22 Reproduction Class Practice 22
advertisement

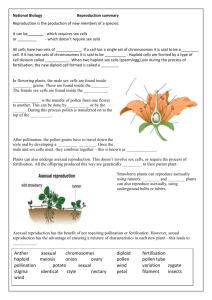
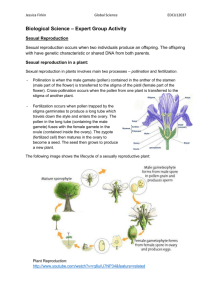
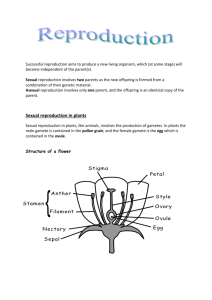
22 Reproduction Class Practice 22.1 What is reproduction? 22.2 Asexual reproduction in bacteria 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F 1. During asexual reproduction, the parent organism produces new 4. individuals simply by mitosis. In sexual reproduction, the gametes are produced by meiosis / zygote is formed after fertilisation. 22.3 Asexual reproduction in flowering plants A. B. Plant Vegetative propagating organ 1. onion bulb 2. ginger rhizome 3. potato tuber 4. Gladiolus corm 1. 2. 3. 4. B A D C 22.4 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants A. 1. D 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. A H G C B E I J 10. F B. 1. 2. 3. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) stamens filament anther pollen sacs carpel ovary style stigma anther (j) stigma (k) species (l) pollen tube (m) style (n) ovary 22.5 Fruits and seeds 22.6 The advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction compared with asexual reproduction in flowering plants Structure Name Function A seed coat protects the embryo B cotyledon provides stored food for seed germination C plumule grows and develops into the leafy shoot D radicle grows and develops into the root 22.7 Sexual reproduction in humans A. 1. (a) testis 2. (b) sperm ducts 3. (c) penis 4. (d) epididymis 5. (e) seminal vesicles (f) prostate glands (g) Cowper's glands B. 6. (h) scrotum 7. (i) urethra 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 1. (j) ovary (k) oviduct (l) uterus (m) vagina (n) cervix 1. D 2. E 2. 3. 4. 5. C B F 6. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A C A D E B 22.8 Human embryos 1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. F 6. F 7. T 2. Fertilisation usually occurs in the oviduct. 3. 5. 6. Implantation takes place in the uterus. The foetus obtains nutrients from the mother's blood through the placenta. Pregnancy begins when implantation takes place. 22.9 The birth process (c) → (b) → (a) → (d) 22.10 Parental care 1. F 2. F 3. T 1. During pregnancy, the mammary glands in the mother's breast start to produce milk. 2. In humans, parental care starts from the birth of a baby and lasts very long. 22.11 Birth control 1. condom, surgical method 2. surgical method 3. 4. 5. surgical method condom, diaphragm IUD 6. 7. 8. natural method condom, diaphragm contraceptive pills, IUD, surgical method Exam Practice A. Multiple Choice Questions 1. C 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. D C D D D B B A C 11. B B. Structured Questions 1. (a) (i) B, E (ii) G (iii) B (iv) C (b) Internal fertilisation takes place in this flower. After the pollen grains have landed on the stigma, they develop pollen tubes to send the male gametes down into the ovule inside the ovary where fertilisation takes place. (c) The anther and stigma are enclosed inside the corolla. The nectary secretes nectar to attract insects. The flower is large and conspicuous. (d) It carries out photosynthesis and protects the flower bud. (e) A, B and C will wither. D will become the fruit wall/fruit. E will become the seed. 2. 3. (a) B – stigma, D – filament (b) C (c) Feathery stigma – to catch pollen grains in the wind (d) (a) (b) (c) (d) 4. (a) (b) (c) Anthers hang out of the flower – to shake off the pollen grains They are light with a smooth surface. (i) urine (ii) kidney F/testis (i) F (ii) F (iii) F (iv) C, E (v) C, D The temperature in G is slightly lower than the body temperature. Sperm production is very sensitive to heat and more sperms are produced in cooler conditions. A – ovary; B – uterus; C – vagina A / ovary E / oviduct (d) No, because the female sex hormones can still be secreted by ovaries (A) and transported by blood to the target organs to exert their effects. 5. (e) Women's urethra (H) is shorter than that of men. It is easier for bacteria to pass from the urethra (H) to the bladder to cause infection. (a) glucose, amino acids, mineral salts (b) urea and carbon dioxide (c) The embryonic tissue would be destroyed by the higher pressure of the maternal blood. (d) It is the amniotic fluid. It acts as a shock-absorber, protecting the embryo from mechanical injury. It prevents the embryo from becoming desiccated and allows some freedom of movement as it grows. C. STS Connections (a) insect pollination (b) No. The flowers have to be from the same species in order for fertilisation to occur. (c) It provides a 'landing platform' for insects.