Literacy Unit Summary
advertisement

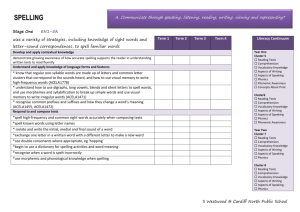
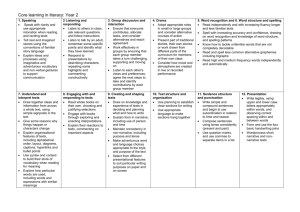
Literacy Unit Summary Name: Class: Year Group: One and Two Non-Fiction Unit 3 Recount, Dictionary Term: Week Beginning: Outcome Year 1 and 2 Objectives The use of dictionaries and alphabetic order is ongoing and needs frequent practical opportunities for assessing progress through purposeful cross-curricular enquiries, games and play. Written outcomes can be used to judge children's understanding of recount and sentence construction and assessments used for future teaching in Year 1 non-fiction unit 5. In order that children make effective progress in core skills across the year, it is important that these Strands are planned for in every unit: Strand 5 – Word Recognition: decoding (reading) and encoding (spelling) at KS1 Strand 6 – Word Structure and Spelling at KS2 Strand 11 – Sentence Structure and Punctuation at both key stages Overview Children describe incidents from their own experience in an audible voice using sequencing words and phrases such as 'then', 'after that'. Some children will find it easier to describe an incident if they have first drawn some pictures showing the series of events. Model listening to a recount and asking questions to prompt extending the recount or providing more detail. Children then listen to one another's recounts and ask relevant questions to provide detailed information or extend the recount. Model writing a short recount of a personal incident in the home. (Something commonplace such as the baby smearing his food all over his face and the furniture or the dog tearing up the unread newspaper will nudge the children to think up equivalent experiences of their own.) Children write simple first-person recounts linked to personal experience. Play games to introduce the use of the alphabet to order items in a dictionary or encyclopedia. Write extended captions for a class display. Read captions, pictures and diagrams on wall displays that explain a process. Draw pictures to illustrate a process and use the picture to explain the process orally. These are in addition to the Objectives listed below 1. Speaking Y1 – Tell stories and describe incidents from their own experience in an audible voice Y2 – Speak with clarity and use appropriate intonation when reading and reciting texts 2. Listening and responding Y1 – Listen with sustained concentration, building new stores of words in different contexts Y2 – Listen to others in class, ask relevant questions and follow instructions 3. Group discussion and interaction Y1 – Ask and answer questions, make relevant contributions, offer suggestions and take turns Y2 – Work effectively in groups by ensuring that each group member takes a turn challenging, supporting and moving on 4. Word recognition: decoding (reading) and encoding (spelling) Y1 – Recognise and use alternative ways of pronouncing the graphemes already taught Y1 – Recognise and use alternative ways of spelling the graphemes already taught Y1 – Identify the constituent parts of two-syllable and three-syllable words to support application of phonic knowledge and skills Y1 – Recognise automatically an increasing number of familiar high frequency words Y1 – Apply phonic knowledge and skills as the prime approach to reading and spelling unfamiliar words that are not completely decodable Y1 – Read more challenging texts which can be decoded using their acquired phonic knowledge and skills, along with automatic recognition of high frequency words Y1 – Read and spell phonically decodable two-syllable and three-syllable words Y2 – Read independently and with increasing fluency longer and less familiar texts Y2 – Spell with increasing accuracy and confidence, drawing on word recognition and knowledge of word structure, and spelling patterns Y2 – Know how to tackle unfamiliar words that are not completely decodable Y2 – Read and spell less common alternative graphemes including trigraphs Y2 – Read high and medium frequency words independently and automatically 6. Word structure and spelling Y1 – Spell new words using phonics as the prime approach Y1 – Segment sounds into their constituent phonemes in order to spell them correctly Y1 – Recognise and use alternative ways of spelling the graphemes already taught Y1 – Use knowledge of common inflections in spelling, such as plurals, -ly, -er Y1 – Read and spell phonically decodable two-syllable and three-syllable words Y2 – Spell with increasing accuracy and confidence, drawing on words recognition and knowledge of word structure, and spelling patterns including common inflections and use of double letters Y2 – Read and spell less common alternative graphemes including trigraphs 7. Understanding and interpreting texts Y1 – Identify the main events and characters in stories and find specific information in simple texts Y2 – Draw together ideas and information from across a whole text, using simple signposts in the text Y1 – Recognise the main elements that shape different texts Y2 – Explain organisational features of texts, including alphabetical order, layout, diagrams, captions, hyperlinks, and bullet points 8. Engaging with and responding to texts Y1 – Visualise and comment on events, characters and ideas, making imaginative links to their own experiences Y2 – Engage with books through exploring and enacting interpretations 9. Creating and shaping texts Y1 – Independently choose what to write about, plan and follow it through Y2 – Draw on knowledge and experience of texts in deciding and planning what and how to write Continued overleaf Prior Learning Check that children can already: Listen attentively to recounts and are able to recall some details including the correct ordering of events. Ask relevant questions and are confident to speak about their own experiences. Y1 – Convey information and ideas in simple non-narrative forms Y2 – Maintain consistency in non-narrative, including purpose of text Y1 – Create short simple texts on paper and on screen that combine words with images and sounds Y2 – Select from different presentational features to suit particular writing purposes on paper and on screen 10. Text structure and organisation Y1 – Write chronological and non-chronological texts using simple structures Y2 – Use planning to establish clear sections for writing Y1 – Group written sentences together in chunks of meaning or subject Y2 – Use appropriate language to make sections hang together 11. Sentence structure and punctuation Y1 – Compose and write simple sentences independently to communicate meaning Y2 – Write simple and compound sentences and begin to use subordination in relation to time and reason Y1 – Use capital letters and full stops when punctuating simple sentences Y2 – Compose sentences using tense consistently (present and past) Y2 – Use questions marks, and use commas to separate items in a list 12. Presentation Y1 – Use the space bar and keyboard to type their name and simple texts Y2 – Word process a short narrative and non-narrative texts Phase 1 – approx 3 days Phase 1 Learning outcomes Resources The teacher models orally a recount of a visit or an event using such phrases as last week, then and after that. Children are given plenty of opportunities to ask the teacher questions about what the teacher has remembered. Phase 2 – approx 2 days Phase 2 Learning outcomes The teacher and children analyse the activity orally and children practise with their response partners a recount of the same event or visit. The teacher and children listen to each other's recounts and make a series of pictures or a simple time line to order events. This could be modelled using digital photographs on an interactive whiteboard (IWB). The teacher demonstrates how to write a simple recount and edits and scribes as children volunteer suggestions. Phase 3 – approx 5 days Phase 3 Learning outcomes Read the recount written by children and the teacher, discuss, identify and record language features. Use this as a lead into Developing early writing, Ref: 0055/2001, Year 1 unit 9: The day the fire engine came to school http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/ primary/publications/literacy/63337/ or any event in school experienced by children. Children talk about an actual event, including generating questions and ordering events with the support of photographs or pictures. The teacher scribes and supports composition. Children work in groups or pairs to make their own simple recount in sentences using the past tense and time connectives. Dictionary work will be ongoing throughout phase 3 with the teacher demonstrating effective use of the dictionary. Children can listen to a recount and ask questions to support their understanding. Children can order events correctly. Children can identify and explain the main features of a sentence. Children can use knowledge of the alphabet to locate words in simple dictionaries. Children can write at least three simple sentences in the past tense and use some time connectives in a recount. Interactive whiteboard (IWB) Digital cameras and PC upload software Speaking, listening, learning: working with children at Key Stage 1 and 2 (Ref: 0627-2003) http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/primary/publications/literacy/81 8497/pns_speaklisten062403acts.pdf (PDF Kb 189) and the accompanying video clip of Year 1 Recount work (Ref: 06282003) Developing early writing (Ref: 0055/2001) Year 1 unit 9: The day the fire engine came to school, pp. 78-82 http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/primary/publications/literacy/63 337 Learning to learn: key aspects of learning across the primary curriculum (Ref: 0526-2004) from Learning and teaching in the primary years http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/primary/publications/learning_a nd_teaching/1041163/ Writing flier 5 - Recount: it happened like this... (Ref: 0532/2001) http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/primary/publications/literacy/63 353/nls_teachwriting053201reco5.pdf (PDF 189 Kb)