Proposed spectral distribution for a Gaussian pulse beam
advertisement

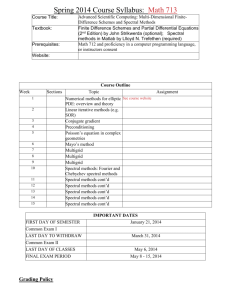
Proposed spectral distribution for a Gaussian pulse beam C.J.R. SHEPPARD†*, P. MOORE†, M. ROY† and M. D. SHARMA †University of Sydney, NSW 2006 Australia *Australian Key Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia mroy@physics.usyd.edu.au Gaussian pulse beams model the emission from a confocal resonator, such as those commonly found in lasers. Such beams assume the relatively simple form of a superposition of coherent waves, each independently the solution of the paraxial wave equation. Various spectral distribuition models have been proposed to describe the Gaussian pulse beam [1]. For physically realisable beams, the spectral distribution includes only positive frequencies Feng and Winful [2] and Caron and Potvliege [3] have investigated functions similar to the Poisson distribuiion. This paper discusses the advantages and limitations of those proposals and offers an alternative model for Gaussian pulse beam. The proposed spectral distribution is based on the function 2 0 0 0 , 1 . f 1 exp s 1 1 1 n where w0, w1 and s are free parameters. The advantages of this proposed spectral distribution are that it is directly Fourier transformable, and can exhibit positive or negative skewness. Various properties of the proposed spectral distribuition such as mean and spectral variance are presented. The amplitude function is also derived using the proposed spectral distribuition for a Gaussian pulse beam. References: [1] C.J.R. Sheppard and X. Gan, 1997, Opt. Comm., 133, 1 [2] S. Feng and H.G. Winful, 2000, Phys. Rev E, 61, 862. [3] C. F. R. Caron and R. M. Potvliege, 1999, J. Mod. Opt., 45, 1881.