WORD - ABC
advertisement
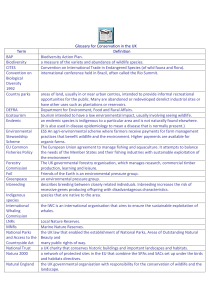
Episode 34 26th November 2013 Activity Stock Routes Key Learning Students will learn about the history, cultural heritage and environmental value of Australia’s stock routes. Students will develop a deeper understanding about wildlife corridors and their role in flora and fauna diversity. The Australian Curriculum Science / Science Understanding / Biological sciences Science / Science Understanding / Biological sciences Living things, including plants and animals, depend on each other and the environment to survive. Year 4. (ACSSU073) The growth and survival of living things are affected by the physical conditions of their environment. Year 6. (ACSSU094) Living things have structural features and adaptations that help them to survive in their environment (ACSSU043) There are differences within and between groups of organisms; classification helps organise this diversity. Year 7. (ACSSU111) Discussion Questions 1. In your own words describe what a stock route is. 2. It is legal to herd livestock across the Sydney Harbour Bridge. True or false? 3. What is a drover? 4. How were stock routes designed to help drovers and their livestock survive the journey? 5. Illustrate the journey of a drover and their livestock travelling via stock routes. 6. Nowadays how can you tell that you are driving on a stock route? 7. How long does Bill Little expect his journey will take from Qld to NSW via stock routes? a. 6 days b. 6 months c. 6 years 8. List the animals that Bill is taking on his journey. 9. Why has Bill decided to transport his cattle via stock routes instead of using a truck? 10. What are some of the benefits of transporting livestock via stock routes? ©ABC 2013 Activities Research Show students the Queensland stock route network map to give them an idea of the number of tracks in the state, and then hold a class discussion. http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0003/99624/ stock-routes-map.pdf What is a stock route? Who uses the stock routes? How many kilometres of Queensland’s roads are stock routes? Research the history, cultural heritage and environmental value of stock routes in Queensland. Department of Environment and Resource Management Wildlife corridors – science and biodiversity Students will develop a deeper understanding about wildlife corridors and their role in flora and fauna biodiversity. What are wildlife corridors? Describe and illustrate. What is the difference between a swamp, grasslands, forest and heath? Wildlife corridors maintain biodiversity. What does this mean? Why are wildlife corridors important for flora and fauna? What are the benefits for wildlife? What are some of the threats to wildlife corridors? What can people do to help preserve wildlife corridors? The diagram above shows some important landscape elements contributing to wildlife corridors. Department of Environment: Wildlife corridors plans http://www.environment.gov.au/node/16547 Find out what plants are native to your community. Consider planting some of these species in your school garden to create your own flora and fauna corridor. ©ABC 2013 Get involved and have your voice heard Explain that students will be constructing a persuasive text about the importance of stock routes for biodiversity. This activity introduces the structural framework and language features of persuasive texts to your students and allows them to gain an understanding of the purposes of each sentence within a paragraph. Refer students to the read, write, think persuasion map to plan their exposition text. Provide students with the following structure to follow when completing this activity. Have your voice heard! Contact your local Member of Parliament and ask them to support stock routes and wildlife corridors. Write a letter to the editor of your local newspaper and tell them about your concerns. Tips for persuasive text writing Who is your audience? For example are you directing your argument at kids, teachers or politicians? Provide facts and evidence to support your argument. Be creative with your word choice to enhance your argument. Convey emotion using thinking and feeling words. Write in the present tense Check your spelling and punctuation. Structure of a persuasive text Introduction What is the point you are trying to argue? Construct an introductory paragraph which states the issue or topic. Introduce the arguments that will be developed in the body of the text. Body Construct arguments that support your point of view. Each paragraph starts with a topic sentence which introduces each point. The rest of the paragraph gives more reasons. Arguments can be ordered from strongest to weakest. Conclusion Restate your position on the argument Construct a concluding paragraph that provides a summary of your arguments and a call to action. Use the read, write, think persuasion map to plan your exposition text. Do you think stock routes should be retained, managed and restored? Have your say on the BtN Stock Routes story page. ©ABC 2013 Related Research Links Preservation Society of Wildlife QLD – Save our stock routes http://www.wildlife.org.au/conservation/issues/2008/stockroutes.html Department of Natural Resources and Mines – About the Queensland stock route network http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/land/accessing-using-land/stock-routes/about Department of Environment – National Wildlife Corridors Plan http://www.environment.gov.au/node/16547 Department of Environment and Conservation (NSW) – Wildlife Corridors http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/nature/landholderNotes15WildlifeCorridors.pdf Greenway: Cooks River to Iron Cove – Wildlife Corridor http://www.greenway.org.au/biodiversity/g-wildlife-corridor Urban Ecology Australia – Wildlife Corridors http://www.urbanecology.org.au/topics/wildlifecorridors.html Behind the News – Stock Routes http://www.abc.net.au/btn/story/s2415295.htm ©ABC 2013