Electrochemical synthesis of Cu and Fe metal organic frame
advertisement

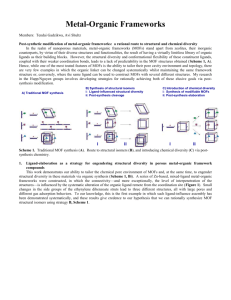
INVESTIGATION ON ELECTROCHEMICAL ROUTE FOR SYNTHESIS OF METAL (CU AND FE) ORGANIC FRAMEWORKS: CHARACTERIZATIONS AND ITS CATALYTIC ACTIVITY R. Senthil Kumar, S. Senthil Kumar and M.Anbu Kulandainathan* CSIR-Central Electro Chemical Research Institute, Karaikudi, India. Email: manbu123@yahoo.com Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are very promising systems due to the virtually unlimited flexibility in their design. The generation of MOFs enables the tailoring of novel solids with regular porosity from the micro to nanopore scale. Nowadays several hundred different types of MOF are known. The self assembly of metal ions, which act as coordination centres, linked together with a variety of polyatomic organic bridging ligands, results in tailorable nanoporous host materials as robust solids with high thermal and mechanical stability. These hybrid organic-inorganic compounds exhibit rather low-dense and relatively robust three-dimensional architectures delimiting systems of well-defined cavities or tunnels and they offer new potential applications include molecular magnetism, ionic conductors, sensors, materials for adsorption applications (gas separation and gas storage, in particular hydrogen storage) and heterogeneous catalysis. In heterogeneous catalysis, MOFs can exhibit high activity and selectivity in oxidation, esterification, epoxide ring openings, asymmetric hydrogenation, etc. The metal organic framework material Cu3(BTC)2 (BTC = 1,3,5- benzene tricarboxylate) has been synthesized using different routes: under solvothermal conditions in an autoclave, under atmospheric pressure and reflux, microwave synthesis, ultra sonic synthesis, solvent free solid state synthesis and electrochemical synthesis. Since electrochemical methods are simple and considerably avoid environmental pollution, many organic compounds are being synthesized by such methods. In this work, we have synthesized Cu-BTC and Fe-BTC of MOFs by electrolysis under the condition of 15V D.C potential were applied in the electrolyte solution, containing methanol with Tetrabutylammoniumtetrafluoroborate (TBATFB) salt at room temperature. Interestingly, the addition of TBATFB in electrolyte solution, increase the conductivity of the electrolyte solution and improve the yield of the products. The synthesized Cu and Fe MOFs were characterized by XRD, XPS, for studied the structure and electronic properties. The SEM and TEM were used for morphology of the MOFs and its surface area was determined by BET. Cyclic voltammetric technique was used to study their surface of electrochemical behavior and its application of electrocatalytic activity towards CO2 reduction and chemical catalysis of nitrophenols reductions.