Matter – any substance that has mass and volume
advertisement

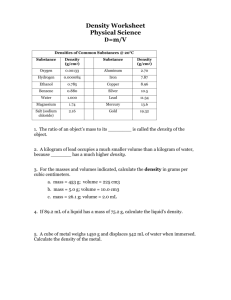
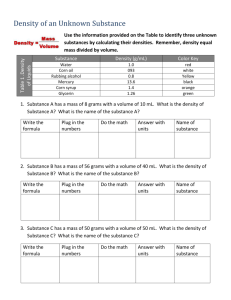
Matter – any substance that has mass and volume. Its amount can be measured and it takes up space. All matter has the property of inertia. Matter can be described by its measurements: Mass – measured on a balance in grams Volume – measured in 3 different ways: Rectangular solids – measure and multiply Length x width x height (cm3) Irregularly shaped objects – water displacement The volume is the difference between the original height in a graduated cylinder and the new height after submerging the object. Remember to read the bottom of the meniscus (curved surface). (mL) Liquids – pour into a graduated cylinder and read the meniscus. Density – a ratio of the amount of mass “packed” in a certain amount of space. It measures how tightly packed the particles are. D = mass (in grams) / volume (in mL or cm3) Density is defined as - the amount of mass in a given volume or space Density is: - expressed in g/mL or g/cu. cm. (g/cm3) - a physical property of matter - is specific for all substances (all substances have their own specific density) - can be used to identify substances - temperature and pressure can change specific density but is still specific to the substance To calculate Density Mass (g) _________________ Volume (m/L) or (cm3) Think: How many grams of the substance are packed into 1 mL of space? Or how many grams are packed into 1 cm3 of space? Density is used to compare substances. Water has a density of 1g/mL. Substances that have a lower density will float in water. Substances that have a greater density will sink in water. Substances with a density very close will float at, near or just under the surface of water. Densities can be used to make predictions about how substances will behave when placed together.