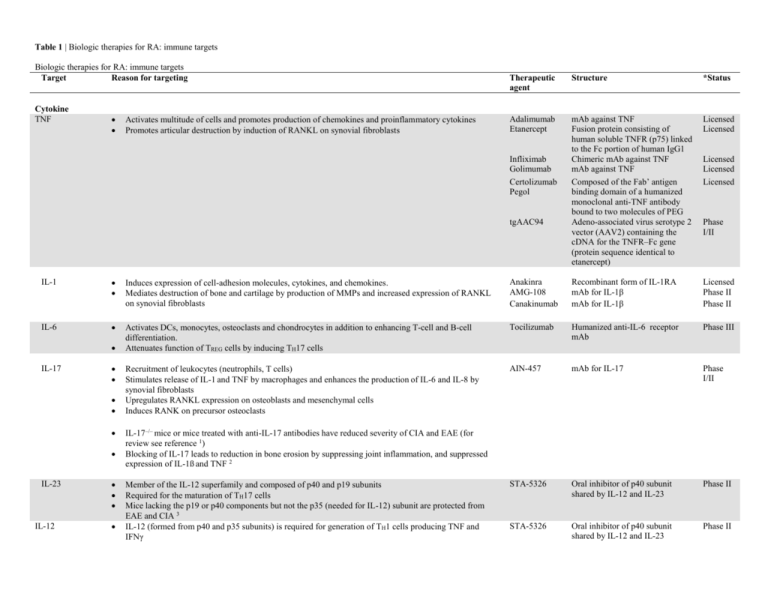
Table 1 | Biologic therapies for RA: immune targets Biologic therapies for RA: immune targets Target Reason for targeting Cytokine TNF Activates multitude of cells and promotes production of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines Promotes articular destruction by induction of RANKL on synovial fibroblasts Therapeutic agent Structure *Status Adalimumab Etanercept mAb against TNF Fusion protein consisting of human soluble TNFR (p75) linked to the Fc portion of human IgG1 Chimeric mAb against TNF mAb against TNF Composed of the Fab’ antigen binding domain of a humanized monoclonal anti-TNF antibody bound to two molecules of PEG Adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vector (AAV2) containing the cDNA for the TNFR–Fc gene (protein sequence identical to etanercept) Licensed Licensed Infliximab Golimumab Certolizumab Pegol tgAAC94 Licensed Licensed Licensed Phase I/II IL-1 Induces expression of cell-adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines. Mediates destruction of bone and cartilage by production of MMPs and increased expression of RANKL on synovial fibroblasts Anakinra AMG-108 Canakinumab Recombinant form of IL-1RA mAb for IL-1β mAb for IL-1β Licensed Phase II Phase II IL-6 Activates DCs, monocytes, osteoclasts and chondrocytes in addition to enhancing T-cell and B-cell differentiation. Attenuates function of TREG cells by inducing TH17 cells Tocilizumab Humanized anti-IL-6 receptor mAb Phase III Recruitment of leukocytes (neutrophils, T cells) Stimulates release of IL-1 and TNF by macrophages and enhances the production of IL-6 and IL-8 by synovial fibroblasts Upregulates RANKL expression on osteoblasts and mesenchymal cells Induces RANK on precursor osteoclasts AIN-457 mAb for IL-17 Phase I/II STA-5326 Oral inhibitor of p40 subunit shared by IL-12 and IL-23 Phase II STA-5326 Oral inhibitor of p40 subunit shared by IL-12 and IL-23 Phase II IL-17 IL-23 IL-12 IL-17–/– mice or mice treated with anti-IL-17 antibodies have reduced severity of CIA and EAE (for review see reference 1) Blocking of IL-17 leads to reduction in bone erosion by suppressing joint inflammation, and suppressed expression of IL-1ß and TNF 2 Member of the IL-12 superfamily and composed of p40 and p19 subunits Required for the maturation of TH17 cells Mice lacking the p19 or p40 components but not the p35 (needed for IL-12) subunit are protected from EAE and CIA 3 IL-12 (formed from p40 and p35 subunits) is required for generation of TH1 cells producing TNF and IFNγ IL-15 Enhances T-cell and NK cell proliferation AMG-714 mAb for 1L-15 Phase II B cells CD20 Expressed on pre-B and mature B lymphocytes but not on plasma cells Rituximab Ocrelizumab Ofatumumab Antibody to CD20 antibody to CD20 Antibody to CD20 Licensed Phase III Phase III TRU-015 Single-chain construct containing a single-chain Fv specific for CD20 linked to human IgG1 hinge, CH2, and CH3 domains but devoid of CH1 and CL domains Phase II CD19 Expressed at earlier stages of B cells, even before expression of pre-BCR Essential for key B-cell differentiative events including the formation of B-1, germinal center, and MZ B cells MDX-1342 Human mAb for CD19 Phase I BAFF A critical factor for B cell maturation and survival Overexpressed by DCs Autoantibody levels and clinical activity correlates with BAFF levels in RA Atacicept Recombinant fusion protein of BAFF and APRIL receptor Phase II Abatacept CTLA4–Ig fusion protein Licensed CD80 on DCs provides a co-stimulatory signal necessary for T-cell activation RhuDex Oral inhibitor of CD80 Phase II Promotes osteoclastogenesis Denosumab mAb against RANKL Phase II CP-690550 Oral JAK3 inhibitor Phase II Costimulatory molecule inhibitors CTLA-4 Expressed on TREG cells, has a key task in maintaining self tolerance Binds the costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 on DCs and blocks interaction with CD28 on T cells CD80 Osteoclastogenesis RANK– RANKL Inhibitors of intracellular signaling molecules JAK3 Signal transduction by receptors that employ the common gamma chain common gamma chain Syk Blocks activation of mast cells, macrophages and B cells Fostamatinib Oral Syk inhibitor Phase II p38 Blocks cytokine production (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF) VX-702 SCIO-469 SB-681323 Oral p38 inhibitor Phase II Phase II Phase II *Posted on Clinicaltrials.gov Abbreviations: APRIL, a proliferation inducing ligand; BAFF, B-cell activating factor of the TNF family; BCR, B-cell receptor; CH, constant heavy; CIA, collagen-II-induced arthritis; CL, constant light; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; DCs, dendritic cells; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; IFNγ, interferon γ; IL, interleukin; IL-1RA, IL-1 receptor antagonist; JAK, Janus kinase; mAb, monoclonal antibody; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MZ, marginal zone; NK, natural killer; PEG, polyethylene glycol; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RANK, receptor activator of nuclear factor κB; RANKL, RANK ligand; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; .TREG cells, regulatory T cells; TH1 cells, type 1 T helper cells; TH17 cells, type 17 T helper cells. References 1. 2. 3. Oukka, M. Th17 cells in immunity and autoimmunity. Ann Rheum Dis 67 Suppl 3, iii26-9 (2008). Koenders, M.I. et al. Blocking of interleukin-17 during reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am J Pathol 167, 141-9 (2005). Murphy, C.A. et al. Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 198, 19517 (2003).