College Prep: Review
advertisement

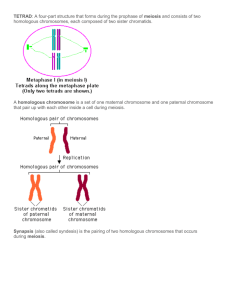
Unit 6: The cell cycle College Prep Review THE CELL CYCLE 1. The collection of stages in a cell’s life is called the cell cycle 2. Chromatin is unwound DNA and is present during the interphase stage of the cell cycle. 3. Draw and label chromosome structure: chromatid, centromere, genes (bands on the chromosome). 4. How are chromosomes, genes and DNA related? Chromosomes are made up of DNA, and genes are sections of the DNA (on the chromosomes) 5. What are homologous chromosomes? 2 chromosomes that are the same size and have the same number of genes but different versions of traits (one from mom and one from dad) 6. Draw a pair of homologous chromosomes. How many chromatids make up a pair of homologous chromosomes? 1 7. 2 3 4 chromatids- makes a tetrad Why do we have 23 PAIRS of chromosomes in our body cells? One set from mom and one set from dad, gives us a “backup” copy of each gene 8. What is a karyotype? Picture of all single chromosomes in a somatic cell 9. How can you determine gender and the presence of genetic abnormalities by looking at a karyotype? What are the chromosomes that represent the different genders. Gender- the 23rd pair is either XX (female) or XY (male) If there are more or less than 2 of each, or if pieces are missing off of a chromosome, then you will see it in a karyotype 10. What are 3 ways you know chromosomes are paired together on a karyotype? Banding pattern, size, and cetromere position 11. What are 2 functions of a karyotype? Determine gender, see any chromosomal abnormalities 12. List the 2 main parts of cell cycle: Interphase and Mitosis (with cytokinesis being a third) 13. What 2 events happen during interphase? Growth and DNA replication (if division is necessary) 14. What is mitosis? Reproduction of somatic (body) cell nuclei- creates diploid cells 15. What is meiosis? Reproduction of gamete (sex) cell nuclei- creates haploid cells 16. Body cells contain 46 chromosomes while sex cells contain 23 chromosomes. 17. What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells? Haploid cell has 1 set of every chromosome (one set of the homologues)- ½ the number of normal cells Diploid cells have 2 of every chromosome (2 sets of homologues) 18. What are two ways that meiosis mixes up genetic information? Crossing over and independent assortment 19. Describe each of the 4 stages of mitosis. Describe how would you be able to identify them? 1. Prophase- nuclear membrane dissolving, chromosomes condensing, cetrioles moving, spindle fibers formed 2. Mataphase- chromosomes lined up signle file in the middle of the cell 3. Anaphase- sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers 4. Telophase- cleavage furrows or cell plate forms, nuclear membrane forms, spindles dissapear 20. What is the function of the centrioles? Grow spindle fibers and move chromosomes 21. How many chromosomes does a body cell start with? End up with after mitosis? Starts with 46 double in one cell=> ends with 46 single in 2 cells 22. Describe what happens during each phase of meiosis (I and II). Prophase I- nuclear membrane dissolving, chromosomes condensing, cetrioles moving, spindle fibers formed Mataphase I- chromosomes line up in homologous pairs (tetrad) in the middle of the cell Anaphase I- Homologous pairs are pulled apart by the spindle fibers Telophase I- cleavage furrows forms, nuclear membrane forms, spindles disappear, 2 haploid cells are produced ProphaseII- nuclear membrane dissolving, chromosomes condensing, cetrioles moving, spindle fibers formed Mataphase II- chromosomes lined up signle file in the middle of the cell Anaphase II- sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers TelophaseII- cleavage furrows, nuclear membrane forms, spindles dissapear 23. What is a tetrad? 2 double chromosomes (4 sister chromatids) formed in metaphase I from homologous pairs 24. What is crossing over and when during meiosis does it occur? When genes are exchanged between homologous pairs of a tetrad during metaphase I. This increases genetic diversity 25. Why is meiosis important? Gametes (sex cells) must have half the number of chromosomes so that when fertilization occurs the resulting zygote has a normal number of chromosomes 26. What are the main differences between mitosis and meiosis in terms of the following. a) number of chromosomes (single or double) at the beginning b) how they line up during metaphase c) their separation d) number of chromosomes (single or double) at the end e) number of cells that are made A.mitosis- double; meiosis I- double; meiosis II- double B. mitosis- single file; meiosis I pairs; meiosis II- single file C. mitosis- sister chromatids; meiosis I- pairs; meiosis II- sister chromatids D.Mitosis- singe; Meiosis I- double; meiosis II- single E. Mitosis- 2 cells; meiosis I- 2 cells; Meiosis II- 4 cells