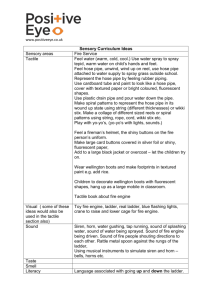
ABC extinguisher
advertisement

ABC extinguisher A fire extinguisher that can be used on fires involving ordinary combustibles, flammable liquids, and energized electrical equipment; may also be known as a multipurpose extinguisher. A/B/C/D Sides At a building fire, the sides of buildings are identified by ABCD sides, with side A being the front of the building, and sides BCD being named around the building in a clockwise fashion. This helps maintain clear communication on the fireground. Academy A training school; a place to train, learn, study, and achieve Accelerator A device attached to a dry-pipe sprinkler system for rapid removal of air in the system; a device to control the speed of a vehicle by regulating the fuel supply. Accordian load A system of loading hose in the hose bed of a fire truck. Accordion Fold A fold for salvage covers. Actuate To set into operation, especially an installed fire protection system. Adapter A device to make a connection when the threads do not match or when they are different sizes. Advanced Life Support Advanced life support (ALS) is medical care provided by paramedics trained to assess a patient's condition, administer drugs, defibrillate and provide advanced airway management prior to transportation to the hospital. Advancing a line A line in the fire service is a line of hose. Advancing a line, therefore, is moving a line of hose forward. Aerial ladders A mechanically-operated ladder on a turn table attached to a ladder truck chassis and manufactured in various lengths, generally from 65 feet to 100 feet. Aerial Truck Also known as a ladder truck or just plain truck. A hydraulically powered ladder, mounted on a vehicle that also carries several different length extension ladders, extrication gear, ventilation equipment, and lighting. May or may not have a bucket or platform on the end. Aerial platform apparatus See elevating platform apparatus AFFF Initials for aqueous film forming foam. A-frame ladders The type of ladders hinged in the middle and used as A-frame stepladders or as baby extension ladders. Air bag An inflatable bag, often made of synthetic rubber, used to lift or stabilize heavy objects. Also a large inflatable bag into which persons can leap to escape danger. Air bottle A thick walled steel, fiberglass wrapped aluminum cylinder or composite metal cylinder equipped with a control valve, pressure gauge, and nipple outlet for a high pressure hose connection. In the fire service these tanks contain compressed air. Each bottle carries approximately 66 cubic feet of compressed air at a pressure of 4500 pounds per square inch. Some departments use SCBA that the air is compressed to only 2200 psi. See SCBA Air mask or air pack Worn by firefighters, a type of self-contained breathing device that provides an air supply from tanks through a regulator. See breathing equipment or SCBA Air pressure sprinkler system A sprinkler system in which air pressure is used to force water from a storage tank into the system. Air supply unit A machine to refill exhausted compressed air Air Tank See Air Bottle. Aircraft fire protection A specialized branch of the fire service dealing with airports or aircraft. Airline mask A mask worn by firefighters, connected to an air supply outside a contaminated area. This line could be 100 feet or more. Used in confined areas of structural collapse. Airway A metal or plastic framework designed to fit the curvature of the mouth and throat to prevent air passageways from closing. Alarm Any signal indicating the need for emergency fire service response; also, the device that transmits the alarm. Alarm Circuit An electrical circuit connecting two points in an alarm system; for example, from the signal device to the fire station, from the central alarm center to all fire stations, or from the sending device to the audible alarm devices. All hands A working fire engaging all apparatus of first-alarm assignment; may be followed by multiple alarms. All service masks A canister-type filter mask resembling a gas mask canister. (No longer approved or recognized for firefighting.) Aluminum alloy ladder A ladder made of aluminum and other materials like magnesium to make the ladder lightweight but strong. Ambulance A special vehicle equipped to transport sick or injured people to medical facilities. Angle of departure Refers to the rear overhang of fire apparatus, the angle between the road surface and a line to the rear point of contact of the rear of the back tire. Also is used in a similar manner to the front of the apparatus. This is necessary to determine the clearance of the vehicle as it traverses over terrain that could hit the under carriage, frame or components of the vehicle. Apparatus A truck or group of trucks of any variety used in the fire service Appliance Any variety of tools or devices carried on an apparatus that connect hoses or stream devices together. Applicator A special pipe or nozzle attachment for applying an extinguishing agent. Area of Origin The specific area where a fire begins. Arson Arson is the willful and malicious burning of the property of another. This meaning has been broadened by statute in many jurisdictions to include one’s own property. Artificial Resuscitation Breathing maintained by an artificial means. (Also called artificial respiration and artificial ventilation.) Asphyxiation A condition that causes death because of a deficient amount of oxygen and an excessive amount of carbon monoxide and/or other gases in the blood. Aspirator A suction device for removing undesirable material from the throat of a victim. Atmospheric pressure Pressure exerted by the atmosphere; about 14.7 pounds per square inch (100 kPa) at sea level. This is important to apparatus operators drafting water from static sources. See Draft and drafting. Attack Any action to control fire. The actual physical firefighting operation using equipment and manpower implementing tactical plans on the fireground in an aggressive manner. Attic Ladder A ladder usually 8-10 feet long that usually can be folded so that the two beams touch each other. Also called a scuttle hull or pencil ladder in some parts of the country. Auditorium raise A system of extending a ladder perpendicular and holding it in place from four opposite points of the compass by four guy ropes attached to the top of the ladder. (Also called church raise or steeple raise.) Auto-ignition temperature The same as ignition temperature except that no external ignition source is required for ignition since the material itself has been heated to ignition temperature; the spontaneous ignition of the gases or vapor given off by a heated material. See ignition temperature. Automatic alarm An alarm actuated by heat, smoke, flame-sensing devices, or the water flow in a sprinkler system conveyed to local alarm bells and/or the fire station. Also applies to alarm boxes that automatically transmit a coded signal to the fire station to give the location of the alarm box. Automatic sprinkler sets An automatic sprinkler kit contains the tools and equipment required to close and service an open sprinkler head. Auxiliary Additional fire fighting equipment or staffing that are not part of the regular complement assigned to the fire service. Ladies group organized to assist the fire department. Axe, fire A fire axe has a pick or fiat head and a blade. B Back pressure A pressure loss or gain created by changes in elevation between the nozzle and pump. Backdraft An explosion or rapid burning of heated gases in a confined structure. A backdraft may occur because of inadequate or improper ventilation procedures. The force of the backdraft depends on variables like the size of the confined area, the extent to which smoldering has occurred (thus providing fuel), the degree of heating of the atmosphere, and the rate at which air or oxygen is introduced. While the risk of such an occurrence is low, a backdraft is almost always fatal to anyone caught in it. Baffles Baffles are dividers put in fire department water tanks to prevent the load from shifting rapidly while the apparatus is in motion; also the divider used to separate beds of hose into two or more compartments. Bale hooks A hook shaped tool for moving bales or other items, and for overhauling stuffed furniture. Also known as a hay hook. Balloon frame A building with studs running two or more stories without fire stops. Balloon throw A salvage cover throw that traps air beneath the cover to assist in spreading by ballooning the cover over the material to be covered. Bangor ladder A large extension ladder that requires tormentor poles to steady the ladder as it is raised and lowered. (Also called a pole ladder.) Basic Life Support Basic life support (BLS) is a level of care provided to patients requiring transportation to the hospital. BLS does not include extensive medical supervision or treatment. Battalion A fire department subdivision consisting of all fire service equipment and personnel in a designated geographic area. The battalion chief is the senior officer within that group. Beam The main structural member of a ladder supporting the rungs or rung blocks. Beam raise Raising a ladder to a vertical position by either beam instead of in a flat horizontal plane. Bed ladder The lowest section of a multisection ladder. Big stick A mechanically-raised main ladder on an aerial ladder truck. Originally aerial ladders were made of wood, and hence the term “big stick.” Blackout As the flame is extinguished, the fire is said to be blacked out. To “knock down” a fire; to reduce a fire by extinguishing all visible flame. (Also called blacken or darkening down.) See knock down. BLEVE Acronym for boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion. Blitz attack A rapid and massive attack on a fire to knock down a fire before it has a chance to grow into a larger fire. Block and tackle The rope and pulley assembly used to obtain a mechanical advantage for hoisting or pulling. Boilover The overflow of crude oil from its container when the heat wave reaches the water level in the tank. The water flashes to steam causing a violent expulsion of the material as a froth. Bolt cutters A cutting tool designed to make a precise, controlled cut. Used for cutting wire, fencing, bolts, small locks and small steel bars. Booster Line Booster line is a hose that is usually one inch in diameter and rubber jacketed. They are used on small fires using the water carried in an apparatus' booster tank and are usually stored on reels. Also referred to as a red line. Many fire departments having to conserve available space for other equipment have eliminated the booster line in favor of fabric line (called forestry line) or relied upon structural attack sized lines. Booster pump A PTO powered pump with less than 500 gallons per minute (1900 L/min) rating used to supply water through small hose line and for pump and roll operations. Booster reel A mounted reel on which booster hose is carried. Booster Tank The tank on a pumper or quint that supplies booster lines and hand lines at a fire until a connection with a water source can be made. The booster tank on most pumpers is between 500-1,000 gallons. The tank on a quint is usually smaller, carrying only a couple of hundred gallons. Bourdon Tube A thin, curved, hollow, pressure-sensitive tube found in pressure gauges to operate the needle of the gauge. Box A short term for public or private fire alarm box. Box Alarm A box alarm is the response to a report of fire or smoke inside or coming from a structure. Usually, multiple companies are dispatched at the same time on a box alarm. Some departments have Haz-Mat and Rescue Boxes for hazardous materials and rescue calls. The term box alarm originates from the original pull boxes located on the street in many communities. A typical structure box alarm would include two or more engine companies, one or more ladder companies, a rescue company and a chief officer. Boyle's Law Boyle’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at a given temperature. The law relates to the compressibility of gas and the effect of temperature and volume on the pressure in a pressurized container. Brass Brass work or brass appliances carried on fire apparatus. Now may be chrome plated or made of lightweight alloys. Breach An opening made in a wall for rescue, hose line operation, or other reasons. Break a line To disconnect hose lines for any purpose, especially to break and roll up hose after a fire operation; to disconnect a hose coupling. Breathing equipment Normally used to describe self-contained breathing equipment (SCBA) consisting of an air or oxygen tank, connecting hoses, regulator, and face piece. Brick Joisted Brick or masonry wall structure with wooden floors and roof. Commonly known as ordinary construction. Bridge To place a ladder to span a gap usually between two structures; a hose bridge to prevent damage to hose from traffic passing over it. BTU British thermal unit. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound (0.45 kg) of water one degree Fahrenheit (-17.240C) at atmospheric pressure. Buff A person, other than a firefighter, who is interested in fires, fire departments, and firefighters. Bugles Insignia depicting early speaking trumpets. Now used to designate the rank of fire department personnel. Building code A list of rules, usually adopted by city ordinance, to regulate the safe construction of buildings. There are several building codes that are widely adopted in the United States including the Southern Standard Building Code, the Uniform Building Code, the Basic Building Code, the International Building code and the National Building Code. Building survey The portion of the pre-incident planning process during which the company travels to a building and gathers the necessary information to develop a pre-incident plan for the building. Bunk A firefighter’s bed. Bunk room The dormitory area where firefighters sleep. Bunker gear An entire set of firefighter’s protective clothing that includes helmet, coat, pants, boots, and gloves; protects from heat, cold, and injury. Also known as turnout gear. Burning point See fire point and ignition temperature. Burning, phases of A fire may progress through three distinct phases or stages of burning: incipient, free burning, and smoldering. Burnout A building that has been denuded of almost all combustible material. Also refers to a burned wild land area. Burns, Degree of First degree: reddened skin; second degree: blisters; third degree: deep skin destruction. Major types of burns: heat, chemical, electrical, and radiation. Butt One coupling of a fire hose; a hydrant outlet; the heel (lower end) of a ladder; the act of steadying a ladder that is being climbed. Butterfly valves A type of control valve that uses a flat baffle operated by a quarter turn handle. C Cable hanger A device used to test the structural strength of aerial ladders. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) A combination of artificial resuscitation and closed-chest cardiac (heart) compression. Catch a hydrant The firefighter gets off the fire apparatus at the hydrant, connects the fire hose to the hydrant and turns on the water. Cavitation If pressure at any point inside a pump drops below the vapor pressure corresponding to the temperature of the liquid, the liquid will vaporize and form cavities of vapor. The vapor bubbles are carried along with the stream until it reaches a region of higher pressure. Then they collapse or implode with a tremendous shock on the adjacent impeller walls. Cellar pipe Special nozzle for attacking fires in basements, cellars, and other spaces below the attack level. Central Fire station Headquarters station that contains administrative offices, special equipment, fire apparatus, and personnel. Centrifugal pump A fire pump using centrifugal force (force to the outside) to develop and impart velocity to the water as it passes through the pump. There are single and multistage centrifugal pumps. Chafing block Blocks placed under hose lines to protect the hose covering from damage due to rubbing against the ground or concrete. Chain hose tools Chain hose tools used to carry, secure, and otherwise aid in handling hose. Chain of Command The order of rank and authority in the fire service. Chain reaction A series of self sustaining changes each of which causes or influences a similar reaction. See tetrahedron. Charge The act of pressurizing a fire hose or fire extinguisher. Charged building A building heavily laden with smoke and gases, and possibly in danger of having a backdraft. Charged line Hose loaded with water under pressure and prepared for use. Charles's Law A gas will expand or contract in direct proportion to an increase or decrease in temperature. If a gas is confined so it cannot expand, its pressure will increase or decrease in direct proportion to temperature. Checklist Detailed lists generally prepared for the maintenance of equipment or apparatus, or for installed fire protection equipment to ensure that the inspector does not overlook an item that needs to be checked regularly. They may also be used during pre-fire planning and fire prevention inspections. Check valve An automatic valve that permits flow in only one direction. Chemical Chain Reaction Vapor or gases are distilled from flammable materials during initial burning. Atoms and molecules are released from these vapors and combine with other radicals to form new compounds. These compounds are again disturbed by the heat releasing more atoms and radicals that again form new compounds and so on. See tetrahedron. Chemical compound A new homogeneous substance consisting of two or more elements and having properties different from the constituent elements. Chemical foam A foam formed when an alkaline solution and an acid solution unite to form a gas (carbon dioxide) in the presence of a foaming agent that traps the gas in fire-resistive bubbles. CHEMTREC Chemical Transportation Emergency Center, a 24-hour emergency hotline for information about hazardous materials. Chief of Department The highest ranking member of the fire department; in some instances, designated as the director or administrator. Chief Officer Any of the higher officer grades, from district or battalion chief to the chief of the fire department. Recognized ranks of Chief Officers, from top to bottom are: Fire Chief, Deputy Chief, Assistant Chief, Battalion Chief Chocks Wooden, plastic, or metal blocks constructed to fit the curvature of a tire; placed against the tire to prevent apparatus rolling. Chuck A portable fire hydrant carried on the apparatus with one or more gated connections for fire hose. The device screws into a special flush hydrant connection on the water main or a special main. Also an air line connection. Church raise See auditorium raise. Chutes A channel constructed of salvage covers for water runoff. Also a means of escape from large aircraft. Cistern A water storage container, usually below grade level, for emergency use including fire protection. Class A fire Refers to a fire involving ordinary combustibles such as wood, paper, cloth, and so on. Class B fire Refers to fires of flammable and combustible liquids, and gases like gasoline, kerosene, and propane. Class C fire Refers to a fire involving energized electrical equipment. Class D fire Refers to fires of combustible metals like magnesium, sodium, and titanium. Claw tool A forcible entry tool having a hook and a fulcrum at one end and a prying blade at the other. Closed circuit breathing apparatus Breathing apparatus in which the wearer’s exhalations are recycled. Carbon dioxide and moisture are removed from the exhalation and, after some oxygen is added, the wearer rebreathes the exhalation. Hence also known as rebreather apparatus. CO2 Carbon dioxide. A heavier than air gas used to extinguish Class B fires by smothering or by displacing the oxygen. A fire gas produced by the complete combustion of a carbonaceous material. Cockloft A concealed space between the top floor and the roof of a structure. Combination Apparatus A piece of fire apparatus designed to perform more than one function, usually called triple combinations, quads, or quints. Combination nozzle A nozzle designed to provide a straight stream and a fog stream. An all purpose nozzle. Combustible liquids Liquids with a flash point at or above 1000F (37.80C) and less than 2000F (93.40C). Combustion A chemical reaction caused by rapid oxidation that produces light and heat. Slow oxidation gives off heat but no light. Command Post The location of the officer in charge and support staff that make tactical decisions for the direction of the incident. Company A basic fire fighting organizational unit consisting of firefighters and apparatus; headed by a sergeant, lieutenant, or captain. Company log A record of the activities of a fire company, usually kept by a company officer. Complement All firefighters assigned to a working unit, or the number of units assigned to a given alarm. Also the equipment assigned to a piece of apparatus. Compound gauge A pressure gauge on fire department pumpers that records the pressure above and below atmospheric pressure. The pressure below atmospheric pressure is usually measured in inches (mm) of mercury and is called a vacuum. The pressure above atmospheric is measured in pounds per square inch or kilopascals. Concealed space An area between walls or partitions, ceilings and roofs, floors and basement ceilings through which fire may spread undetected. Also soffits and other enclosed vertical or horizontal shafts through which fire may spread. Conduction The transfer of heat from one body to another by direct contact (electric stove electrode to the utensil) within the same body (metal bar heated at one end), or through another heat-conducting medium (double boiler). Also means transmission of electrical current. Confinement Fire fighting operations required to prevent fire from extending to uninvolved areas or structures. Conflagration A large, uncontrollable fire covering a considerable area and crossing natural fire barriers such as streets; usually involves buildings in more than one block and causes a large fire loss. Forest fires can also be considered conflagrations. Control The overall program of fire confinement and suppression. A fire is under control when the fire advance has been halted. Control Center A communications or dispatch center used by the fire service for emergency communications. There are also mobile command posts that can be taken directly to the fire scene and function as the incident operational control center. Convection The transfer of heat by circulation currents in liquids and gases. See law of heat flow. Convection column The rising column of heated air or gases above a continuing heat or fire source. Also known as thermal column. Cooling The reduction of heat by the quenching action or heat absorption of the extinguishing agent. Cornice A concealed space near the eave of the building used for decoration. Coupling The metal device used to connect two hose lines together or a hose line to an appliance or pump. Cover The practice of surrounding fire departments to “fill” units into depleted areas to provide emergency service; to cover exposures by placing primary fire streams in advantageous positions to protect buildings or rooms exposed to heat and fire; to protect with salvage cover. Crawl space The area between ground and floor, ceiling and floor, or ceiling and roof, the dimensions of which are such that a person cannot stand up; often used for duct work, water pipes, and similar structural adjuncts. Crowbar A prying tool used in forcible entry to start or widen an opening, or pry a window or door. D Dead end main A water main supplied from only one direction, usually resulting in poor flow. Deck Gun A large and fixed water nozzle attached to an engine. Deck guns deliver larger amounts of water than hand-held hose. (See also Master Stream). Deck pipe One of several master stream appliances mounted on a fire department pumper or a fireboat and connected directly to the pump. Deck pipes are sometimes referred to as deck guns or turret pipe. Defensive mode The committing of the fire department’s resources to protecting exposures and limiting risk to firefighters when the fire has progressed to the point that an offensive attack will accomplish nothing. The goal is to simply confine the fire to the building/area of origin. No aggressive interior firefighting operations take place in the defensive mode. All fire streams are operated onto the fire from the outside. This strategy is employed when a fire has advanced to the point where attack operations are too dangerous, and/or the fire is beyond the capabilities of on scene resources. Deflagration A chemical reaction producing vigorous heat and sparks or flame, moving through the material (as black or smokeless powder) at less than the speed of sound. A major difference among explosives is the speed of the reaction. Can also refer to intense burning. A characteristic of Class B explosives. Deluge system A fire protection sprinkler system in which the sprinkler heads are always open. The system is controlled by a valve that operates automatically by a thermostatically actuated device. Demand A self-contained breathing apparatus that supplies air to the wearer on demand. Density A term used to denote the weight per unit volume of a substance. The density of any substance is obtained by dividing the weight by the volume. Differential Dry Pipe Valve A valve in dry-pipe sprinkler systems in which air pressure is used to hold the valve closed and thus hold the water back. Dispatch To direct fire companies to respond to an alarm. The office where this action takes place. Distributor Nozzle A nozzle used to create a broken stream usually used on basement fires. Dosimeter A small, nuclear-radiation detection device that registers the total amount of radiation to which it has been exposed. Draft The process of obtaining water from a static source into a pump that is above the source’s level. Atmospheric pressure on the water surface forces the water into the pump where a partial vacuum has been created. Drafting Drafting is the pulling of water from a source other than accepting pressurized water from a hydrant or another fire apparatus. Cisterns, lakes, ponds and swimming pools are often used in drafting operations. Many departments in rural areas without fire hydrants use drafting. Drafting pit An underground reservoir of water usually located at a training center to draft from for pumper testing. Drag A procedure of dragging hooks through water to find drowning victims. A rescue procedure for removing victims from a fire area. Drill A training session to practice fire fighting operations. Drill tower A training structure normally more than three stories used by training personnel to develop realistic fire service situations. Dry Chemical An agent used for Class A, B, and C fires that extinguishes fire by interrupting the chemical chain reaction in the combustion zone. Dry pipe sprinkler system A fire protection sprinkler system that has air instead of water under pressure in its piping. Dry systems are often installed in areas subject to freezing. Dry Powder The extinguishing agent suitable for use on combustible metal fires. Dust explosion The rapid burning with explosive force of any combustible dust. Dust explosions generally are two explosions. A small explosion or shock wave creates additional dust in an atmosphere causing the second and larger explosion. E Eductor A device that by the rapid jetting of a liquid or gas causes additional liquid or gas to be moved or picked up. Common use is as a foam eductor, water eductor, or smoke ejector. Egress A place or means of exiting a structure. Elevated Storage system A system of storing impounded water supplies above the grade level at which the water will be used. Elevating Boom The elevating mechanism of two or more booms on articu1ating-aerial tower apparatus. Elevating platform apparatus A hydraulically-raised platform mounted on fire apparatus and designed for rescue and fire fighting. Endothermic reaction A chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed. Engine A fire department pumper.The engine is also referred to as a pumper because of its ability to pump water. In most cases, an engine carries small ground ladders, supply line to connect it with a hydrant, hand lines to fight the fire with and a tank holding between 500 and 1,000 gallons of water. Engine Company An engine company is a combination of a fire engine and the manpower used to staff it. A standard engine company will include an officer, driver/engineer and two firefighters on a pumper truck. Engineer A driver and operator of fire apparatus; a fire protection or fire prevention person qualified by credentials. The engineer is also responsible for all of the equipment that is on the engine and making sure that it is clean and in good working condition. They also run the pumps, etc. when they are at a fire. Exit A means for going out of a structure through normal openings. A fire exit is especially designed and located for emergency evacuation. Exothermic A chemical reaction in which heat is given off during the formation of chemical compounds. An example is the heat given off during the formation of carbon dioxide produced by the chemical reaction of oxygen with carbon during a fire. Most exothermic compounds are stable; that is, they cannot be easily decomposed. Exposures Exposures are buildings or structures that are near the structure on fire and that are placed at risk by the fire. A primary focus of the responding fire department will be to protect the exposures, thus reducing the risk of the fire spreading and causing additional damage to life and property. Exposure People or property that maybe endangered by a fire, smoke, or runoff. Extend A line may be extended by adding hose, straightening, or rerouting the hose already laid. Also, to extend the reach of an extension ladder by raising the fly section. Extension ladder A sectional ladder of two or more parts that can be extended to various heights. Extinguish To put out a fire completely. Extinguisher A portable fire fighting appliance designed for use on specific types of fuel and classes of fire. F Face piece The portion of a self-contained breathing apparatus that fits over the face by means of an adjustable harness. It may or may not have the regulator attached to it. False ceiling An additional suspended ceiling below the true original ceiling forming a concealed space. False front An additional facade on a building applied after the original construction or for decoration that creates a concealed space. FAST (Firefighter Assist and Safety Team) Truck A FAST truck is a company of firefighters (usually from a truck or rescue company) whose sole function at a fire is to stand by in case a firefighter becomes injured or trapped and needs assistance. The company assigned to the FAST truck is usually a highly trained group and reports only to the incident commander. In some departments, this group is call a RIT (Rapid Intervention Team). Fast attack mode When the first arriving unit at a fire makes an offensive attack on the fire. Fast Attack Fast attack is when the first arriving engine company attacks the fire using water carried in the booster tank, relying on the second company to secure a water supply. This tactic is used when the fire is in its first stages and most likely can be controlled until additional help arrives. Feeder A line used for water supply. Usually 4" or 5" LDH. Also known as a supply line. Common fire ground orders are to "lay a line" Fill hose A short section of hose carried on apparatus equipped with booster tanks to fill the tank from a hydrant or another truck. Fire The rapid oxidation of combustible materials accompanied by a release of energy in the form of heat and light. Fire alarm An audible or visual signal indicating a hostile fire. Fire behavior The manner in which fuel ignites, flames develop, and heat and fire spread. Sometimes used to refer to the characteristics of a particular fire. Fireboat A specially-built boat for fighting fires. Firebreak An open, clear area maintained through ground cover like grass, brush, and trees to prevent the spread of fire. Fire Brigade An organization of industrial plant personnel trained to use fire fighting equipment within the plant and to carry out fire prevention activities. In Canada, the local fire department may be referred to as the fire brigade. Fire broom A broom used in ground cover fire fighting. Fire bucket A bucket with a round bottom usually painted red and marked with the word fire to discourage use for purposes other than fire fighting; frequently kept filled with water, sand, or other fire extinguishing material. Also called a fire pail. Fire bug A common term to describe an arsonist or pyromaniac. Also describes a person who does not only set fires, but enjoys watching them. Fire building Used to describe the training building in which fire fighting is practiced; the building in which a fire is in progress. Fire Department connection Applied to the connections at ground level through which the fire department supplies sprinkler systems and/or standpipe systems. Fire detection devices The devices and connections installed in a building to detect heat, smoke, or flame. Fire District A designated geographic area where fire protection is provided, usually through a supporting tax, or an area where fire prevention codes are enforced. Fire door A specially-constructed, tested, and approved door installed to prevent fire spread. Fire escape A means of escaping from a building in case of fire; usually an interior or exterior stairway, or slide independently supported and made of fire-resistive material. Firefighter An active member of the fire department. Firefighter's axe A hand forcible entry tool equipped with a blade on one side and a pick or flat head on the other. Firefighter's carry One of several methods of lifting and carrying a disabled victim to safety. Fire flow The volume of water required for fire protection in a given area. Fire flow is measured in gpm and required duration. Water for fire flow is in addition to the water supply required for normal consumption. Fire flow test A procedure to test the rate of flow in gallons per minute (L/min) in a predetermined area. Fire gases Those gases produced as combustion occurs. Fireground An area around a fire and occupied by fire fighting forces. Fire guard A person trained and assigned to watch for fires and life safety for specific periods or events. Sometimes called fire watch. Fire hazards Conditions conducive to fire or that are likely to increase the extent or severity of fire. The terms hazard or hazardous are also used to indicate the type of Fire hose float A water-rescue flotation device made from inflated fire hose. Fire lines Boundaries established around a fire area to prevent access except for emergency vehicles and persons having a right and need to be present. Also used in ground cover fire fighting to describe a line scraped clean of combustibles around the fire perimeter to remove fuel and contain the fire Fire load The weight of the combustible materials found in the structure and contents of a building; expressed as weight per square foot. Fire mark A distinctive metal marker once produced by insurance companies for their policyholders' buildings. Fire Marshal The highest fire prevention officer of a state, province, county or municipality. Fire point The temperature at which a material evolves sufficient vapors that when ignited will continue to burn. See ignition temperature. Fire Prevention That part of the science of fire protection that deals with preventing the outbreak of fire by eliminating fire hazards through inspection, education, and investigation programs Fire Prevention Bureau A division of the fire service responsible for conducting fire prevention programs of inspection, education, and investigation. Fire Prevention Code or Ordinance A law enacted by a political jurisdiction to enforce fire prevention and safety regulations. Fire Prevention Week A week proclaimed each year by the President of the United States to commemorate the anniversary of the great Chicago conflagration of October 9, 1871; takes place the week in which October 9 falls. Fireproof The word fireproof is a misnomer because it means that something will not burn. Other terms, such as fire resistive or fire resistant should be used to indicate the degree of resistance to fire, since most items will burn at some temperature. Fire Protection Engineer A graduate of an accredited institution of higher learning who has specialized in engineering problems related to fire protection. Fire pump A water pump used in private fire protection to provide water supply to installed fire protection systems. Also, the water pump on fire apparatus. Fire report The official report on afire, generally prepared by the officer in charge of the fire operation, and kept as a permanent record. Fire resistance A relative term referring to the amount of time a material will resist a normal fire as measured on a standard time-temperature curve. Fire-resistive Refers to material and building design meant to withstand the maximum effect of a fire for a specific period of time. Fire-retardant A term used to indicate that materials or substances have been treated to retard ignition or the spread of fire. Fire Service Organized fire prevention, fire protection, and fire fighting services; members of fire prevention, suppression, and training organizations individually and collectively; all allied organizations who assist in preventing and combating fires. Fire Station The building in which fire suppression forces are housed. Fire stopping Blocking off concealed spaces within the walls, floors, and ceilings of structures to prevent the unseen spread of fire through these areas. Fire storm An atmospheric disturbance caused by heat rising from a conflagration. Violent convection caused by a rising column of heated air creates intense winds toward the fire center encompassing the entire fire area. Fire stream A stream of water from a fire nozzle used to control and combat fires. Fire Tetrahedron A model of the four elements required to have a fire. The four sides represent fuel, heat, oxygen, and chemical chain reaction. Fire trap Usually an old structure in such a deteriorated state that it is highly susceptible to fire, with inadequate protective equipment and exits, and considered likely to contribute to major loss of life in case of fire. Fire triangle A plane geometric figure in which the three sides of an equilateral triangle represent oxygen, heat, and fuel, the elements necessary to sustain combustion. Fire wall A solid wall of masonry or other noncombustible material capable of resisting fire for a prescribed time period. Fire walls extend through roofs and use parapets above the roof to divide large sections of buildings to prevent the overlapping or spread of fire. Fire Whirlwind A revolving mass of air created by a fire, normally a forest fire. First alarm The initial alarm fire department response. First -in The first company or apparatus to arrive at a fire location. Flame The burning gas or vapor of a fire that is visible as light of various colors. Flame front The outermost edge or surface of the flame. Flame interface The area or surface between the gases or vapors and the visible flame. Flame propagation rate The velocity at which combustion travels through a gas or over the surface of a liquid or solid. Flame spread The movement of a flame away from the ignition source. Flammable The term used to refer to combustible material that ignites easily, burns rapidly, or has a rapid rate of flame spread. Also see flammable liquids. Flammable limits The upper and lower limits beyond which a vapor-oxygen mixture is too rich or too lean to ignite or sustain combustion. (Also called explosive limits.) Flammable liquids Liquids that have a flash point below 1000F (37.80C). See combustible liquids. Flammable range The range between a substance's flammable limits. (Also called explosive range.) Flashback The tendency of flammable liquid fires to reignite from a source of ignition after they have been extinguished. Vapors of a flammable liquid may serve as a fuse leading from a source of ignition back to the flammable liquid's container. (Also called backflash.) Flash fire A type of fire that spreads rapidly through a vapor environment. Flashover The stage of a fire in which a room or other confined area becomes heated so much that flames flash over the entire surface of the area. The sudden ignition of all flammable material in a room or structure. As the fire burns and heat is generated and stored in the room on fire, it is possible for the heat to accumulate faster than it can use fuel. Once this reaches critical mass, the heat then turns all items that can burn in a room into burning fuel at one time. The danger is that this causes an inversion of the thermal layers because the new fuel is almost always near the floor. Despite superb protective gear, a firefighter has less than two seconds to evacuate a room that has a flashover. Flash point The lowest temperature at which a substance will emit sufficient vapors to ignite momentarily near the substance surface. This fire will not continue to burn because vapors are not being emitted rapidly enough to sustain combustion. See burn point. Flat load An arrangement of fire hose in a hose bed or compartment in which the hose lies flat with successive layers 4 one upon the other. Flat raise The raising of a ladder with the heel of both beams touching the ground. Floor runner A salvage tool usually of canvas or similar fabric placed on a floor before firefighters walk on it to protect the floor surface or covering. Flush hydrant A hydrant installed in a pit below wound level such as near the runway area of airports or other locations where aboveground hydrants would be unsuitable. Fly The extendable sections of an extension or aerial ladder. Fly rope The rope used to hoist fly sections of extension ladders. Also called a halyard. Foam An extinguishing agent formed by mixing a foam-producing compound with water and aerating the solution for expansion. Foam may be protein, synthetic, aqueous film forming, high expansion, or alcohol type. Foam is applied to any material that is on fire or could potentially catch fire. The foam creates a barrier between the material and the heat, preventing ignition of flammable gases. Foam is commonly used on flammable liquid fires (gas or oil), but is also being used in some areas for automobile & structure fire applications. Foam bucket A covering of foam applied over a burning surface to produce a smothering effect; can be used on nonburning surfaces to prevent ignition. Foam eductors Devices for mixing foam concentrate in proper proportions with a stream of water to produce foam solution. Fog pattern The angular description of the water spray as it leaves the fog nozzle. Fog stream A water stream of finely-divided particles used for fire control. Folding ladder A short, collapsible ladder easy to maneuver in tight places for reaching through openings in attics and lofts. Forcible Entry Techniques used by the fire service to get into buildings, automobiles, aircraft, or other areas of confinement when normal means of entry are locked or blocked. Frequently, firefighters must force open doors that are locked or remove security doors and bars in order to enter a structure to search for victims & extinguish a fire. A variety of hand, power & hydraulic tools can be used for forcible entry. Forestry Line A forestry line is a small-diameter, cotton-jacketed handline used to fight brush and forest fires. Its construction reduces the weight a firefighter has to pull and therefore reduces fatigue. Also used to replace booster or red lines. Formula Any variety of mathematical computations used primarily in the fire service to determine pressures, flows, and gallons per minute (L/min). Forward Lay A forward lay is when fire hose is laid from the hydrant to the fire. (See also reverse lay). Free burning The second phase of burning in which materials or structures burn in the presence of adequate oxygen. Friction loss The loss of pressure resulting from water rubbing against and being agitated by the interior walls of fire hose, pipe, fittings, adapters, and nozzles. Friction loss is measured in psi per 100 feet or kilopascals per 30 meters. Front mount pump A fire department pump mounted in front of the radiator of a vehicle and powered off the crankshaft. Fuel A material that produces heat through combustion. Fully involved When an entire area of a building is completely involved in heat, smoke and flame. Immediate access to the interior is not possible until some control measures are taken to make the interior attack possible. Fused head Automatic sprinkler head that has operated from exposure to heat. Fusible link A connecting link device that fuses or melts when exposed to heat. Used in sprinkler heads, fire doors, dampers, and ventilators. G Gallon Unit of liquid measure. One U.S. gallon (3.785 L) has the volume of 231 cubic inches (3785 cubic meters). One imperial gallon (4.546 L) equals 1.201 U.S. gallons (4.546 L). Gate valve A type of control valve with a solid plate operated by a handle and screw mechanism. Operation of the handle moves the plate down into and up out of the waterway. Gated wye A hose appliance with one female inlet and two or more male outlets with a gate valve on each outlet. Gauges Instruments to show the operating conditions of an appliance or piece of equipment. General alarm An alarm called because a large fire requires calling additional firefighters and equipment. General order A standing order, usually written, that is communicated through channels to all units and remains in effect until further notice. Gin poles Poles held upright at an angle by guy lines used with a block and tackle for lifting. Gloves Hand protection necessary to complete the firefighters protective clothing ensemble. Governor A built-in pressure regulating device to control pump discharge pressure by manipulating engine rpm; a device that governs the maximum rpm of an engine. GPM Gallons per minute; the measure of water flow used to measure the output of fire department pumpers, hose streams, nozzles, hydrants, and water mains. Grading schedule A schedule of deficiency points by which insurance engineers grade the fire defenses of a community. Gravity tank An elevated water storage tank for fire protection and community water service. A water level of 100 feet (30 m) provides a static pressure head of 43.4 psi (300 kPa) minus friction losses in piping when water is flowing. Grid map A map of an area overlaid with a grid system of rectangular coordinates or azimuth bearings (polar coordinates) that are used to identify ground locations. Grid system water mains An interconnecting system of water mains in a criss-cross or rectangular pattern. Ground cover fire Any fire involving natural ground cover like grass, brush, or timber. Ground jack A heavy jack attached to the frame or chassis of an aerial ladder truck to provide additional stability before raising the ladder. Ground ladder A descriptive term to designate the difference between ladders raised on the ground and those raised hydraulically on the apparatus. H H.A.D. Heat actuating devices thermostatically controlled and used to activate fire equipment, alarms, or appliances. Half life The period of time required for any radioactive substance to lose half of its strength or reduce by one-half its total present energy. Halligan tool An all-purpose steel prying bar used as a forcible entry tool. A forcible entry tool with a claw on one end and a spike or point at a right angle to a narrow wedge on the other. Halogenated Hydrocarbons The compounds formed when the atoms of the halogens replace the atoms of hydrogen in simple hydrocarbons. Many halogenated hydrocarbons can be used as extinguishing agents. Halogens The name given to the family of elements that includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Halon Halogenated extinguishing agent. Halon extinguishes fires by inhibiting the chemical reaction between fuel and oxygen. See tetrahedron. Halyard Rope used with extension ladders to extend the fly sections. Handline A handline is a small diameter hose usually used inside a burning structure to directly apply water on to the fire. Handlines are usually 1.5 or 1.75 inches in diameter that can be handled and maneuvered without mechanical assistance. Lines as large as 2.5 inches in diameter (also called the "deuce and a half") can be used for heavy fire conditions Hard suction A heavy non-collapsible suction hose used for drafting water from static supply such as lakes, ponds or swimming pools. Haz-Mat Hazardous Materials By federal guidelines, all firefighters are required to be trained in hazardous materials. There are three levels of training. Each level is more technical than the previous level. The first level is Awareness. This is the basis for all levels for identification and recognition of a hazardous material or indicators of the presences of a hazardous material. The next level is Operations. This level is where the hands on training will give the firefighter basic knowledge in certain mitigation techniques. The third level is Technician. This level, firefighters use all the resources available to control the spill or leak from becoming worse and determine certain factors that possibly could react with the situation at hand. The training in the technician level is in depth. Personnel have many other training certifications as well as having their health conditions monitored before, during and after any incident. Head pressure Pressure measured in feet (meters) or psi (kPa) resulting from the elevation of water. Head pressure amount to 0.434 psi per foot (10 kPa per meter) or 2.304 feet per psi (0.10 meter per kPa) Heat A form of energy measured in degrees of temperature to signify its intensity. Heat transfer The movement and dispersion of heat. Heat is transferred by convection, conduction, and radiation. See law of heat flow. Heavy duty appliances Master stream equipment with large tips generally fed by two or more separate hose lines. Heavy stream A large stream too heavy for conventional manual operation; a stream of 400 gpm (1,514 L/min) to 1,200 gpm (4542 L/min) or more. Heel The base of a ladder, the steadying of a ladder while it is being raised or, to secure a raised ladder. Also known as the butt. Heel plate A metal reinforcement at the heel or butt end of a ladder, generally shaped to give the ladder more stability. Helmet The regulation protective headwear for firefighters that provides protection from falling objects, side blows, the fire environment elements, and eye injuries. Helmet A clear protective plastic shield attached to a helmet to protect the face. Helmet identification shield The insignia or plaque fastened to the front of the firefighter's helmet that generally displays the name of the city, initials, unit, rank, and number. Higbee cut A special cut at the beginning of the thread to provide positive identification of the first thread and to eliminate cross threading. Higbee indicators Notches or grooves cut into coupling lugs to identify by touch or sight the exact location of the Higbee cut. High pressure fog A fog stream operated at high pressures and discharged through small-diameter hose. High rise building Any building that requires fire fighting on levels above the reach of the department's equipment. High rise pack A special kit for high-rise operations containing hose, adapters, nozzle, and spanner wrenches. High value district A section of a city in which valuable property is located and in which additional companies and apparatus are needed to combat a fire. Hitch A loop of rope that secures the rope, but is not part of a standard rope knot. Hook Curved metal devices installed on the tip end of roof ladders to secure the ladder to the highest point on the roof of a building. Plaster hooks are devices resembling a pike pole for pulling down plaster and ceilings. Hook and Ladder A term for a type of ladder truck. Traditionally, this apparatus is in two parts. The tractor pulls a long trailer with a mechanical extension ladder over 100 feet and a compliment of ground ladders. The trailer is known as tiller, which is guided by a person that sits on the end of the trailer and steers the trailer around corners. This person is known as the tillerman. The 'hook' of hook and ladder comes from early days when large hooks were used to assist in fighting fires. Pike poles with hooks on the end of the pole have replaced earlier hooks. Hooking up Connecting a fire department pumper to a hydrant or connecting a discharge hose to the pumper. Horseshoe load Hose loaded in the hose bed compartment in the form of a horseshoe. Hose Hose is used to deliver water onto a fire and to provide water from hydrants to firefighting apparatus. The types of hose used include handline, booster lines and large diameter hose. Hose belt A leather belt or nylon strap used for securing and handling charged hose lines, tools, or tying off a ladder. Hose body The main hose compartment of a pumper or other piece of apparatus designed for carrying hose. Also called hose bed. Hose bridge A device placed astride hose so traffic can pass over without damaging the hose. Hose cabinet (rack) A recessed cabinet in a wall that contains a wall hydrant and connected hose. Hose clamp A mechanical or hydraulic device to compress fire hose to stop the flow of water. Hose dryer An enclosed cabinet containing racks on which fire hose can be dried. Hose hoist A metal device having a roller that can be placed over a windowsill or roofs edge to protect a hose and make it easier to hoist. Hose jacket The fiber jacket(s) around the rubber inner liner of a hose. A device placed around a broken hose to contain the leak or around damaged or dissimilar couplings to join them. Hose rack Racks for storing and drying fire hose. Hose reel Cylinders around which fire hose can be manually or mechanically rolled to keep it neat and orderly. Hose strap A strap or chain with a handle suitable for placing over a ladder rung used to carry and secure a hose line. Hose tower Part of a fire station or building designed so fire hose can be hung vertically to drain and dry. Hotel raise A method of raising a fire department extension ladder in line with several windows so individuals can simultaneously escape from more than one floor. (Also called factory raise.) House lights The lights throughout the fire station that are controlled from the alarm or watch desk which makes it possible to illuminate the entire station in case of an emergency. House line A permanently fixed, private standpipe hose line. House watch The duty of maintaining the fire station alarm center for a prescribed period of time. Hydrant An upright metal casting connected to a water supply system and equipped with one or more valved outlets to which a pumper or hose line can be connected. Also this has been given the name 'plug' or 'catch a plug'. This term comes from early days of firefighting when water mains were nothing more than hollowed out trees, buried in the ground. When a fire company needed water, they would dig down to the log, and open a hole in the tree for a water supply. After the fire, the hole had to be 'plugged' in order to stop the flow of water. Hydrant adapter An adapter, fitting, or coupling to connect hose or pumper intake hose to a fire hydrant. Hydrant wrench A specially-designed tool used to open or close a hydrant and to remove hydrant caps. Hydraulics The study of the use and movement of fluids at rest and in motion. Hydrocarbons Combinations of hydrogen and carbon that form many compounds. Petroleum products and natural gas are mixtures of several hydrocarbons. Hypergolic A chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidizer that causes immediate ignition on contact without the presence of air. An example is the contact of fuming nitric acid and UDMH (unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine). Hypergolic mixtures Certain fuels and oxidizers that will ignite on contact with each other without an ignition source. Hyperventilation Rapid breathing that over oxygenates the blood. I ICC Interstate Commerce Commission; now the U.S. Department of Transportation. Ignition The beginning of flame propagation or burning; the start of a fire. Ignition temperatures The lowest temperature at which a fuel when heated will ignite in air and continue to burn; the temperature required to cause ignition of a substance. See fire point Impeller A rotating disc on a shaft at the center of a centrifugal pump housing. The slanted vanes of a rotating impeller impart the centrifugal force that expels water from the pump. Impeller eye The opening through which water flows into the center of an impeller. Incendiary A fire believed to have been deliberately set; an incendiary agent like a bomb. Inches of mercury A scale used in measuring negative pressure; used to measure barometric pressure. Incident Command System (ICS) A management system of procedures for controlling personnel, facilities, equipment and communications from different agencies to work together towards a common goal in an effective and efficient manner. Is the chain of leadership and command at the scene of an emergency. The flexible on scene incident management system that identifies key roles and tasks that must be filled to safely manage an emergency incident. It stipulates that one person (Incident Command) is responsible for overall operations during the incident. The IC delegates responsibility to other officers by assigning them into pre-defined roles that are understood by everyone operating in the incident. Below are some of the key IMS positions typically assigned at a fire incident: Incident Management System (IMS) COMMAND - The officer responsible for the overall incident SAFETY - The officer responsible for monitoring the safety of all personnel operating within the incident perimeter. STAGING - The officer responsible for collecting and allocating needed personnel and resources into and out of the incident. DIVISION - The officer responsible for operations within a geographical area of the incident. Residential house fires and small commercial structure fires may require a Division assignment. Large fires may require all four sides of a building to have a DIVISION officer assigned to conduct operations on their side of the building. A variation on the Division is called SECTOR. Incipient fire stage The first phase of the burning process where the substance being oxidized is producing some heat, but the heat has not spread to other substances nearby. During this phase, the oxygen content of the air has not been significantly reduced. Incrustation A deposit on the inner wall of a water pipe creating additional friction and loss of pressure. Indirect application A method of extinguishing fire by putting water fog into a closed superheated atmosphere to obtain the maximum heat absorption and steam generation for smothering and cooling the fire area. Inhalator A mechanical device for administering breathing oxygen to an individual who is breathing. See also aspirator and resuscitator. Inhibitors Chemicals added to unstable substances to prevent violent reaction. (Also called stabilizers.) Initial attack The first attack when hose lines are employed to prevent further extension of fire and to safeguard life and property while additional lines are being laid and other forces put in motion. Inititators Cylinder-shaped explosive or gas pressure devices used to create gas or mechanical pressure to activate another device; usually found in the seat and canopy ejection mechanism of jet military fighter aircraft. Insurance Services Office (ISO) Formed January 1971, a national insurance organization licensed as a fire rating organization; an advisory organization to other property-liability insurance companies. Intake hose Noncollapsible hose used to draft water into pumpers from static sources lower than the pump; formerly called hard suction hose. Flexible intake hose is a short length of large-diameter hose used to connect pumpers to hydrants. Intake screen Screen used to prevent foreign objects from entering a pump. Inversion Horizontal layers of air through which the temperature increases with increasing altitude. Investigative mode When the first-arriving companies go on standby because the cause of the alarm is not readily ascertainable. Involved The actual room, portion, area, or building involved in or affected by fire. Ion An unbalanced atom; any atom that has an electrical charge, either positive or negative. J Jack A portable device used to lift heavy objects with force applied with a lever, screw, or hydraulic press. Jake A term used to refer to a good firefighter. One story has the term originating from the corruption of the phrase, "J-key." Years ago, the bed was the most expensive piece of furniture in a dwelling. Since firefighters weren't as good at stopping fire as they are today, they would attempt to remove as many belongings as possible. The bed was too large to carry out in one piece and had to be disassembled using a bed key. The key was shaped like the letter J and called a J-key. Jake Brake Many modern fire apparatus have a auxiliary braking system to assist the main air brakes to stop or slow a vehicle. Many commercial over the road trucks also have them. The exhaust system is used to help slow the engine down. Jaws A generic term applied to a type of rescue tool that can cut, push or pull material (most often pieces of an automobile). Jaws of Life is a synonym, but is the copyrighted product name of Hurst. Holmatro and Amkus are also major manufacturers of jaws. Jet A stream of water coming from a nozzle (English). Jet pump A water-operated pump that creates a suction by using the venturi principle. Jib A lever used with a block and tackle to lift or lower. Joist A supporting member used in building construction to support a floor or ceiling. Journal The log book, day book, or record book in which all activities of a fire shift are recorded. Jump Line A jump line is a handline stored in an extended bumper (also called a jump bumper) and preconnected to the engine to allow for a quicker attack. K Kelly day A rotating off-duty shift in addition to the normal off-duty schedule of the firefighter. Kelly tool A metal forcible entry tool similar to the claw tool but with an adze blade at one end and a forked blade at the other. Kinetic energy The motion of material bodies and the forces and energy associated with any moving thing or movement. Kink hose To make a sharp bend in a fire hose that restricts water flow. Kit A collection of tools or appliances kept in one location for a specific purpose. Knockdown To reduce flame and heat and prevent the danger of further extension of fire; to bring a fire to the overhaul stage. Bring a fire under control. L Ladder Company Also known as a truck company. A ladder company is a combination of a fire truck with an aerial ladder, an assortment of ground ladders and forced entry tools and the manpower used to staff it. Ladder trucks can have straight aerial ladders as short as 65 feet or longer ladders with platforms (buckets) on the end. In many department's ladder companies are responsible for ventilation and forcible entry duties. A standard ladder company will include an officer, driver/operator and two firefighters on a ladder truck. Ladder Truck The ladder truck is referred to as such because of its ability to carry a full compliment of ground ladders as well as contains either a telescoping ladder or a platform. Large Diameter Hose The biggest hose used by firefighters, large diameter hose (LDH) is sometimes referred to as a water main above ground. LDH is usually 4-5 inches in diameter and is used to supply water from the hydrant to pumper trucks. See also supply hose. Leader Line A leader line is a line usually having a gated wye on the end. Leader lines are usually 3 or 2.5 inches in diameter and the wye usually feeds two or three 1.5 or 1.75 inch attack lines. M Master Stream A master stream is a large and fixed stream of water. Master streams are used on the end of aerial ladders on ladder trucks and on top of pumper trucks. Master streams can deliver larger amounts of water than hand-held hose. Monitor A type of master stream similar to a deck gun, but removable from the apparatus. Hose can be laid into it, making it mobile. O Overhaul Commonly viewed as "cleaning up" after a fire, overhaul is the process of putting a structure in the safest condition following a fire. Additionally, it is during the overhaul phase of an incident that firefighters verify that the fire has not extended into unknown areas and that hidden "hot spots" are extinguished. P Positive Pressure Ventilation (PPV) Panic Hardware Hardware mounted on exit doors in public buildings; permits the door to open when pressure is applied to the hardware. Parallel operation Operation of a multistage pump when each of its impellers receives water from a common source and contributes volume directly to the discharge. (Also called volume.) Parapet Extension of a fire wall above a roof to prevent fire from extending. See fire wall. Part Paid (call) Firefighters who are paid on the basis of time that they are used. Party wall A wall common to two buildings. Pattern The shape of the water stream as it is discharged from a fog nozzle. Pedestal, control A panel on the turntable that has all of the controls and instruments for controlling, hoisting, extending, and rotating aerial ladders. Pendant sprinkler An automatic sprinkler head designed for placement and operation with the head pointing downward from the piping. Phases of fire The degree of flame progression. Phase I: fire in incipient stage and beginning to grow. Phase II: free burning, flame propagation at its greatest. Phase III: oxygen deficient in the burn area producing smoldering. Pike pole A sharp prong and hook of metal on a wood, metal, plastic, or fiber glass handle used for pulling, dragging, probing, and other purposes. Piston pump A positive-displacement pump using one or more reciprocating pistons to force water from the pump chambers. Pitot tube An instrument that is inserted into a stream of water and has a pressure gauge attached that indicates the discharge pressure of the stream. Plaster hook A barbed collapsible hook on a pole for puncturing and pulling down materials. Plates Construction members used to form the top and bottom of a frame wall. Platoon The entire shift of a fire department; may indicate only those who are on or off duty. Play a stream To direct a stream of water at the fire that extends from the hose coupling to the shutoff. Playpipe Used to describe the base part of a three-part nozzle Plug A fire hydrant. Plug pressure The pressure available at the hydrant; generally refers to static pressure, but could refer to residual pressure during operations. Pneumatic power Power derived by using the properties of compressed air at rest or in motion; generally used with a pressure regulator. Pole The sliding pole from upper stories to the apparatus area of a fire station; ladder poles to assist in raising; a pike pole. Pompeir A scaling ladder with a single beam and a large curved metal hook that can be put over windowsills for climbing. Pompeir belt Life belt. Portable pump A small gasoline-driven fire pump designed to be transported on fire apparatus and capable of supplying nozzle streams through hose or relaying to a fire department pumper. Position Specific assignment during a fire operation. Positive displacement pump Any of several piston or rotary-gear pumps that move a given quantity of water through the pump chamber with each stroke or cycle. Positive Pressure Apparatus Breathing apparatus with a regulator that supplies air when the wearer inhales and also allows a small, constant flow to the face piece. This lessens the likelihood that contaminants can enter the and lessens the likelihood that contaminants can enter the face piece. Also known as pressure-demand apparatus. Constant airflow gives the face piece a slight positive pressure Post-fire operations The operations of overhauling to search for and extinguish hidden fires, determining the cause of fire, identifying and preserving evidence of arson, and making the building and area safe; returning to quarters; preparing equipment for future use; and writing reports. Post indicator valve (PIV) A valve that provides a visual means of indicating “open” or “shut” position; found on the supply main of installed fire protection systems. Power train A means of transferring power from an engine to a pump; includes all power-transmitting components. Pre-action system A type of automatic sprinkler system in which thermostatic devices charge the system with water before individual sprinkler heads are fused. Preconnected A procedure whereby hose is connected to the intake or the outlet of the pump before a fire to expedite hose operations and fire fighting procedures. Pre-incident planning The act of preparing to fight a fire in a particular building or group of buildings by advance planning of possible fire fighting operations. Pressuredemand system See positive-pressure apparatus. Pressure operation See series operation. Pressure regulator A device used to maintain a constant pressure within a pump while operating. Pressure tank A system of storing water in tanks under pressure for fire fighting or fire protection purposes; used instead of elevated tanks or auxiliary pumps in private fire protection. Primer oil tank A tank of oil used to seal and lubricate the priming pump. Priming A procedure of filling the pump with water to prepare for pumping from draft. Priming pump Any of several small positive-displacement pumps used to prime a centrifugal pump by removing the air to let water flow into the pump. Private hydrant Hydrant provided on private property or on private water systems to protect private property. See yard hydrant. Products of combustion Materials produced and released during burning. Proportioner A device to introduce the correct amount of agent into streams of water especially foam and wetting agents. Proprietary System A fire protection system owned and operated by the property owner. Protective Clothing A general term used to describe firefighters clothing including helmets, coats, boots, pants, gloves, and self-contained breathing apparatus. Proximity Suit Proximity clothing includes hoods, coats, trousers, and mittens that have outer surfaces with better heat reflection properties than normal or traditional bunker clothing and that let the wearer get closer to the fire. PSI Pounds per square inch (kiloPascals). Pressure measurement usually used for pump pressure, nozzle pressure, friction loss, and pressure losses in appliances, hose, and hydrants. PSIA Pounds per square inch (kiloPascals absolute. Absolute pressure equals atmospheric pressure (14.7 psi) plus the gauge pressure. At 100 psig, absolute pressure equals 114.7 psia. PSIG Pounds per square inch (kiloPascals) gauge. The pressure above atmospheric pressure. At sea level, 0 psig (0 kPa gauge) is equal to 14.7 psia (100 kPa absolute). Pulmonary Resuscitation See artificial resuscitation. Pump can Another term for a water filled pump-type extinguisher. See pump tank. Pumper, Class A A pumper that will deliver its rated capacity of 150 psi (1000 kPa) net pump pressure at a lift of not more than 10 feet (3 m) with a motor speed of not more than 80 percent of the certified peak of the brake horsepower curve; will deliver 70 percent of rated capacity at 200 psi (1350 kPa) and 50 percent of rated capacity at 250 psi (1700 kPa). Also called an Engine Pumper, Class B A pumper that will deliver its rated capacity of 120 psi (800 kPa) net pump pressure with not more than 10 foot (3 m) lift and motor speed not exceeding 80 percent of the certified peak of the brake horsepower curve; will deliver 50 percent of its rated capacity at 200 psi (1350 kPa) and 331/3 percent of its rated capacity at 250 psi (1700 kPa). Class B pumps have not been manufactured since the mid 1950s. Pump panel The instrument and control panel located on the pumper. Pump tank A small water filled fire extinguisher having a built-in hand pump and an attached hose and nozzle. Puncture nozzle A specially-designed nozzle for puncturing and inserting into walls to extinguish hidden fires. (Also called a bayonet or piercing nozzle.) Pyromania An irresistible impulse to start fires. Pyrometer A device used to measure temperatures by wavelength or electrical generation. Pyrometers connected to thermocouples record the heat at various points. See thermocouple. Pyrophorics Chemicals that will ignite or react violently on contact with air or oxygen; must be maintained under an inert atmosphere. Pyrotechnics Fireworks. Q Quad A four way combination fire apparatus; sometimes referred to as quadruple combination, a quad combines the water tank, pump, and hose of a pumper with the ground ladder complement of a truck company. Quarters A fire station. Quench To extinguish a fire by cooling. Quint Same as quad, but with an aerial ladder added. R Radiation Heat The transmission of heat through the medium of heat rays. See conduction and convection. Radiation, Nuclear The product of a process known as radioactivity; the emission of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. Radiator fill line A small waterline leading from, the fire pump to the radiator of the apparatus; used to refill the radiator during pumping at a fire scene. Radioactivity The process whereby isotopes of certain elements spontaneously emit particles and/or rays from radioactive materials. Radio System Regulations FCC rules that govern the operation of radio systems Raise Any of several accepted methods of raising and placing ground ladders into service. Rappel A method of descending for emergency escape by means of a rope and descending friction device from locations above the reach of fire department ladders. Rate meter A nuclear-radiation detection device. Rate of Rise Alarm System One of the systems installed to detect fire by an abnormal rate of heat increase; operates when a normal amount of air in a pneumatic tube expands rapidly when heated and exerts pressure on diaphragms. Rating Bureau See Insurance Services Office. Reaction, Chemical Any change in the composition of matter that involves a conversion of one substance into another. Recall To call off-duty firefighters back to duty. Red Line Red line is a hose that is usually one inch in diameter and rubber jacketed. This type of hose is used on small fires using the water carried in an apparatus' booster tank and are usually stored on reels. Same as booster line. Reducer Couplings Couplings with a large and small connector for connecting hose couplings of two different sizes. Rekindle The reignition of a fire because of latent heat, sparks, or smoldering embers; can be prevented by proper overhaul. Relative Humidity The percentage of moisture in the air compared with the maximum amount of moisture that air will hold at a given temperature. Relay The use of two or more pumpers to move water distances that would require excessive pressures if only one pumper were employed. Relief Valve A spring-loaded device used to bypass water in a pump when pressures exceed preset operating pressures. Rescue Saving a life from fire or accident; removing a victim from an untenable or unhealthy atmosphere. Rescue Squad A fire company specially trained and assigned for rescue work. Rescue Company A rescue company is a term used to describe a rescue truck and the firefighters used to staff it. A rescue company is equipped and trained to handle a variety of duties including search and rescue, medical treatment of victims, suppression at the scene of a fire and the extrication of victims in motor vehicle accidents. The actual duties of a rescue company can vary in different parts of the country as does the term to describe one. A Rescue Company is called a Squad in some areas while other areas use the term when referring to their ambulances. Reserve Apparatus Apparatus not scheduled to respond to fires in normal or first-line duty, but available for emergencies or replacing first-line equipment. Reset To return fire protection or detection equipment to its original standby position after operation; to reset a fire alarm box or a sprinkler system. Residual Pressure Pressure remaining at a given point in a system while water is flowing. Resources The personnel and materials available to the fire department to aid in providing fire service to the public. Respiration See artificial resuscitation. Respiratory hazards Gases and by-products of combustion that are hazardous to firefighters and rescue workers when inhaled. Resuscitation See artificial resuscitation. Reverse lay When supply hose is laid from the fire to the water source, placing the pump at the source of water. (See also forward lay) Rig Any piece of fire apparatus. RIT (Rapid Intervention Team) Same as FAST Truck Riser A vertical water pipe used to carry water for fire protection systems above grade, such as a standpipe riser, or sprinkler riser. Road Performance Test A series of tests required to determine the performance ability of fire apparatus Roof ladder A straight ladder with folding hooks at the top end; the hooks anchor the ladder over the roof ridge. Rookie Academy A special school to indoctrinate newly-appointed firefighters in the rudiments of all fire service subjects. Rope Hose tool A piece of rope spliced to form a loop through the eye of a metal hook; used to secure hose to ladders or other objects. See hose strap and hose belt. Run A response to a fire or alarm. Rung The step portion of a ladder running from beam to beam. Running fire A ground cover fire that spreads rapidly. See ground cover fire. S Salvage The process of protecting the contents of a building from fire, smoke and water damage. Tools used include salvage covers (water proof tarps) that are placed over furniture, preventing damage from water and debris. Salvage cover A waterproof cover made of cotton duck, plastic, or other material and used by fire departments to protect unaffected furniture and building areas from heat, smoke, and water damage; a tarpaulin. Salvage kit An assortment of tools and appliances used for a specific purpose during salvage. SCBA Self-contained breathing apparatus. SCUBA Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. Seat of fire The area in which the main body of fire is located Series operation An operation of a multistage centrifugal pump in which the first impeller provides its water volume and pressure to the second impeller, thus building pressure until the final impeller delivers the same volume of water at increased pressure to the discharge. S-hooks Metal hooks placed through the grommet holes of a salvage cover to secure the cover. Shoulder carry A procedure of carrying fire hose on the shoulder. Siamese A hose appliance that has two or more female inlets and one male outlet. Size-Up A mental process of evaluating all of the influencing factors at a fire scene before committing personnel and equipment to a course of action. This usually includes hazards, life safety, fire involvement and plan of attack. Skid load A system of loading fire hose such that the top layer can be pulled off at the fire. Smoke ejector A mechanical device to force smoke from a building or to blow fresh air into a building; sometimes equipped with a flexible tube. Smoldering phase The third stage of burning in which flames cease to exist because the area of confinement is air tight and lacks enough oxygen. Solid stream A hose stream that stays together as a solid mass as opposed to a fog or spray. Spanner wrench A tool used to tighten or loosen hose couplings, pry with, or use as a gas key. Spontaneous heating Heating resulting from chemical or bacterial action in combustible materials which may lead to spontaneous ignition. Sprinkler connection A siamese connection used by the fire department to increase the water supply and pressure to a sprinkler system. Stabilizer An additive in foam liquid used to hold air in suspension for an extended time. Standpipe A fire protection system consisting of a piping arrangement either wet or dry to take water to upper floors or remote areas of buildings where fire department outlets and private hose lines are provided. Steam conversion Water applied to areas of high heat concentration (above 1,0000 F) turns to steam rapidly. This water absorbs a tremendous amount of BTUs, and the generated steam forces smoke and fire gases from the confined fire area Steamer connection A large-diameter outlet, usually 4 1/2 inches, at a hydrant or the base of an elevated water storage container. Stick The aerial of a ladder truck. Aerials vary in length depending on the needs and finances of a department. Some are as short as 65 feet, while others reach lengths greater than 100 feet Still Alarm A still alarm is a call requiring only one company. Examples of a still alarm include a small fire or a medical call. Straight ladder A one-section ladder. Straight lay Hose laid from the hydrant or water source to the fire. Also called a forward lay Strainers Wire or other metal guards used to prevent debris from clogging the intake hose of fire pumps. Strategy The overall plan for fire control and attack. Stretch hose To lay out hose as a line, or advance it into a building. Strike team A group formed of five similar units meeting established manpower and equipment requirements with a strike team leader. Strike the Box .To transmit or strike an alarm over the radio for a full first alarm assignment. Suction A misnomer used to describe the drafting process; large hose used for drafting; the inlet side of the pump that is better referred to as the intake. Supply Hose Hose line used to supply water from a hydrant to fire apparatus. Many departments use large diameter hose (see above) for this purpose. LDH is sometimes referred to as a water main above ground and is usually 4-5 inches in diameter. However, some departments use smaller 3-inch hose to supply water at a fire. Suppression Another meaning of the word control; however, suppression also implies overcoming; another name for the operational section of the department. T Tanker A fire truck that is used primarily for carrying water to a fire scene. Tankers can be in size from 3000 gallons to 10,000 gallons. Tiller Is a type of ladder truck with a second cab at the rear of the truck where a firefighter will steer the rear wheels. Because tiller trucks can steer in the front and the back, they are able to navigate turns that other ladder trucks could not. Trash Line Same as jump line, although not necessarily carried on the front bumper. Truck Company See Ladder Company. U Up and Over A standard ventilation operation conducted by a team of firefighters wherein ladders are raised at a working fire involving a row house-type dwelling to gain access to the roof to allow the firefighters to ventilate the involved dwelling. The intent is to get the upper floor opened up as quickly as possible. This is accomplished by opening skylights and/or scuttles and ensuring windows in the rear and front are taken out at the same time. The advantage of this operation is that many times, it is difficult to bring portable ladders to the rear of a row-type dwelling in some areas due to trash-strewn, overgrown, narrow, winding alley-ways. A 6-foot hook allows the one firefighter venting the rear to reach down (carefully where wires are involved) and take out (break) the windows. Any blinds, curtains, or drapes can be snagged with the hook to remove them and thereby facilitate the speedy evacuation of super-heated smoke and gases. V Ventilation Ventilation is the systematic removal of smoke from a building. Ventilation is usually accomplished with one of two methods: positive and negative pressure ventilation. Positive pressure ventilation increases the atmospheric pressure in the building until it is grater than the pressure outside the building. With negative pressure ventilation, the pressure inside the building is reduced until its less than the pressure outside the building.