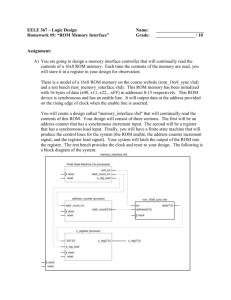
Active / Resisted ROM – pain, discomfort can indicate muscle
advertisement

Injury Assessment Through ROM Testing Active / Resisted ROM – pain, discomfort can indicate muscle / tendon injury Passive ROM – pain, discomfort can indicate an injury to bone, cartilage and/or ligament Must do other stress tests to determine more specific injury Do Active, then Passive, then Resisted ROM tests Knee ROM Tests: Flex, ext, hip add, hip aBD Begin test by having patient lie on a table, legs fully extended. Next: Ankle ROM Tests: Inversion, eversion, plantarflexion, dorsiflexion Have patient sit or lie face up on a table. Next: Shoulder ROM Tests: Full Arc Test Apley’s Scratch Test Individual ROM Tests (keep elbow at 90 degrees) Flexion, extension (like pumping arms when running) Abduction, ADDuction Internal rotation, external rotation Protraction, Retraction Elevation, Depression