Answers to Chapter 7 HW
advertisement

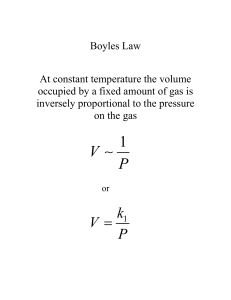
Answers to Chapter 7 HW **It is your responsibility to correct your own HW if it was graded honest attempt. **If you find any discrepancies, see me with the problem. Page 1 1. atm or kPa 2. /760 3. leave it alone 4. leave it alone 5. L 6. Change to L /1000 7. Leave alone 8. K 9. +273 10. leave alone 11. .0821 Latm/mol K 12. 8.314 LkPa/mol K 13. 273K 14. 1.00 atm OR 101.325 kPa 15. 22.4 L page 2 skip notes Page 3 WS Gas Problems Ideal Gas Law Review 1. 5.01 g CO2 2. 4.53 g 3. 7.36 x 1022 molecules 4. .0826 moles 5. 4.16 L of O2 at .550 atm and 283 K Page 4 and 5 skip notes Page 6,7,8 (side by side notes you already have these on a separate sheet) Page 9 WS Gas Stoichio @STP 1. 3.83 L of H2 2. 2.06 L of H2 3. .0494 moles H2 4. 102 L of Cl2 5. 1.25 g H2O page 10 WS Gas Stoichio NOT @ STP 1. 10.1 L and 11.1 L @755mmHg and 298K 2. .0389 g of Mg 3. .174 mol F2 4. 19.3 g of O2 5. 20.3 L of H2 @ 25C and 755mmHg page 11 WS Gas Problems Practice 1. .0478 g of Mg 2. 4.75 L of H2 3. 1.5 L of H2 @ 15C and 725 mmHg 4. 36.34 L @ 35C and 740. mmHg 5. 8.563 L of H2 @STP 6. 6.9 L of Cl2 @ STP 7. 14.6 L @25C and 103.8 kPa 8. 1.25 g of H2O 9. 79 g of Mg page 12 WS Gases 1. 13.4 g 2. 12.2 g 3. 93.86 x 1022 molecules 4. .683 moles 5. 291.2 L 6. 864.5 L 7. .1071 g 8. 7.134 g/L 9. 18 g/mol 10. 2.93 x 1023 molecules page 13 WS Gases 1. 40.1 L of F2 2. 12.8 L of CO2 3. .100 L of NH3 4. 5.25 L of O2 5. .250 L of H2O page 14 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. skip skip same temp so same Kinetic energy but lighter molecules move faster the collisions of molecules with the wall increase temp, then increase kinetic energy then more collisions so increase pressure and increased volume page 15 6. .47 L CO2 7. 78855 mL 8. 41.87L 9. 5.49g page 16 1. 10.4 L 2. 39.8L 3. 30.4 atm 4. 4.10 g HBr 5. .613 g page 17 6. .269 atm 7. 25.5 g 8. 3.58 g 9. 265 mL 10. 47.2 L 11. .612 mol MgO page 18 12. 2.77 g/L 13. .0699 mol 14. 56.9 L H2O 15. .910 L 16. 23.0 L NH3 17. 4.37 g N2 page 19 18. 13.7 L O2 19. 5.92 g O2 20. 2.86 g/L 21. 1.20x 1024 atoms Ne 22. 31.9 mL page 20 Notes: The kinetic molecular theory 1. explain, describe 2. explanation, behave 3. tiny particles, small distances, volume negligible, constant random motion container, attract repel, kinetic energy directly proportional, Kelvin 4. temperature, motion 5. n (quantity), temp, kinetic energy, collisions, pressure 6. n, increase, kinetic energy, collisions, pressure, expland, volume 7. increased, decrease, collisions, away, decrease page 21 Calculations Ideal Gas Law and Combined Gas Law 1. 9.81 atm 2. 45.8 L 3. .191 moles 4. 667K 5. .173 atm page 22 6. .08282L 7. .0575 mol 8. .844 L 9. 94.0 kPa 10. 305 K