Monday Popquiz:
advertisement

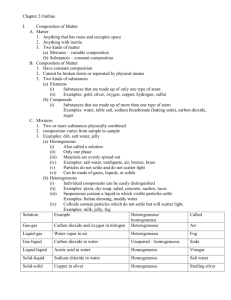
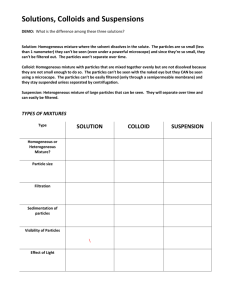
Name: ____________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ___________________ Self assessment Ch 2 & 3 Matter Place: CP if it is a chemical property CC if it is a chemical change PP if it is a physical property PC if it is a physical change 1. _____ you can get the original material back 2. _____ color 3. _____ flammability 4. _____ reacts with acid 5. _____ you can observe it, but it changes the material into something else 6. _____ cutting bread 7. _____ melting point 8. _____ density 9. _____ phase changes (change in state of matter) 10. _____ copper turns green 11. _____ salt dissolves in water 12. _____ a liquid bubbles when a powder is put in 13. – 14. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures and give an example of each. Solve these problems. Show your work. Be sure to use correct sig figs and units. D = m/V. 15. _____________________________ You have a 50. mL bottle with 163 g of a green liquid. What is its density? 16. _____________________________ A piece of metal has a density of 11.3 g/cm3 and a volume of 6.7 cm3. What is its mass? 18. 21. 17. 20. 19. Identify the phase or state of matter this substance is in. 17. __________________________ or __________________________ 18. __________________________________ 19. __________________________________ 20. __________________________ or __________________________ 21. __________________________________ 22. #17’s temperature is called the ____________________ __________________. 23. #20’s temperature is called the ____________________ __________________. 24 – 27. Draw the “Matter tree” for the following terms: Pure substance mixture Heterogeneous compound Suspension solution homogeneous element Self assessment Ch 2 & 3 Matter Place: CP if it is a chemical property CC if it is a chemical change PP if it is a physical property PC if it is a physical change PC__ you can get the original material back 1. _ PP__ color 2. _ CP__ flammability 3. _ CP_ reacts with acid 4. _ CC__ you can observe it, but it changes the material into something else 5. _ PC__ cutting bread 6. _ PP__ melting point 7. _ PP_ density 8. __ PC_ phase changes (change in state of matter) 9. _ CC__ copper turns green 10. _ PC_ salt dissolves in water 11. __ CC_ a liquid bubbles when a powder is put in 12. __ 13. – 14. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures and give an example of each. Homogenous means the particles are evenly spread out, you can’t see any different kinds of particles in it. Iced tea, Kool Aid, salt water and coffee are all examples Heterogenous means the particles are unevenly spread out, you can see any different kinds of particles in it. Salad, Italian salad dressing, and salsa are all examples. Solve these problems. Show your work. 3.3 g/mL____You have a 50. mL bottle with 163 g of a green 15. ___ liquid. What is its density? D = m/v 163 / 50 3.26 76 g_______A piece of metal has a density of 11.3 g/cm3 and a 16. _________ volume of 6.7 cm3. What is its mass? D = m/v 11.3 = m/6.7 (mult both sides by 6.7) 18. 21. 17. 19. 75.71 Identify the phase or state of matter this substance is in. evaporation_____ or __condensation___ 17. __ gas__________________ 18. ___ 20. solid_____________________ 19. ____ 20. ___melting________ or _____ solidification/freezing_______ liquid__________________ 21. _____ 22. #17’s temperature is called the ___ boiling_______ ___point_____. 23. #20’s temperature is called the ___ melting_____ ____point______. 24 – 27. Draw the “Matter tree” for the following terms: Pure substance mixture Heterogeneous compound Suspension solution homogeneous element matter pure substance mixture heterogeneous suspension compound element homogeneous solution