Name: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date: 7th Grade Review Packet Science
advertisement

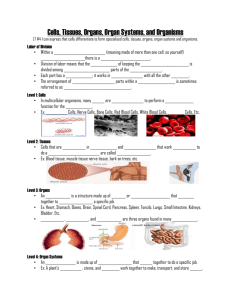
Name:_____________________________ Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date:__________________ 7th Grade Review Packet Science Standards and Vocabulary The following will be a list of the 7th grade science standards and objectives we have covered throughout the year. For each standard please write down the information you have learned about the standard, science labs that were done while learning the standard, and any additional information that is now being taught about the standard. Also please define as many scientific words as you can that are found in the standards and objectives. Kingdoms and Classification Unit (DAYS 1 & 2) 1. Categorize at least 10 nonliving objects based on their external structures. 2. Write 5 examples of living, once living, and nonliving things. 3. Why is observation so important in scientific classification? (Write at least 3 sentences) 4. You need to take 10 animals and classify them several different ways, by putting them into groups based upon their characteristics. 5. Using the 10 animals above develop an animal classification system based on observed structural characteristics. (Things you can physically see not behavior patterns) 6. Make a list of several rules that you use whenever you classify things. Must have at least 4 rules! 7. Why are classification systems important in the development of science knowledge? 8. Describe how classification is used by scientists to detect patterns in nature. 9. List as many organisms as you can that are not classified as plant or animal. 10. List 2 examples of organisms that fall into the kingdoms of animals, plants, monera, fungi, and protists. 11. Describe in detail how you could use a classification key or a field guide to identify unknown organisms. 12. Do classification keys and systems ever change? If so why? 13. What are the 7 characteristics of living things? 14. Describe the 6 kingdoms of life. 15. What are the 7 levels of classification? Classification and Kingdoms Vocabulary – Define the following words 1. Classification 2. Classification Key 3. Kingdom 4. Organism 5. Species 6. Animal 7. Plant 8. Monera 9. Protists 10. Genus 11. Bilateral Symmetry 12. Radial Symmetry 13. Vertebrate 14. Invertebrate 15. Respiration 16. Viruses Ecology and Human System Unit (DAYS 3 & 4) 1. Why would certain traits (structure of teeth, body structure, coloration) offer an advantage for survival of an organism. What are examples of these traits and environments that allow an organism to survive? 2. What are some examples of traits that provide an advantage for survival in one environment but not other environments? 3. List 2 examples of adaptations that have been influenced by humans and 2 examples of adaptations that have occurred naturally in the wild. 4. List 2 adaptations that organisms specifically have to their organs. 5. Describe cells, organs, organisms, organ systems, and tissues. Also list them from smallest to biggest and from biggest to smallest. 6. List as many organs and organ systems as you can think of. 7. Organs are the basic component parts of an organ system. How does an organs structure and function influence their role in the organ system that they belong in? 8. Describe how the needs of an organism at the cellular level for food, air, and waste removal are met by tissues and organs. Ecology and Human System Vocabulary – Define the following words 1. Osmosis 2. System 3. Diffusion 4. Adaptation 5. Stimulus-Response 6. Traits 7. Structure 8. Function Cells, Microscopes, and Cellular Reproduction Unit (DAYS 5 & 6) 1. Draw and label the overall structure of a microscope. How does it magnify small organisms or objects? Also draw what an onion cell looks like. 2. Draw and describe an animal and a plant cell. Make sure and include the following cell organelles: cell wall, mitochondria, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, and cytoplasm. For each cell organelle please include an accurate definition of the organelles function. 3. What are the primary differences between a plant cell and an animal cell? (List 3) 4. What is diffusion and what is osmosis? What examples or demonstrations did we do in class to model both of these processes? 5. How are the basic processes of extracting energy from food, removing waste, and producing food done at a cellular level? 6. What is the difference between inherited and acquired traits? Please list at least 4 examples of each along with your definitions. 7. Describe the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. Include how many parents are involved in each, benefits and disadvantages of each, and the amount of genetic variation in each. 8. List 5 examples of organisms that reproduce sexually. 9. List 5 examples of organisms that reproduce asexually and describe the process that they undergo to reproduce. (Example: Binary Fission) 10. In sexual and asexual reproduction describe the inherited structural traits of the offspring as compared to their parents. 11. Describe the definitions for genotype, phenotype, and a Punnett Square. Also describe how each of these influences our genetic traits and their probabilities. 12. What is the difference between a recessive and a dominant gene or allele? Cells, Microscopes, and Cellular Reproduction Vocabulary – Define the following words 1. Acquired Trait 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Genetics 4. Nucleus 5. Inherited Trait 6. Offspring 7. Sexual Reproduction 8. Cytoplasm 9. Membrane 10. Chloroplast 11. Cell 12. Cell Wall 13. Prokaryotic 14. Eukaryotic Matter and Density Unit (DAYS 7 & 8) 1. Can atoms be seen with a microscope? Yes or No and why? 2. What do atoms have to do with molecules? 3. What are the various parts that make up an atom? Describe these parts in detail and draw an atom. 4. Draw a diagram and describe the arrangement of particles in the physical states. (solid, liquid, and gas) 5. What are some of the limitations of using models to represent atoms? 6. How has our knowledge of the structure of matter been developed over time? What is the history of our knowledge with regards to atoms? Why has it changed so much? 7. How do we take the mass of solids and liquids? Be specific because it is more difficult to take the mass of a liquid. 8. How could you predict what the relative density of a solid or liquid would be? 9. How can you calculate the density of a solid? How can you calculate the density of an irregularly shaped solid? How can you calculate the density of a liquid/ 10. What is the relationship between mass and volume as it relates to density? If mass goes up what happens to density? If mass goes down what happens to density? If the volume goes up what happens to the density? If the volume goes down what happens to the density? 11. How could you measure the mass and volume of a gas? 12. Are particles in a solid, liquid, and gas in constant motion? Please describe! 13. How could you compare the motion of particles at various temperatures by measuring changes in volume of gases, liquids, and solids? 14. What is the relationship between temperature and motion with regards to particles? 15. Describe the impact of expansion and contraction of solid materials on the design of buildings, highways, and other structures. 16. What objects densities could you compare to the densities of known earth materials? (Hint: We did a lab in class where we created density layers in a jar) 17. How would you describe the sorting of earth materials in a mixture based on density and particle size. 18. Materials are sorted in streambeds, road cuts, and beaches. How are the different materials sorted in nature? 19. List all of the layers of the Earth’s exterior and interior and put them in order from most dense to lease dense. Also put them in reverse order from least dense to most dense. It might be helpful to draw a picture for this question. 20. What does density have to do with the relative positioning of Earth’s atmosphere, water, crust, and interior layers. 21. Distinguish between models of Earth with accurate and inaccurate attributes. (Hint: you could talk about the relative size and consistency of the layers or we even talked about the Hollow Earth believers theories) Matter and Density Vocabulary – Define the following words 1. Atmosphere 2. Atom 3. Crust 4. Density 5. Gas 6. Liquid 7. Models 8. Mass 9. Matter 10. Molecule 11. Particle 12. Solid 13. Temperature 14. Heat Energy 15. Volume