251094_Fall_final_2015_ANSWERS
advertisement

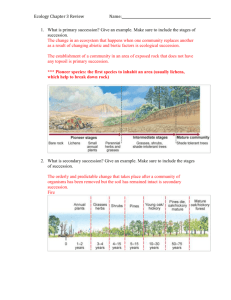
Biology Review Sheet 2015 Periods 1, 3,5,6 The following concepts will be covered on the fall test exam. A. ECOLOGY: On the side of the page; 1. Draw an ecological pyramid; Place the following groups in their proper location on the pyramid and define each: A.Sun B. Herbivores C. Onmivores D. 1st order consumer E. 2nd order consumer F. Carnivores G. Autotrophs H. Heterotrophs I. decomposers J. trophic level K. show direction of energy flow & the % transfer of energy up trophic levels 2.Distinguish between the terms Organic & Inorganic ORGANIC: compounds based on Carbon; produced by life processes INORGANIC: not based on carbon; “of the earth” ie rock 3. Write the chemical formula for glucose, and sucrose GLUCOSE: C6H12O6 SUCROSE C12H22O11 4. Write the chemical formula for photosynthesis CO2 + H2O ----- C6H12O6 + O2 5. What 2 roles or events define decomposers? 1. Decomposers are the final energy acceptors in the ecosystem 2. Decomposers make nutrients available again for plants to take up Succession in a Boreal forest 6. Compare and contrast primary succession to secondary succession. Primary succession begins with brand new ground (devoid of nutrients) Succession begins with “pioneer plants”; plants that can fix Nitrogen in their roots; it continues similar to secondary succession toward a “climax” stage SECONDARY SUCCESSION: starts with soil already containing nutrients: begins with “annual plants”, shrubs, deciduous trees, conifers 7. Name 3 significant events (disturbances) that result in primary succession. 1. erosion by rivers & flooding. 2. Receding glaciers 3. Landslides/rockslides 8.Name 3 significant events that result in secondary succession. 1. Fires 2. Avalanches 3. Disease 9. List the 3 primary abiotic factors that determine the plants and animals that can live in the Boreal forest. 1. Sunlight 2. Temperature 3. precipitation 10. Identify 3 biotic and 3 abiotic factors that affect the ecosystem. Biotic: 1. competition from other organisms; 2. disease; 3. Cover Abiotic: 1. Space 2. Temp 3. Elevation 4. Water 5. pH STREAM ECOLOGY: Define and state the role of the following 11. Detritivores: Breakdown matter into small pieces with lots of surface area. Increase surface area for decomposers 12. Decomposers & their role: breakdown matter and release nutrients that plants can take up again. 2. They consume the last amounts of stored energy 13. Identify 2 Biotic and 2 Abiotic factors of a stream ecosystem and what they affect: Biotic: cover; predators; food Abiotic: water temp; water clarity; water velocity; pools for feeding; slow areas for resting POPULATIONS: 14. What is meant by “resource” when discussing populations? Anything the population needs from the environment, ie food space, cover, mates Taxonomy: 15. Aristotle’s criterion for classifying organisms was based on whether it is a plant or animal 16. Morphology defines an organisms_____ external characteristics 17. Phylogeny looks at organisms based on their evolutionary relationships such as embryonic development; DNA similarity 18. Which 2 taxon are used when writing binomial nomenclature? Genus & species 19. What are 2 rules to use when writing or reading binomial nomenclature? Genus is always capitalized; species is always lowercase. Both may be italicized 20. The scientific name for the wolf is Canis lupis lupis represents what taxon? species; it is lowercase21. The kingdom that was split into 2 new kingdoms under the systematics method of classification is _Monera_____ the 2 new kingdoms created are __________Archaebacteria & Eubacteria___ 22. List the taxonomic hierchy in order from broadest to smallest beginning with Kingdom. Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 30. Name the scientist who developed the system of taxonomy we use today: Carolus Linnaeus Scientific method: 31. Which part of the scientific method should be stated as a question? The Problem or Purpose 32. In which step of the scientific method do you accept or reject your hypothesis? Conclusions 32b. It was difficult to count Daphnias heart rate accurately in some cases, cause it moved around a lot. This may have resulted in data that was not very accurate. Where should you mention this in you lab report at? Experimental Error 33. 219 meters = .219 kilometers? 34. 1mm equals 1000 micrometers? (microns) 35. The standard metric unit for measuring mass is the____gram____ 36. The metric standard for calculating volume is the ___liter______ 37. The metric standard for calculating mass is the _gram (repeat question) 38. The metric standard for calculating distance is the meter 39. Be able to convert inches to centimeters and vice versa Example: A chinese millipede is 5.5 inches long, how long is this in centimeters? Given 2.54 cm = 1 inch 5.5in X 2.54cm = you can do the math inch 40. Define accuracy in a lab instrument: the smallest amount the instrument was designed to measure 42. Name the variables used when constructing a graph and tell which axis they go on Control variable: aka independent variable belongs on the X axis horizontal axis) Experimental: Experimental variable: aka independent variable belongs on the Y axis vertical axis) 43. What is a graphs range? Its increment? Range: the total value the data covers from high to low increment: the value that has been chosen to represent given distances on the graph. (grid or tick marks) 45. How do you find the total magnification of a given combination of lenses on a microscope? Multiply their individual magnifications together. For example a 10X ocular lens, and 4X objective lens = 40X total magnification 46. Name the units used when measuring a cell. Compare them to a millimeter. The micrometer, or micron; abbreviated um. 1000um = 1 mm 47. Define a condensation reaction and a hydrolysis reaction Condensation reaction: When 2 monomers combine chemically, a water molecule is produced when OH & H molecules are removed from the functional groups of the monomers. The instability created by the removal allows the 2 monomers to join chemically to make a larger molecule. Hydrolysis: Chemistry CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 48. Name the reactants: CO2 & H2O 49. Name the products C6H12O6 & O2 50. The arrow means: “YIELDS” 51. Name the 3 particles found in an atom and their charges. PROTONS: + charge, found in the nucleus NEUTRONS: no charge (neutral), found in the nucleus ELECTRONS: - charge, orbit the nucleus 52. How many electrons can the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd energy levels hold? 1st 2electrons 2nd 8 electrons 3rd 8 electrons 53. When is an element most stable? When its outer shell is full of electrons 54. List the 3 shapes that organic molecules we are studying can take. Rings: sugars Straight chains: Fats Branched chains: Proteins 55. Describe the difference between a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic substance Hydrophillic means “water loving”A hydrophilic substance is charged and will thus easily dissolve in water Hydrophobic means “water fearing” these substances are nonpolar and will not dissolve or readily dissolve in water 56. Draw the structure of a water molecule, and show how it is charged: Look up 57. How many covalent bonds will the following elements want to create with other elements? Carbon___4_ Oxygen__2__ Nitrogen__3__ Hydrogen__1_ Biochemistry 57. Be able to determine if a compound is organic or inorganic. Organic compounds contain Carbon, are produced by living processes (like Photosynthesis and respiration) Determine which compounds are organic or inorganic C6H12O6___Organic_______ CH4___Organic_ H2SO4_____Inorganic___________ CO2_Inorganic_ 53. What are the functional groups found in sugars, fats and proteins? Sugars- functional group is the Hydroxide OH Fats- functional groups are the Hydroxide OH, and the Carboxyl COOH- Proteins-functional groups are the Amino group NH2 and the Carboxyl group; COOH 54. Name 3 common simple sugars or monosaccharides Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose 55. Name 3 common double sugars or disaccharides Sucrose, Maltose, and Lactose Dimensional analysis 56. A cheetah is the fastest mammal on land and has been clocked running at 70 miles per hour. What is the Cheetahs speed in meters per second? Show this dimensional analysis work on the back of your scantron and circle your answer. Show your math. Note: 1 yard = .914 meters 1760 yards = 1 mile 3600 seconds = 1 hour Consider the steps of Dimensional Analysis. 1. Ask: What am I given? 2. What am I being asked to find? 3. Start with what you are given. 4. Only multiply (by conversions) 5. Watch the units when multiplying 57. Salmon life cycle stages; their order of development and requirements Egg, Alevin, Fry, Smolt, Adult 58. Why do salmon need cold water? In which stages? Cold water holds more Oxygen than warmer water. Egg & Alevin stages need especially colder waters. Adult stage has the widest range, and can tolerate warmer waters ( up toward 20 degrees Celsius) 59. Why do salmon need clear water? Highest saturation of Oxygen occurs in cold water 60. Why do salmon need slow water? (pools) Feeding & resting 61. Why do salmon need cutbanks? Cutbanks provide cover from predators and slower water for resting.