Cell Division in Eukaryotes
advertisement

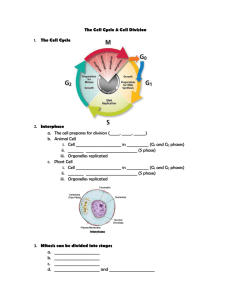
Cell Division in Eukaryotes There are two types, mitosis and meiosis The cell cycle is the repeating set of events that make up a cells life. o 3 Parts of the cell cycle Interphase- the time between cell division M-phase also called mitosis- the nucleus of a cell divides Cytokinesis- the division of the cytoplasm Interphase Cells spend most of their lives in this phase. It consists of; o G1 phase- offspring cells grow to a mature size o S phase- DNA is copied o G2 phase- cells prepare for division by copying organelles o G0 phase- cells are fully mature and are no longer going to divide Mitosis The division of the nucleus. It is how unicellular organisms reproduce and how multicellular organisms grow and replace old cells. Mitosis has 4 phases o Prophase DNA shortens and coils into rod shapes Nucleolus and nuclear membrane break down and disappear Centrosomes form and move to opposite poles Spindle fibers form from centrosomes. They help divide the cell o Metaphase Chromosomes move with the help of the spindle fibers and line up in the center of the cell Karyotype pictures are taken in this phase o Anaphase Chromatids of each chromosome separate at the centromere and slowly move toward opposite poles o Telophase Spindle fibers disassemble Chromosomes become less tightly coiled to a chromatin state Nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes (there are 2 sets) Nucleolus forms in each new cell Cytokinesis During telophase the cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis. o In animal cells the cell membrane will pinch inward forming a cleavage furrow. Eventually two new daughter cells will exist. Each having identical DNA. o In plant cells a cell plate will form between the two new nuclei. It will start forming in the middle and eventually extend to both ends of the cell. It will result in two cells with identical DNA. Production of Gametes Meiosis Meiosis is the process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number of the original cells. It produces haploid reproductive cells called gametes. o Human gametes are the sperm and the egg, each contains 23 chromosomes. o The fusion of sperm and egg produces a zygote that contains 46 chromosomes. Stages of meiosis o Cells preparing to divide by meiosis undergo interphase. o Meiosis I Prophase I DNA coils tightly into chromosomes Spindle fibers appear Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disassemble Chromosomes line up next to its homologue. This pairing is called synapsis. Each pair of homologous chromosomes is called a tetrad. During synapsis homologous chromosomes move close and the chromatid wrap around one another. Parts of chromatids break off and reattach to its homologue. This allows exchange of genetic material between maternal and paternal chromosomes. It is called crossing over and results in genetic recombination by producing a new mix of genetic material. Metaphase I Tetrads line up randomly in the center of the cell Spindle fibers from opposite poles attach to each pair of tetrads so they can be pulled in opposite directions Anaphase I Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell The random separation of homolgous chromosomes is called independent assortment Telophase I Chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell The nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear Cytokinesis occurs During meiosis I the original cell produces 2 new cells. Each new cell contains one chromosome from each homologous pair. These cells are NOT identical to each other like they are in mitosis. o Meiosis II Interphase does not occur Prophase II Spindle fibers form and begin moving chromosomes toward the middle of the cell. Metaphase II Chromosomes finish moving to the middle of the cell Anaphase II Chromatids separate and move to opposite poles Telophase II Nuclear membrane forms around genetic material in each pole in each cell o Cytokinesis II Cytokinesis II occurs resulting in 4 new cells which have half the genetic material of the original cell. Meiosis produces haploid reproductive cells. It only occurs in the reproductive organs, the testes and ovaries. o Spermatogenesis The production of sperm cells through meiosis It results in 4 spermatid cells that mature into sperm o Oogenesis The production of mature egg cells through meiosis It produces 1 viable egg and 3 polar bodies The viable egg can be fertilized but the polar bodies do not receive everything they need to mature so they are smaller and unable to be fertilized.