Transdisciplinary Skills Scope and Sequence – Research Skills
advertisement

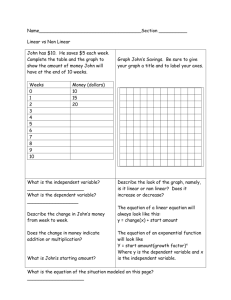
St. Dominic´s International School Portugal Library Junior School Research & Literature Skills Overview Preschool – Year 6 1 I introduce P practice Preschool A apply Prep One Two Three Four Five Six Students will be introduced to inquiry based learning using a modeled example: The NSW information skills process www.schools.nsw.edu.au/schoollibraries/pdf/infoskills.pdf (define, locate, select, organise, present, assess) The Big Six www.big6.com The Super 3 for lower elementary http://www.big6.com/kids/K-2.htm 8Ws model http://eduscapes.com/info/topic71.htm And others: Info Literacy Models http://www.shambles.net/pages/learning/infolit/InfoLitMod/ DEFINE: Formulating Questions Brainstorm topics in groups – recall known information Asks questions to seek clarification Uses a question to expand on an idea in a discussion Pose realistic and investigative questions Continue to formulate and refine research questions Identify and interpret keywords, questions & ideas in a task Organises focus questions into headings from clustered ideas using modeled examples I P P I P I I A A P A A I I I P P P A A A Observing Understands that information can be received through all the senses Has developed observation skills by using their senses to gather and record information Uses their own observations to identify simple patterns, make predictions and discuss ideas Discusses a given topic in response to an audio +/or visual stimulus I P A I P A I P A I P A Planning Propose & discuss search strategy Establish goals and priorities Establish a time line and action plan Delegate duties, plan, set goals, organize, take action (group work, collaborative) Engages in reflective thinking to analyse and clarify a problem I I P A I P I P A I P 2 Preschool Prep One Two Three Four Five Six LOCATE Collecting Data Identify parts of a book- front & back cover, spine, spine label, barcode, title page, Verso/copyright page, Dedication/acknowledgement Use cover and title to indicate contents Identify author and illustrator Identify structural features of a text e.g. contents page, introduction/preface/forward, index, glossary, appendix, bibliography, page numbers, headings and captions Is aware of different areas of the library Differentiate between fiction and nonfiction Use first three letters of an authors name to locate fiction Use subject index book Use OPAC Inquiry to identify & locate resources – uses author, title, subject, keyword access Uses simple and combined terms to search internet sources e.g. Boolean and truncation etc Use of Dewey Decimal System: Recognises & uses the call number to locate non fiction Is aware of primary resources as a source of information e.g. 1st hand experience, people, concrete objects Is aware of secondary resources as a source of information e.g. books, pictures, AV materials Use of specialist sources material to extract information: I P I I P P I I A A A P A P I I P P I I P I A A A P A A P I P . A I P A I P A . P A o Dictionaries o Thesaurus o Encyclopedias o Atlases – mapping skills – from simple to more complex I P o Interviews/experts I P o Newspapers o Periodicals/magazines o Online databases I P o TV & radio broadcast I P I I P A I I P A A I P I I o 3 Uses several strategies for finding information in texts: o Selects materials by assessing readability and scanning cover, title, illustrations and other structural features of text (index, glossary) o skimming and scanning techniques Use of community resources to satisfy information needs e.g. Government agencies, public libraries Use of graphic organizers: o KWL chart o Describing wheel o T chart o Flow chart o T chart o Cluster/word web o Brainstorming web o Venn diagram o fishbone Uses range of electronic equipment to access information: o telephone o fax o scanner o digital camera o intranet o CD ROMS o Internet o Email as a communication tool and information source Participates in on-line projects to locate, contribute and gather information I I P P A I I P P A . I I P P I I I I I P I P P P Two Three Four I Preschool Prep One A P A A A Five Six SELECT / ANALYSE Recording Data Uses pictures, objects, live specimens to extract information Records relevant information (Note taking skills as age appropriate) using modeled examples by: o Arranges ideas, events & facts in sequence from oral, pictorial & written sources o Listens in group discussions and records key issues (pictorial or written) o Contributes to class summary after reading, viewing or listening I P I A P I I P A P A A 4 o o o o o o o Understands that different accounts of the same even may vary List key words Uses appropriate note taking templates & strategies using modeled examples e.g. o concept mapping o main idea o list making o clustering notes under sub-headings Constructs sentences using identified key words Summarise and paraphrasing key information Recognizes when a statement is a generalisation Makes brief relevant notes (including outlining strategies) I Preschool I P I P P P I I P One I P P I Two A A I Prep A Three Four A P I P Five Six ORGANISE / SYNTHESISING Organising Data Participates in teacher led discussion to categorise information I Participates in group discussion to propose solution to a problem Learns that charts, diagrams, recipes, news recounts & documentaries present information in different ways Interprets maps, charts, diagrams, graphs, photos, graphics Constructs timelines Label diagrams Compile charts Categorise information according to specified criteria Selects main idea and supporting details Organizes ideas and information logically Categorizes information according to a framework of heading and subheadings using modeled examples Categorise information according to specified criteria Makes simple generalizations and draws simple conclusions Makes notes using modeled techniques e.g. written, bulleted points, graphic organisers Combine information from different sources Translates information from one form to another I Makes simple generalizations and draws simple conclusions A A I I I P I I P A P P A P P I A A I I I I P P P P I A P A P I P A P A A A I P 5 Use of word processing and typing skills: o To draft and edit writing Extends the use of Word Processing Skills (as age appropriate)by: o Move pointer with mouse o Click, hold and drag mouse o Can select quit/close from the file menu o Use the delete key o Can shut down the computer o Can save document o Create, open, close, Save & Save as o Entering and editing text o Justifying text o Changing text – font/colour/bold/italic/underline o Resizing text o Changing text alignment o Highlighting text o Using tab function & indent o Understand difference between cut and copy o Copying selected text o Cuts and pastes text o Making notes directly from screen o Basic keyboarding (use of letters) o Practicing keyboard drills e.g. hand and finger placement o Using spell checker & synonyms o Using columns o Changing page orientation (Landscape/portrait) o Changing size of page, e.g. 75% view o Inserting graphics o Manipulating graphics e.g. resizing o Insert borders, word art, shading, background o Using lists/bullets o Wrapping text around graphics o Formatting text appropriate to text type o Insert tables and grids o Use drawing toolbars to create graphic organisers o Create computer generated organisational strategies, e.g. Low charts, time lines using modeled examples o Use print preview to check work document o Print preview & Print & Print two to one page I I I I P I I I P I I A P P P A P I P P A A A A A P A I I I P I P I I I I I A P P I I A P P P P P I I I I I I I I I I A A P A P P A A A A P P P P P P P I A A A A A A A P I P P I I I I P P P A A 6 Manipulate software e.g. Kidpix, Jellybean hunt, My Friend Use multimedia program o KidPix or Paint o Powerpoint – slide show o Microworlds Spreadsheet skills o I I I P P P A A A I I P P I Interpreting Data Understands limitations of reference books e.g. old atlases, encyclopedias, bias, international publications Aware of fact, opinion, propaganda, bias, stereotyping and points of view in information Aware of strategies to assess the value of internet sites Makes inferences from gathered information Compares different ways information is presented in e.g. TV documentaries, news bulletins, encyclopedias & newspapers Verifies results of experiments using modeled examples Explains their own interpretation of ideas, information and events Verify accuracy of information according to copyright date, authority, bias I P I I I P P I I I P A P Four Five P I Preschool Prep One Two Three P Six PRESENT Presenting Research Findings Talks about what they have found from their data collection Shares knowledge and information with others within a group Oral reports Uses supporting evidence to argue a personal view point Examine & report on findings ( May use notes as prompts when speaking) Gives sustained reports on generalized, researched topics Uses ICT technology and extends desktop publishing skills to record data and present research findings Consider the nature of the audience in the selection of appropriate presentation Selects the most appropriate method/media to present information Is aware of Web page structure (years 6 – 7) I I P P A A I P I I I I P A P P P I P I P I 7 Academic honesty: Demonstrates an understanding of plagiarism: Prep-1: discusses role of ownership e.g. Author, illustrator, producer. Yr 2- 4: recognizes importance of expressing information in the student’s own words Yr 5-6: defines plagiarism and uses full citation of information used for research Bibliographic skills, simple to more complex e.g. book, encyclopedia, magazine, internet, using modeled examples Understands and complies with copyright requirements using modeled examples Uses online citation tools to record bibliographic sources Shows appropriate ethical conduct when accessing Internet I P I P I I P I Preschool Prep I I P One Two Three P Four Five Six ASSESS Assessing Express opinions Respects the rights and opinions of others & acknowledges their contributions Identify alternative strategies & sources to use for future research Develops the concept of peer evaluation by giving and receiving feedback Analyse and evaluate various viewpoints Uses a variety of evaluative strategies using modeled examples to assess and review learning re their strengths & weaknesses e.g. learning logs, reflective journals, rubrics Evaluates understanding and implementation of set task criteria using modeled examples Discuss how they could improve their research next time Discusses the appropriateness of the presentation in relation to the original task Identifies further questions and issues arising from action and decisions A P A I I P P I I P P I I P A P I I A P I I P 8 Lifelong Reading Skills: Otsego Northern Catskills BOCES School Preschool Prep One Two Three Four Five Six Library System (2006) Information literacy scope and sequence [online] Available http://encompass.cerfinfo.com/TOC.htm Accessed 10 November 2006. Listening, Viewing, and Reading for Comprehension and Enjoyment o Develops personal interests and forms lifetime recreational and informational reading habits o Demonstrates reading, listening and viewing skills o Recognizes cultural diversity in literature o Recognizes various literary forms: o ABC books o Autobiography o Biography o Drama o Fables o Fairy tales o Folk tales/folk lore o Legends & Mythology o Non-fiction o Novel o Nursery rhymes o Picture book o Poetry o Short story o Wordless picture book o Recognises genres of fiction: o Adventure o Fantasy o Historical fiction o Mystery o Realistic fiction o Science fiction o Recognises components of fiction: o Beginning/Middle/End o Cause & effect o Character o Climax o Details o Plot/sequence o Point of view I P I A P I I A P A A I I P I I I P P I I I I I P I A P P I P I I P A A A P P A P A P A A I P P I I P I I P I I A P P A P A P P I P I I A A I I A A P I A A P A A P 9 o o o o o Setting o Style o Theme/main idea Differentiates between an author & other contributors to a work: illustrators, editors, publishers, webmasters, etc. Chooses fiction and non-fiction materials at appropriate interest and reading levels Recognizes the value and guidance provided by appropriate literary awards and reviews such as: o Caldecott Award for illustrators o Newbery Award for authors o Australian Children’s Book of the Year o Newspaper and magazine book review columns Recognizes and appreciates the artistic components of a work and their contribution to: o Usefulness and appeal o Illustrative styles o Type face o Page or screen layout Listening, Viewing and Reading for Media Literacy o Recognizes various media forms (media literacy) o Advertisements – commercials, billboards, posters, print, online o Audio recordings o Cartoons – print, animated o Internet communication o Magazine – print, online o Movies/Documentaries o Newspapers – print, online o Radio o Television o Web pages o Compares and contrasts print and non-print versions of an information source o Compares and contrasts print and non-print versions of a piece of literature I P I I P A P A I I P P A I P I P A I I P A I P I A I I P I I I P I P P P P A P A I P I P 10 Bibliography / References: Board of Studies NSW (2006). English Syllabus: K.6 [online] http://k6.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au/english/#english-syllabus. Accessed 12 October 2006. Borgmeyer, Val. Resource based learning at Parndana Area School, South Australia. Information literacy skills continuum. [online] Available Edna online: http://www.edna.edu.au/edna/page2521.html Bundy, Alan (ed). (2004). Australia and New Zealand Information Literacy Framework – principles, standards and practices. Australian & New ZealandInstitute for Information Literacy: Adelaide. [online]. Available Edna online: http://www.caul.edu.au/info-literacy/InfoLiteracyFramework.pdf Evans, S & Kirby-Barrett, Y. (1995) Information skills, the library and the curriculum. [unpublished research document]. Houghton Mifflin Education Place, Graphic organizers [online]. Available: http://www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer/. Accessed 11 October 2006. Kansas State Board of Education (May 2001). Kansas Curricular standards for library media [online]. Available: http://www3.ksde.org/outcomes/library.html. Accessed 12 October 2006. Leslie, Suzanne (200?). Scope and sequence of information skills for the students of Lindfield Primary School [online]. Available: http://www.lindfield.nsw.edu.au/library/libss.html . Accessed: 11/07/2006. Library curriculum guidelines; scope and sequence (2005) [online] Available as PDF: www.arlingtondiocese.org/offices/schools/form/Library%20Spreadsheet%202005%20Curriculum.pdf Otsego Northern Catskills BOCES School Library System (2006) Information literacy scope and sequence [online] Available http://encompass.cerfinfo.com/TOC.htm Accessed 10 November 2006. Rochester (NY) Regional library Council (2006) Core Library & research skills grade 9-14+ [online]. Available: http://rric.org Ryan, Jenny & Capra, Steph. (2000) ILPO Information literacy planning overview P/K-7 for primary school revised edition. CRA, Australia. Skirrow, Ingrid (2006). The IBO learner profile as a model of lifelong learning and for information literacy in the library [online]. Available: Online Curriculum Centre, IBO Library Resources. http://occ.ibo.org/ibis/occ/guest/home.cfm Accessed June 2006. Acknowledgement: Although various resources were used &/or referred to in the creation of this document, acknowledgement and thanks are especially noted to: Ryan, Jenny & Capra, Steph. (2000) ILPO Information literacy planning overview P/K-7 for primary school revised edition. CRA, Australia. Developed by: Yvonne Barrett, Teacher Librarian Primary. Australian International School Singapore 2006. 11