6/22/98
advertisement

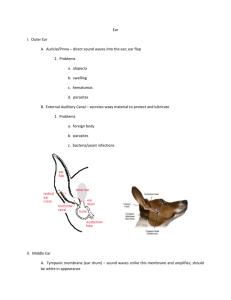
1 Phys Dx 6/22/98 To review tests with her -- SIGN UP Remember--she bases test on her study questions --she asks definitions EAR EXAM Components Hx external ear middle ear inner ear nervous innervation Why do -- Hx, complaints, risk factors Hx--personal Hx, family Hx complaints--ex--can’t hear as well risk factors --job exposure --music tastes/hobbies --trauma (head, ear) Reasons to do an ear exam part of a complete physical c/o hearing loss (c/o= complaint of) vertigo/dizziness tinnitus--ringing in the ear otorrhea--discharge from the ear prutitis--itching Risk factors head trauma whiplash job/environmental exposure medication toxicity (ex.-aspirin) water sports (dampness in ear) Hx of herpes (ex.-herpes simplex) wrestlers tend to get this around ear spreads rapidly once in ear canal -can destroy tympanic membrane -can mess up nerve headache -can be sign of infections Hearing loss unilateral or bilateral (may occur slowly or abruptly) when did it first appear what makes it better/worse past treatments family Hx transient? Medications 2 some meds are ototoxic 6/22/98 salicylates and diuretics transient hear loss possible streptomycin and gentamicin can destroy hair cells can be permanent loss cisplatin--ototoxic cancer drugs UNILATERAL HEARING LOSS--TRAUMA, INFECTION, WAX BUILDUP BILATERAL HEARING LOSS--SYSTEMIC, MEDICATIONS NOTE: IF YOU USE SAME SPECULUM FOR BOTH EARS AND CHANCE OF AN INFECTION IT COULD SPREAD SO DO GOOD EAR FIRST OR USE SEPARATE SPECULUM. Speculum--can get disposable ones or clean them with alcohol If developed slowly, probably sensorineural If developed suddenly, more likely to be meds, infection Can put traction on nasopharyngeal portion of Eustachian tube from inside the mouth in an attempt to open it up and get it to drain. People with sensorineural losses tend to talk loudly People with conductive losses tend to talk softly Table 8-4 (IN LIBRARY) Common Causes of Deafness Sound waves => tympanic membrane vibrates => => ossicles => waves in endolymph/perilymph => distorts hair cells of organ of Corti => converts to chemical signals => cortex Mastoid air cells--direct connection to tympanic membrane (why you can hear yourself talk even if ears are blocked) External otitis = swimmer’s ear Cerumen = wax (made in distal 1/3 of canal) associated with hydration level if get dehydrated (ex.: too much Coke & Pepsi) Eustachian tube blockage--can lead to pressure buildup Viral meningitis--middle ear Cholesteatoma--tumors (can rupture) Otosclerosis--scarring of tympanic membrane or ossicles due to previous infection Meniere’s Disease--inner ear considered idiopathic or autoimmune or viral (not really known) 3 Dx by exclusion affects endolymph 6/22/98 triad episodic vertigo fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss tinnitus (usually unilateral, often severe) episodic--multiple episodes in 1940-70 grouped with MS MS--different phases dizziness ringing in ears no fever eventually shows up in CSF or on an MRI Tx--both MS & Meniere’s--PREDNISONE (steroid) Acoustic neuroma--buildup of tissue along CN VIII See text--conduction loss vs sensorineural conduction--minor sound distortion speak softly concentrate more if environmental noise any age sensorineural--more distortion of sound(esp. upper patient tends to speak loudly since can’t hear middle age or elderly problem is not visible frequency) own voice Unilateral loss--may bend their ear toward you early years--turn bad ear your way later years--turn good ear toward you Vertigo--sense of self spinning or room turning while in a resting position, usually associated with a loss of equilibrium Subjective vertigo = sense of self spinning Objective vertigo = sense of room spinning Table 2.2 (text) consider onset, duration, course any vomiting, etc. alcohol intoxication TIA (transient dizziness with decreased strength, hearing, and visual disturbances drug toxicity True Vertigo--problems with CN VIII vestibular canals temporal cortex Causes Meniere’s 4 otitis media Herpes Zoster Herpes simples tumors otosclerosis obstructed Eustachian tube vestibular neuronitis drug toxicity (esp. hard liquors) alcohol (also toxic to eyes) opiates diuretics motion sickness (problem between optic and oto apparatuses) diplopia--abnormal input circulatory--TIA’s neurogenic MS skull fractures encephalitis meningitis tumors of pons leukemias myelomas 6/22/98 Benign positional vertigo rolling over in bed turning to look at someone turning head to back up car ARTICLE--JMPT-1991 Cervicogenic Vertigo-Fitzgibbon Chiro Report-David Chapman Smith Dr. Cyriac tapes on spinal manipulation one of past foremost authorities on allopathic care still seen as an authority did not like chiro Vestibular neuronitis--acute labyrinthitis drugs--streptomycin (ototoxic) Tumors--can affect CN 5,6,7 as well as 8 (variable symptoms) Table 8.6 Tinnitus (IN LIBRARY) sensation of buzzing or ringing in the ears in the absence of environmental input can be pulsatile/clicking or monpulsatile (doesn’t help in differentiation) external ear infection/inflammation occlusion bullous myringitis--fluid bubbles in TM foreign bodies--cerumen 5 middle ear otitis media vascular anomalies neoplasm 6/22/98 otosclerosis Eustachian tube dysfunction inner ear Meniere’s labyrinthitis drug toxicity presbycussis CNS vascular hypertension syphilis degenerative disease cerebral atherosclerosis drugs aspirin antidepressants (even for CTS, etc) anti hypertension caffeine pain meds (ex.: Flexoril) anti-inflammatory (at least 11 of these) otorrhea (discharge from ear) often due to infection of trauma clear & watery--CSF--skull fracture bloody--carcinoma or trauma pus--bacterial ask about any dryness any pain any use of ear drops any sore throat swimming recently Otalgia--ear pain MOST COMMON CAUSE => INFECTION external otitis and otitis media referred pain from teeth, pharynx, C-spine, TMJ inflammation, trauma, or neoplasm anywhere along course of CN V,VII,VIII,IX,X or cervical nerves C2 or C3 CN V-tensor tympani muscle-sensory to external ear CN VII-stapedius muscle CN VIII-semicircular canals and cochlea CN IX-sensory to TM CN X-sensory to inner canal Pruritis—itching Disease of external auditory canal Discharge from middle ear infections 6 Systemic disease Diabetes Hepatitis Lymphoma usually general itching 6/22/98 Exam External ear Symmetry Helix—smooth and round—check for any nodules Check behind ear Otoscopic exam—canal and tympanic membrane (TM) Use otoscope Look at Hairs, wax Color of drum Position of drum Light reflection Look for perforations Auditory exam Ear—auricle—cartilage covered by skin Bony part—covered by skin Sebaceous glands in distal 1/3 Middle ear 3 bones air filled mastoid cells tympanic membrane Eustachian tube—regulates atmospheric pressures Inner ear Semicircular canal Cochlea Vestibule Innervations— CN V, VII, VIII, IX, X External ear Look for discharge, lesions, cysts, tophi, etc. Look for swollen lymph nodes esp. if chronic infections present DO NOT SQUEEZE SEBACEOUS CYSTS Could lead to infection of fascial planes Use cool, moist cloth to decrease inflammation then warm, moist cloth Keloids—scar tissue Tophi Uric acid crystals (gout) Hard, painful May open up and discharge white chalky crystals 7