DOMAIN I: PLANNING AND PREPARATION
advertisement

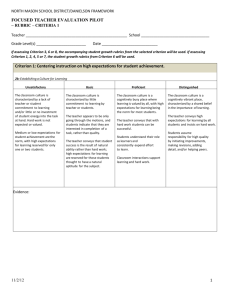
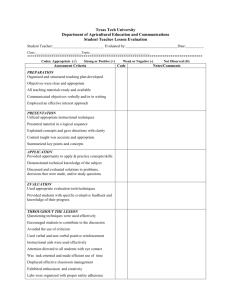
Form #008a, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1a: Demonstrating Knowledge of Content and Pedagogy Elements: Knowledge of content and the structure of the discipline * Knowledge of prerequisite relationships * Knowledge of content-related pedagogy LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Knowledge of content and the structure of the discipline In planning and practice, teacher makes content errors or does not correct content errors students make. Teacher is familiar with the important concepts in the discipline but may display lack of awareness of how these concepts relate to one another. Teacher displays solid knowledge of the important concepts in the discipline and how these relate to one another. Teacher displays extensive knowledge of the important concepts in the discipline and how these relate both to one another and to other disciplines. Teacher’s plans and practice display little understanding of prerequisite relationships important to student learning of the content. Teacher’s plans and practice indicate some awareness of prerequisite relationships, although such knowledge may be inaccurate or incomplete. Teacher’s plans and practices reflect accurate understanding of prerequisite relationships among topics and concepts. Teacher’s plans and practices reflect understanding of prerequisite relationships among topics and concepts and a link to necessary cognitive structures by students to ensure understanding. Teacher displays little or no understanding of the range pedagogical approaches suitable to student learning of the content. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect a limited range of pedagogical approaches or some approaches that are not suitable to the discipline or to the students. Teacher’s plans and practices reflect familiarity with a wide range of effective pedagogical approaches in the discipline. Teacher’s plans and practices reflect familiarity with a wide range of effective pedagogical approaches in the discipline, anticipating student misconceptions. Knowledge of prerequisite relationships Knowledge of content-related pedagogy Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008a, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1a: Demonstrating Knowledge of Content and Pedagogy Elements: Knowledge of content and the structure of the discipline * Knowledge of prerequisite relationships * Knowledge of content-related pedagogy LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Knowledge of content and the structure of the discipline Knowledge of prerequisite relationships Knowledge of content-related pedagogy Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED Form #008b, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1b: Demonstrating Knowledge of Students Elements: Knowledge of child and adolescent development * Knowledge of learning process * Knowledge of students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency * Knowledge of students’ interests and cultural heritage* Knowledge of students’ special needs LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Knowledge of child and adolescent development Teacher displays little or no knowledge of the developmental characteristics of the age group. Teacher displays partial knowledge of the developmental characteristics of the age group. Teacher displays accurate understanding of the typical developmental characteristics of the age group, as well as exceptions to the general patterns. Knowledge of the learning process Teacher sees no value in understanding how students learn and does not seek such information. Teacher recognizes the value of knowing how students learn, but this knowledge is limited or outdated. Teacher’s knowledge of how students learn is accurate and current. Teacher applies this knowledge to the class as a whole and to groups of students. In addition to accurate knowledge of the typical developmental characteristics of the age group and exceptions to the general patterns, teacher displays knowledge of the extent to which individual students follow the general patterns. Teacher displays extensive and subtle understanding of how students learn and applies this knowledge to individual students. Knowledge of student’s skills, knowledge, and language proficiency Teacher displays little or no knowledge of students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency and does not indicate that such knowledge is valuable. Teacher recognizes the value of understanding students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency but displays this knowledge only for the class as a whole. Teacher recognizes the value of understanding students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency and displays this knowledge for groups of students. Teacher displays understanding of individual students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency and has a strategy for maintaining such information. Teacher displays little or no knowledge of students’ interests or cultural heritage and does not indicate that such knowledge is valuable. Teacher recognizes the value of understanding students’ interests or cultural heritage but displays this knowledge only for the class as a whole. Teacher recognizes the value of understanding students’ interests and cultural heritage and displays this knowledge for groups of students. Teacher recognizes the value of understanding students’ interests and cultural heritage and displays this knowledge for individual students. Teacher displays little or no understanding of students’ special learning or medical needs or why such knowledge is important. Teacher displays awareness of the importance of knowing students’ special learning or medical needs, but such knowledge may be incomplete or inaccurate. Teacher is aware of students’ special learning and medical needs. Teacher possesses information about each student’s learning and medical needs, collecting such information from a variety of sources. Knowledge of students’ interests and cultural heritage Knowledge of students’ special needs Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008b, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1b: Demonstrating Knowledge of Students Elements: Knowledge of child and adolescent development * Knowledge of learning process * Knowledge of students’ skills, knowledge, and language proficiency * Knowledge of students’ interests and cultural heritage* Knowledge of students’ special needs LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Knowledge of child and adolescent development Knowledge of the learning process Knowledge of student’s skills, knowledge, and language proficiency Knowledge of students’ interests and cultural heritage Knowledge of students’ special needs Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED Form #008c, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1c: Setting Instructional Outcomes Elements: Value, sequence, and alignment * Clarity * Balance * Suitability for diverse learners LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT Value, sequence, and alignment Clarity UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Outcomes represent low expectations for students and lack of rigor. They do not reflect important learning in the discipline or a connection to a sequence of learning. Outcomes represent moderately high expectations and rigor. Some reflect important learning in the discipline and at least some connection to a sequence of learning. Outcomes are only moderately clear or consist of combination of outcomes and activities. Some outcomes do not permit viable methods of assessment. Outcomes reflect several types of learning, but teacher had made no attempt at coordination or integration. Most outcomes represent high expectations and rigor and important learning in the discipline. They are connected to a sequence of learning. All outcomes represent high expectations and rigor and important learning in the discipline. They are connected to a sequence of learning both in the discipline and in related disciplines. All the instructional outcomes are clear, written in the form of student learning. Most suggest viable methods of assessment. All the outcomes are clear, written in the form of student learning, and permit viable methods of assessment. Outcomes reflect several different types of learning and opportunities for coordination. Where appropriate, outcomes reflect several different types of learning and opportunities for both coordination and integration. Most of the outcomes are suitable for most of the students in the class based on global assessments of student learning. Most of the outcomes are suitable for all students in the class and are based on evidence of student proficiency. However, the needs of some individual students may not be accommodated. Outcomes are based on a comprehensive assessment of student learning and take into account the varying needs of individual students or groups. Outcomes are either not clear or are stated as activities, not as student learning. Outcomes do not permit viable methods of assessment. Balance Outcomes reflect only one type of learning and only one discipline or strand. Suitability for diverse learners Outcomes are not suitable for the class or are not based on any assessment of student needs. Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008c, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1c: Setting Instructional Outcomes Elements: Value, sequence, and alignment * Clarity * Balance * Suitability for diverse learners LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Value, sequence, and alignment Clarity Balance Suitability for diverse learners Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED Form #008d, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1d: Demonstrating Knowledge of Resources Elements: Resources for classroom use * Resources to extend content knowledge and pedagogy * Resources for students LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Resources for classroom use Teacher is unaware of resources for classroom use available through the school or district. Teacher displays awareness of resources available for classroom use through the school or district but no knowledge of resources available more broadly. Teacher displays awareness of resources available for classroom use through the school or district and some familiarity with resources external to the school and on the Internet. Teacher’s knowledge of resources for classroom use is extensive, including those available through the school or district, in the community, through professional organizations and universities, and on the Internet. Resources to extend content knowledge and pedagogy Teacher is unaware of resources to enhance content and pedagogical knowledge available through the school or district. Teacher displays awareness of resources to enhance content and pedagogical knowledge available through the school or district but no knowledge of resources available more broadly. Teacher displays awareness of resources to enhance content and pedagogical knowledge available through the school or district and some familiarity with resources external to the school and on the internet. Teacher’s knowledge of resources to enhance content and pedagogical knowledge is extensive, including those available through the school or district, in the community, through professional organizations and universities, and on the Internet. Resources for students Teacher is unaware of resources for students available through the school or district. Teacher displays awareness of resources for students available through the school or district but no knowledge of resources available more broadly. Teacher displays awareness of resources for students available through the school or district and some familiarity with resources external to the school and on the Internet. Teacher’s knowledge of resources for students is extensive, including those available through the school or district, in the community, and on the Internet. Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008d, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1d: Demonstrating Knowledge of Resources Elements: Resources for classroom use * Resources to extend content knowledge and pedagogy * Resources for students LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Resources for classroom use Resources to extend content knowledge and pedagogy Resources for students Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED Form #008e, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1e: Designing Coherent Instruction Elements: Learning activities * Instructional materials and resources * Instructional groups * Lesson and unit structure LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT Learning activities Instructional materials and resources Instructional groups Lesson and unit structure UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Learning activities are not suitable to students or instructional outcomes and are not designed to engage students in active intellectual activity. Only some of the learning activities are suitable to students or instructional outcomes. Some represent a moderate cognitive challenge, but with no differentiation for different students. Some of the materials and resources are suitable to students, support the instructional outcomes, and engage students in meaningful learning. All of the learning activities are suitable to students or to the instructional outcomes, and most represent significant cognitive challenge, with some differentiation for different groups of students. All of the materials and resources are suitable to students, support the instructional outcomes, and are designed to engage students in meaningful learning. Instructional groups partially support the instructional outcomes, with an effort at providing some variety. Instructional groups are varied as appropriate to the students and the different instructional outcomes. Learning activities are highly suitable to diverse learners and support the instructional outcomes. They are designed to engage students in high-level cognitive activity and are differentiated, as appropriate, for individual learners. All of the materials and resources are suitable to students, support the instructional outcomes, and are designed to engage students in meaningful learning. There is evidence or appropriate use of technology and of student participation in selecting or adapting materials. Instructional groups are varied as appropriate to the students and the different instructional outcomes. There is evidence of student choice in selecting different patterns of instructional groups. The lesson’s or unit’s structure is clear and allows for different pathways according to student needs. The progression of activities is highly coherent. Materials and resources are not suitable for students and do not support the instructional outcomes or engage students in meaningful learning. Instructional groups do not support the instructional outcomes and offer no variety The lesson or unit has no clearly defined structure, or the structure is chaotic. Activities do not follow an organized progression, and time allocations are unrealistic. The lesson or unit has a The lesson or unit has a recognizable structure, clearly defined structure although the structure is not around which activities are uniformly maintained organized. Progression of throughout. Progression of activities is even, with activities is uneven, with reasonable time allocations. most time allocations reasonable. Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008e, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1e: Designing Coherent Instruction Elements: Learning activities * Instructional materials and resources * Instructional groups * Lesson and unit structure LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Learning activities Instructional materials and resources Instructional groups Lesson and unit structure Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED Form #008f, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1f: Designing Student Assessments Elements: Congruence with instructional outcomes * Criteria and standards * Design formative assessments * Use for planning LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT Congruence with instructional outcomes Criteria and standards Design of formative assessments Use for planning UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT DISTINGUISHED Assessment procedures are not congruent with instructional outcomes. Some of the instructional outcomes are assessed through the proposed approach, but many are not. All the instructional outcomes are assessed through the approach to assessment; assessment methodologies may have been adapted for groups of students. Proposed approach to assessment is fully aligned with the instructional outcomes in both content and process. Assessment methodologies have been adapted for individual students, as needed. Proposed approach contains no clear criteria or standards. Assessment criteria and standards have been developed, but they are not clear. Assessment criteria and standards are clear. Assessment criteria and standards are clear; there is evidence that the students contributed to their development. Teacher has no plan to incorporate formative assessment in the lesson or unit. Approach to the use of formative assessment is rudimentary, including only some of the instructional outcomes. Teacher has a welldeveloped strategy to using formative assessment and has designed particular approaches to be used. Approach to using formative assessment is well designed and includes students as well as teacher use of the assessment information. Teacher has no plans to use assessment results in designing future instruction. Teacher plans to use assessment results to plan for future instruction for the class as a whole. Teacher plans to use assessment results to plan for future instruction for groups of students. Teacher plans to use assessment results to plan future instruction for individual students. Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson Form #008f, updated 5/22/08 DOMAIN 1: PLANNING AND PREPARATION Component 1f: Designing Student Assessments Elements: Congruence with instructional outcomes * Criteria and standards * Design formative assessments * Use for planning LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE ELEMENT UNSATISFACTORY BASIC PROFICIENT Congruence with instructional outcomes Criteria and standards Design of formative assessments Use for planning Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching C. Danielson DISTINGUISHED