11_SpaceTimeMappingUsingBMElib
advertisement
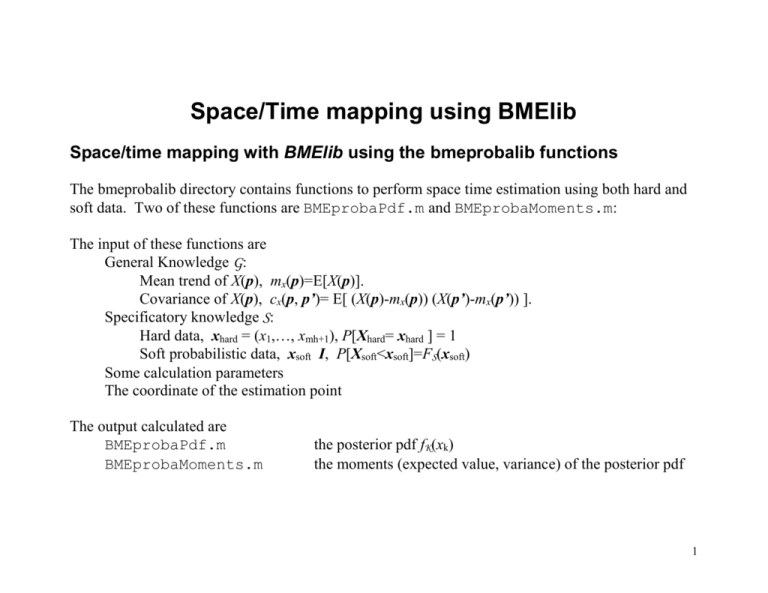
Space/Time mapping using BMElib
Space/time mapping with BMElib using the bmeprobalib functions
The bmeprobalib directory contains functions to perform space time estimation using both hard and
soft data. Two of these functions are BMEprobaPdf.m and BMEprobaMoments.m:
The input of these functions are
General Knowledge G:
Mean trend of X(p), mx(p)=E[X(p)].
Covariance of X(p), cx(p, p’)= E[ (X(p)-mx(p)) (X(p’)-mx(p’)) ].
Specificatory knowledge S:
Hard data, xhard = (x1,…, xmh+1), P[Xhard= xhard ] = 1
Soft probabilistic data, xsoft I, P[Xsoft<xsoft]=FS(xsoft)
Some calculation parameters
The coordinate of the estimation point
The output calculated are
BMEprobaPdf.m
BMEprobaMoments.m
the posterior pdf fK(xk)
the moments (expected value, variance) of the posterior pdf
1
BMEprobaPdf.m
Posterior pdf at the estimation point
fK(k)
General
knowledge
m(s,t) cx(r,)
BMElib
Specificatory
knowledge
Hard data
Soft proba data
BMEprobaMoments.m
Moments of the posterior pdf:
Expected value, variance
2
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Spatial example
% The SRF X(s) is a function of space only in a 2D spatial domain
% This SRF has a mean trend equal to zero, and a covariance
% C(r)=c0*exp(-3r/ar) with c0=1, ar=5
% Additionally we have hard data at two hard data points.
% At s=(0,4) X(s)=1.2 and at s=(5,2) X(s)=1.7
% We want to estimate the posterior pdf and it's moments at one
% estimation point of coordinate (1,1)
% specify the general knowledge
order=NaN;
% The mean trend is equal to zero
covmodel='exponentialC'; % covariance is exponential, C(r)=c0*exp(-3r/ar)
covparam=[1 5];
% parameters for the covariance model, c0=1, ar=5
% specify the specificatory knowledge
ch=[0 4;5 2];
% Hard data has two data points, at (0,4) and (5,2)
zh=[1.2;1.7];
% Value of hard data at (0,4) is 1.2, and at (5,2) it is 1.7
cs=[];
% There is no soft data
softpdftype=1;
%
(no soft data)
nl=[];
%
(no soft data)
limi=[];
%
(no soft data)
probdens=[];
%
(no soft data)
3
% specify calculation parameters
nhmax=10;
% max number of hard data in estimation neighborhood
nsmax=0;
% max number of soft data in estimation neighborhood
dmax=[100];
% dmax=max spatial search radius for estimation neighborhood
options=BMEoptions;
% Use default options
% specify the coordinate of estimation point
ck=[1 1];
% The estimation point is (1,1)
% calculate BME posterior pdf using BMEprobaPdf
[z,pdf,info]=BMEprobaPdf([],ck,ch,cs,zh,softpdftype,nl,limi,probdens,covmodel,covparam,nhmax,nsmax,dmax,or
der,options);
figure;hold on;
plot(z,pdf);
title('BME posterior pdf of variable z_k at coordinate (x,y)=(1,1)');
xlabel('z_k');
ylabel('f_K(z_k)');
% calculate moments of BME posterior pdf using BMEprobaMoments
[moments,info]=BMEprobaMoments(ck,ch,cs,zh,softpdftype,nl,limi,probdens,covmodel,covparam,nhmax,nsmax,
dmax,order,options);
expecvalk=moments(:,1)
vark=moments(:,2)
4
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Space/time example
% The S/TRF X(s,t) has mean trend equal to zero, and the following covariance
% C(r,t)=c0*exp(-3r/ar)*exp(-3t/at) with c0=1, ar=5, at=10
% Additionally we have hard data at two hard data points.
% At s=(0,4) and t=30, X(s)=1.2, and
% at s=(5,2) and t=10, X(s)=1.7
% We want to estimate the moments at two points of coordinate
% (1,1,15) and (1,1,16)
% specify the general knowledge
order=NaN;
% The mean trend is equal to zero
covmodel='exponentialC/exponentialC'; % covariance model
covparam=[1 5 10];
% covariance parameters
% specify the specificatory knowledge
ch=[0 4 30;5 2 10];
% Hard data coordinate
zh=[1.2;1.7];
% Value of hard data
cs=[];
% There is no soft data
softpdftype=1;
%
(no soft data)
nl=[];
%
(no soft data)
limi=[];
%
(no soft data)
probdens=[];
%
(no soft data)
5
% specify calculation parameters
nhmax=10;
% max number of hard data in estimation neighborhood
nsmax=0;
% max number of soft data in estimation neighborhood
dmax=[100 10 5/10];
% dmax(1)=max spatial search radius for estimation neighborhood
% dmax(2)=max temporal search radius for estimation neighborhood
% dmax(3)=space/time metric, usually equal to ar/at
options=BMEoptions;
% Use default options
% specify the coordinate of estimation point
ck=[1 1 15;1 1 16];
% The estimation points
% calculate moments of BME posterior pdf using BMEprobaMoments
[moments,info]=BMEprobaMoments(ck,ch,cs,zh,softpdftype,nl,limi,probdens,covmodel,covparam,nhmax,nsmax,
dmax,order,options);
expecvalk=moments(:,1)
vark=moments(:,2)
6
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Space/time example with nested covariance model
% The mapping situation is the same as for the S/TRF X(s,t) above
% Except that we now use the following covariance
% C(r,t)=c02*exp(-3r/ar1)*exp(-3t/at1) + c02*exp(-3r^2/ar2^2)*exp(-3t/at2)
% with c01=1, ar1=5, at1=10 and c02=1, ar2=50, at2=100
% all the other Input parameters are the same as above
% except for the covariance model given as follow
covmodel={'exponentialC/exponentialC','gaussianC/exponentialC'};
covparam={[1 5 10],[1 50 100]};
% calculate moments of BME posterior pdf using BMEprobaMoments
[moments,info]=BMEprobaMoments(ck,ch,cs,zh,softpdftype,nl,limi,probdens,covmodel,covparam,nhmax,nsmax,
dmax,order,options);
expecvalk=moments(:,1)
vark=moments(:,2)
7