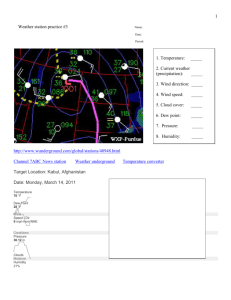
Name: :____________Date
advertisement

Name:__________________________________________Period:_______________Date:______________ Chapter 27 Test 1. The amount of water vapor actually in the air is called the a. specific humidity b. relative vapor content c. specific gravity d. condensation nuclei 2. Which of the following instruments measures relative humidity without thermometers? a. psychrometer b. hair hygrometer c. pedometer d. barometer 3. Which of the following instruments measures relative humidity with a thermometer? a. psychrometer b. hair hygrometer c. pedometer d. barometer 4. The air in a cumulonimbus cloud is moving a. upward b. downward c. horizontally d. up and downward 5. The air in a growing stratus cloud is moving a. upward b. downward c. horizontally d. up and downward 6. Rain falls from a. cirrostratus clouds c. stratocumulus clouds b. nimbostratus clouds d. cirrocumulus clouds 7. Which is not a form of precipitation? a. fog c. rain b. hail d. sleet 8. Rain occurs a. b. c. d. on the leeward side of mountains in areas where air rises in areas where air sink in areas of dry air 9. Water exists in the atmosphere in the form of a. water vapor b. cloud droplets c. ice crystals d. all of the above 10. Dew point is the point at which a. rain turns to snow c. Air is saturated b. air is supersaturated d. air is unsaturated 11. If air cools below its dew point temperature and fails to condense, which is true? a. starts to snow b. air is supersaturated c. air is saturated d. air is unsaturated Imagine a sample of air with the following properties: Specific humidity of 12.3 grams Capacity at 23ºC: 18.1 grams Capacity at 8ºC: 6.8 grams Capacity at 17ºC: 12.3 grams Answer each of the questions below about this sample. 12. What is the dew point of this air? 13. If the temperature is 23ºC, what is the relative humidity? 14. If the temperature is 8ºC, what is the relative humidity? 15. Would the extra water from question be dew or frost? Why? Draw the station model symbol for each of the following: 16. Drizzle 17. Snow 18. Shower 19. Funnel Cloud 20. Sleet 21. Fr. Rain 22. Hail 23. Thunderstorm 24. Use the mountain peak below to explain why and where it rains in mountainous regions. 25. What are at least two differences between sleet and hail? 26. Briefly sketch a diagram of the water cycle and use short explanations for each part telling what happens. 27. to 29. What are the 3 major types of clouds? Sketch each and describe what weather they indicate. Name the process of the water cycle best represented by each statement. For #’s 30. to 44. 30. Rivers and streams 31. Water filtering into the ground 32. Snow, sleet, rain, hail etc. 33. Formation of a cloud 34. Solid into a gas 35. Liquid into a gas 36. Water evaporated from plants and trees 37. Formation of fog 38. Cricks and waterfalls 39. Freezing rain, frogs, cats, and dogs 40. Water stored in a well 41. Snow evaporating instead of melting 42. Steam from boiling water 43. Leaves dying on trees during a hot and dry summer 44. The web bulb thermometer gets cooler than the dry bulb thermometer because of this process Answer questions #45. to 57. based on the cloud formation lab 45. Which lab procedure involving the bottle was representative of compressing air which leads to high pressure which leads to warming of the air? 46. Releasing the bottle from a squeezed position demonstrated which earthly process? 47. What did the 2 Liter bottle represent? 48. What did the cap represent? 49. Which lab material symbolized fires, smoke, nuclei, pollution, volcanic eruptions, and factories? 50. Lightning and human activity best represented which lab material? 51. What did the warm water in the 2 Liter bottle represent? 52. Why was cold water not used in the cloud lab? 53. Why were the cotton balls not used in the cloud lab? 54. to 56. Which 3 things and/or processes are necessary for cloud formation? Just having 2 of these 3 would be insufficient for cloud formation. 57. Where are you more likely to find clouds based on this lab, Northern Canada or Florida? Answer questions #58. to 71. based on the Relative Humidity Lab Air temperature (needed to find capacity) Dew Point temperature (needed to find specific humidity) = 22 degrees Celsius = 17 degrees Celsius 58. What is the capacity? 59. What is the specific humidity? 60. What is the relative humidity? Air temperature Dew Point temperature = 14 degrees Celsius = 14 degrees Celsius 61. What is the capacity? 62. What is the specific humidity? 63. What is the relative humidity? 64. Relative humidity is 40%. Capacity is 8.3 grams. What is the specific humidity? 65. Specific humidity is 2.5 grams. Capacity is 7.8 grams. What is the relative humidity? Dry bulb temperature Wet bulb temperature = 32 degrees Celsius = 26 degrees Celsius 66. What is the difference between temperatures? 67. What is the relative humidity? Dry bulb temperature Wet bulb temperature 68. What is the difference between temperatures? 69. What is the relative humidity? 70. On a typical day, when is the relative humidity lowest? 71. On a typical day, when is the relative humidity highest? = 13 degrees Celsius = 10 degrees Celsius