ecology test review and sample questions
advertisement

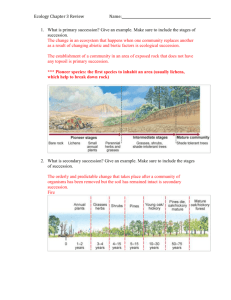
Biology Chapter 2/3.1 Review Vocabulary: Ecology Biosphere Biotic factor Abiotic factor Population Community Ecosystem Biome Niche Habitat Predation Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Competition Autotroph Heterotroph Carnivore Omnivore Herbivore Detritivore Food web Biomass Matter Nutrient Biogeochemical cycle Limiting factor Tolerance (zone or range) Ecological succession Primary succession Secondary succession Climax community Green technology Ecological footprint Practice questions on the back! Test will be on Weds (6th) or Thursday(all other periods) You may use any handwritten notes on the test Concepts/Skills: Identify abiotic and biotic factors Define and describe the different levels of biological organization Identify the type of relationship between two organisms given a description of their niche Diagram the flow of energy in an ecosystem using a food web Analyze a food web to get information about an organism’s feeding relationships Describe the basic events of the H2O, C, O, N and P cycles Recognize that every organism has a range of conditions (abiotic and biotic) that it can survive Sequence the stages of succession Give examples of primary and secondary succession Practice questions: 1. The broadest level of biological classification is: a) ecosystem b) biome c) biosphere d) community 6. Which of these are detritivores? a) a photosynthetic bacteria b)a clam that filters food from water c) a plant d) a fungus that gets nutrients from a dead log 2. Which would be an abiotic factor for a tree in a forest? a) a caterpillar eating its leaves b) a bird nesting in its branches c) wind blowing through its branches d) fungus growing on its roots 3. A fungus helps a tree get minerals from the soil. The tree shares it’s sugars with the fungus. This is an example of: a) commensalism b) mutualism c) parasitism d) competition 7. According to the diagrams above, for every 100 units of energy contained in the producer level, there are ___ units available at the secondary consumer level: a) 10 b) 1000 c) 100 d)1 8. A factor that can lead to primary succession is: a) a forest fire b) a lake drying up c) glacial retreat d) a city flooding 9. Esox lucius thrives in waters with temperatures between 9ºC-23ºC. This is known as it’s: a) ecologic zone b) zone of tolerance c) habitat d) interaction 10. The sum of the resources that are used or contribute to your life and lifestyle is called your: 4. In the diagram above, the plankton is a: a) herbivore b)detritivore c)heterotroph d) autotroph a) biomass b)ecological footprint c) green technology d) energy cycle 5. In the diagram above, which is a carnivore? a) mussels b)seal b) shrimp d) plankton Key: 1)C, 2)C, 3)B, 4)D, 5)B, 6)D, 7)D, 8)C, 9)B, 10)B