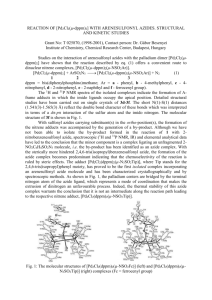
Heavy Metal Azides CAS No.No multiple
advertisement

UCSF Lab Standard Operating Procedure Chemical Process, Name or Hazard Class: Heavy Metal Azides Please fill out the form completely. Insure all users have access to this SOP. Refer to instructions for assistance. Enter text. Department: Date SOP was written: Enter date. This lab specific SOP has been reviewed and approved by: Principal Investigator Name: Enter text. Principal Investigator Signature Lab Manager/Supervisor: Type of SOP: ☐ Process Enter text. ☐Hazardous Chemical ☒ Hazardous Class Purpose Heavy metal azides are used predominantly as percussion sensitive explosives in such items as bullet primers and explode-on-contact ordnance. Some laboratory uses, such as the use of barium azide for the small scale generation of nitrogen gas, also exist. These compounds combine the explosive and toxicity hazards of azides with the toxicity hazards of heavy metals, and therefore must be handled with great care. Physical & Chemical Properties/Definition of Chemical Group CAS#: Barium Azide [18810-58-7], Lead Azide [13424-46-9], Mercury Azide [38232-63-2] Class: Potentially Explosive Chemical Molecular Formula: Barium Azide [160OC] Lead Azide [N/A] Mercury Azide [N/A] Form (physical state): Solid Color: Varies Boiling point: Barium Azide Ba(N3)2 Lead Azide (Pb(N3)2 Mercury Azide Hg2(N3)2 Heavy Metal Azides 1 Date: Click here to enter a date. Modified from SOP templates developed by UCLA EH&S (http://www.sop.ehs.ucla.edu/) Potential Hazards/Toxicity Heavy metal azides are common components of explosive compositions. The risk of explosion by shock, fire, friction or other ignition sources is extremely high. They must be handled gently and away from heat, naked lights, and any other possible ignition sources. Azide ion has a similar toxicity as that of cyanide ion (LD50 = 27 mg/kg in rats). When protonated to become hydrazoic acid, it is volatile and therefore risk of exposure is greatly increased. For heavy metal azides, the toxicity of the metal itself must be taken into account. Mercury and lead azides are acutely and chronically hazardous reagents for this reason. Engineering Controls Handle in a chemical fume hood. A blast shield should be in place around the experimental set up. Ground all lines and equipment to prevent static discharge. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirator Protection If lab personnel would like to use respirator on a voluntary basis, they must be trained and fit-tested by EH&S. This is a regulatory requirement. (http://www.ehs.ucsf.edu/respiratory-protection-program) Hand Protection Chemical resistant gloves. For mercury azide, skin contact is extremely dangerous. Elbow length gloves made of PVC or other resistant materials are essential. NOTE: Consult with your preferred glove manufacturer to ensure that the gloves you plan on using are compatible with heavy metal azides. Refer to glove selection chart from the links below: http://www.ansellpro.com/download/Ansell_8thEditionChemicalResistanceGuide.pdf OR http://www.allsafetyproducts.biz/page/74172 OR http://www.showabestglove.com/site/default.aspx OR http://www.mapaglove.com/ Eye Protection ANSI Z87 safety glasses with side shields. ADDITIONALLY, a full face shield may be appropriate depending on scale of use, for protection from both chemical splashes and flying debris if an explosion occurs Skin and Body Protection Please wear full-length pants or its equivalence, closed-toe shoes, and a flame-resistant lab coat. Nonsparking footwear is essential. Avoid wearing clothing made of synthetic material to reduce the risk of human static discharge. Hygiene Measures Handle gently. Keep away from ignition sources and static discharge. Be very cautious about acidifying any mixtures containing azide ion, as hydrazoic acid will form and volatilize quickly. Avoid all skin contact. Heavy Metal Azides 2 Date: Click here to enter a date. Modified from SOP templates developed by UCLA EH&S (http://www.sop.ehs.ucla.edu/) First Aid Procedures If inhaled Remove to fresh air. Lay person down and keep warm. Seek medical attention immediately. In case of skin contact Remove all contaminated clothing. Flush contaminated area with running water, and soap if available. FOR MERCURY AZIDE: Immediately flush body and clothing with running water, preferably in a safety shower. THEN, begin to remove contaminated clothing. Continue flushing with water until advised to stop by emergency response personnel or a poison control center. Transport to a doctor’s office or hospital without delay. In case of eye contact Flush eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention without delay. If swallowed Seek medical attention without delay. Urgent hospital treatment is likely needed. NOTE: Azide ion protonates in the stomach. Hydrazoic acid can therefore be released from vomitus. Keep patient in a well-ventilated area and isolate and dispose of any vomitus. FOR MERCURY AZIDE: Give a slurry of 3 tablespoons charcoal in 8 oz water to drink immediately, then seek medical attention immediately. Special Handling and Storage Requirements Handle gently. Avoid all personal contact, including inhalation. Avoid heat, friction and ignition sources. Store in a cool, well-ventilated area appropriate for the storage of explosives. Rotate stock to prevent aging. Spill and Accident Procedure Chemical Spill Dial 9-911 from campus phone or 415-476-1414 from cell phone or 415-2068522 (SFGH only) Spill – Assess the extent of danger. Assist contaminated or injured persons. Evacuate the spill area. Avoid breathing vapors. If possible, confine the spill to a small area using a spill kit or absorbent material. Keep others from entering contaminated area (e.g., use caution tape, barriers, etc.). Small (<1 L) – If you have training, you may assist in the clean-up effort. Use appropriate personal protective equipment and clean-up material for chemical spilled. Double bag spill waste in clear plastic bags, label and take to the next chemical waste pick-up. Large (>1 L) – Dial 9-911 from campus phone or 415-476-1414 from cell phone or 415-2068522 (SFGH only) for assistance. Chemical Spill on Body or Clothes – Remove clothing and rinse body thoroughly in emergency shower for at least 15 minutes. If discomfort persists, proceed to the Emergency Department. If no further discomfort is experienced, have the SDS ready and contact Poison Control Hotline at 1-800Heavy Metal Azides 3 Date: Click here to enter a date. Modified from SOP templates developed by UCLA EH&S (http://www.sop.ehs.ucla.edu/) 222-1222 for further exposure information. Notify your direct supervisor and EH&S at 415-4761300 during work hours, or 9-911 during non-working hours and weekends. Chemical Splash Into Eyes – Immediately rinse eyeball and inner surface of eyelid with water for 15 minutes by forcibly holding the eye open. If discomfort persists, proceed to the Emergency Department. If no further discomfort is experienced, have the SDS ready and contact Poison Control Hotline at 1-800-222-1222 for further exposure information. Notify your direct supervisor and EH&S at 415-476-1300 during work hours, or 9-911 during non-working hours and weekends. Medical Emergency Dial 9-911 (campus phone) or 476-6911 (cell phone) Note: All serious injuries must be reported to EH&S at 415-476-1300 within 8 hours. Non-Life Threatening Emergency– Go to Occupational Health Programs (OHP) Clinic, 415-8857580, 2330 Post Street, Suite 460 Hours of Operation for Appointments: Monday - Friday 7:30 a.m. - 4:00 p.m. (except Holidays). Note: All serious injuries must be reported to EH&S at 415-476-1300 within 8 hours. Needle stick/puncture exposure (as applicable to chemical handling procedure) – Wash the affected area with antiseptic soap and warm water for 15 minutes. For mucous membrane exposure, flush the affected area for 15 minutes using an eyewash station. Page the needle stick nurse by dialing 415-353-7842 (STIC). Decontamination/Waste Disposal Procedure Clean contaminated surfaces with soap and water and paper towels. Dispose of the paper towels as hazardous waste. Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Location Online SDS can be accessed at http://www.ehs.ucsf.edu/safety-data-sheet-sds-1 Protocol/Procedure Quantities covered by this SOP: ______ (g , ml) to _______ (g, ml) Temperature range covered by this SOP: __ °C – __ °C General Overview and Purpose: Enter the experimental purpose Procedure: Enter experimental procedure. You can copy procedure from your lab notebook or from literature. Heavy Metal Azides 4 Date: Click here to enter a date. Modified from SOP templates developed by UCLA EH&S (http://www.sop.ehs.ucla.edu/) NOTE Any deviation from this SOP requires approval from the Principal Investigator. Heavy Metal Azides 5 Date: Click here to enter a date. Modified from SOP templates developed by UCLA EH&S (http://www.sop.ehs.ucla.edu/)