AP Biology Chapter 20 Worksheet

AP Biology Chapter 20 Worksheet
1.
Explain what is meant by recombinant DNA and what in vitro means.
2.
Explain what genetic engineering is and an application of this technology.
3.
Explain what biotechnology is and it’s use.
4.
Contrast the use of early biotechnology to its more modern uses.
5.
Explain what is meant by gene-cloning and why it is useful.
6.
What general factors does gene cloning include?
7.
Give the 2 main uses for cloned genes.
8.
Explain what a restriction enzyme is and what it is used for both naturally and artificially.
9.
Explain what a restriction site is and what it looks like.
10.
What are restriction fragments and how are they formed?
11.
Explain what a sticky end is and how it is formed.
12.
What are formed as a result of these sticky ends?
13.
Explain what DNA ligase is and what it does.
14.
Explain how ligase and restriction enzymes can be used in recombinant DNA.
15.
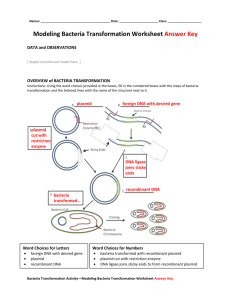
Explain how recombinant plasmids are formed.
16.
Explain what a cloning vector is and what it is used for.
17.
What happens to the recombinant plasmid once inside a bacteria?
18.
Give 2 reasons for the use bacteria for cloning?
19.
What is the first step in the cloning of a human gene?
20.
What is normally the source plasmid for human cloning?
21.
Give the 2 genes this bacterial plasmid carries and what they do.
22.
Explain how many human DNA fragments with both sticky ends.
23.
What happens after we mix human DNA fragments and plasmids?
24.
Explain how bacterial cells are introduced to the cloned vectors.
25.
Explain the pool of bacteria that will develop from these vectors and their characteristics.
26.
What does it mean that the bacteria are lacZ-
27.
Explain what is in the nutrient medium we plate these bacteria out on and what that means.
28.
What is the X-gal used for?
29.
Which bacteria stain blue and which ones stain white on this plate and why
30.
What is the final step of cell cloning?
31.
Explain what is meant by nucleic acid hybridization.
32.
Explain what a nucleic acid probe is and what it is used for.
33.
How is this probe labeled?
34.
What will this probe bond to and why?
35.
What does denaturing mean and what happens to the DNA strands after this process?
36.
Explain what an expression vector is and how it is necessary.
37.
What happens once the bacterial host recognizes this promotor?
38.
Explain what an intron is and why it can be a problem in cloning.
39.
How does fully processed mRNA act in a the expression of eukaryotic genes in bacteria?
40.
Explain how cDNA and any promotor are related.
41.
Explain how using eukaryotic cells as host can avoid problems and examples of eukaryotic cells that can be used.
42.
Explain what a yeast artificial chromosome is.
43.
Explain what a posttranslational modification is with an example.
44.
Give 3 alternate means of getting eukaryotic cells to take up DNA from their surroundings.
45.
Explain the shotgun cloning approach.
46.
Explain what is meant by a genomic library and how they are formed.
47.
Explain how bacteriophages can be used as cloning vectors.
48.
Explain what is meant by a cDNA library and how it is advantage for the researcher.
49.
Explain what a polymerase chain reaction is and it’s advantages.
50.
What was the key to easy PCR automation.
51.
Give at least 4 sources of sources for PCR DNA.
52.
What are the 4 basic questions we need to answer once we have our samples of homogeneous DNA?
53.
Explain what is meant by genomics.
54.
Explain what is meant by gel electrophoresis and what it is used for.
55.
What are the macromolecules separated using electrophoresis? What affects their rate of movement?
56.
How are the bands in the gel formed? How are they used?