Key to Biome Table - Seattle Central College
advertisement

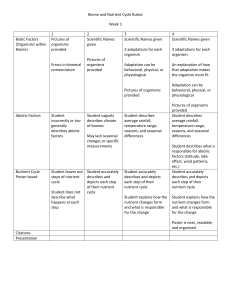
GROUP: _________ (T = terrestrial; A = Aquatic) Name: _________________________________ Using the internet or one of the textbooks on reserve in the library, research the following information. Suggested websites include: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/glossary/gloss5/biome/ http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/world_biomes.htm http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Laboratory/Biome/ https://royercenter.cwc.psu.edu/biodiversity/defined/biosphere/biomes-p5.html Terrestrial Biomes Biome Precipitation (amount) Temperature (range) Tropical rainforest Wet tropical – 200-400 cm Dry tropical – 150-200 cm with seasonality 25-29 deg C Desert less than 30 cm/ year Deserts can be very hot (such as Mohave or Sahara) or very cold (Gobi Desert) Savanna seasonal, 3050 cm 24-29 deg C Dominant plants (trees, shrubs, cacti, herbs, grasses etc…) dominated by multiple strata of woody plants Major animals- insects, grazers, predators, reptiles, mammals etc… High diversity in all animal phyla Human impacts succulents, deeply rooted shrubs and ephemeral herbs reptiles, insects, nocturnal mammals Human Impact – loss of aquifers, conversion to agriculture, urbanization large herbivores, some predators, invertebrate herbivores urbanization, overhunting, agriculture scattered thorny trees, grasses and forbs (annual herbs) Population growth leading to mass loss of forest and species Biome Precipitation (amount) Temperature (range) Dominant plants (trees, shrubs, cacti, herbs, grasses etc…) Plants: succulents, deeply rooted shrubs and ephemeral herbs; special adaptations to dry environments Major animals- insects, grazers, predators, reptiles, mammals etc… reptiles, insects, nocturnal mammals Human impacts Chaparral less than 30 cm/ year Hot summers, mild winters Temperate grassland seasonal, 30100 cm/ year hot summers, cold winters Plants: grasses and forbs large grazing mammals, burrowing mammals conversion to agriculture, urbanization Temperate broadleaf forest seasonal, 70200 cm/year winter – 0 deg C; summer hot and humid deciduous trees in multiple strata with a closed canopy nesting migratory birds; small mammals logging, conversion to agriculture, urbanization Tundra seasonal, 20-60 cm/ year long cold below freezing; summers warm short, less than 10oC Plants: lichens, mosses, grasses, forbs large migratory animals; carnivores oil extraction Aquatic Biomes loss of aquifers, conversion to agriculture, urbanization Type Freshwater or saltwater or both? Oxygen rich or oxygen poor? Nutrient rich or nutrient poor? Thermocline present? If yes, it is always present or seasonal Major photosynthesizers (e.g. plants, algae, phytoplankton) Major animals Human impacts Lakes Fresh with a few exceptions – Great Salt Lake and Mono lake have high salinity (more than the ocean!!!) Can be both – depends on nutrient load Can be both Oligotrophic – is nutrient poor, oxygen rich Eutrophic is nutrient rich, oxygen poor Seasonal in most lakes phytoplankton Zooplankton, invertebrates, fish Water pollution, draining, construction Wetlands both poor rich absent Aquatic and marsh plants Rich bird, mammal and invertebrate fauna Urbanization, pollution Streams and rivers fresh Usually rich is moving fast Can be rich in slow moving ones absent Some algae and Fish and aquatic plants invertebrates Dams, pollution, rechannelization, draw down for irrigation Estuaries Brackish – mix of salt and fresh poor rich absent Algae, aquatic plants, marsh plants (cattails and other grasses) Filled in for urbanization, pollution, Invertebrates, fish; waterfowl Type Freshwater or saltwater or both? Oxygen rich or oxygen poor? Nutrient rich or nutrient poor? Thermocline present? If yes, it is always present or seasonal Major photosynthesizers (e.g. plants, algae, phytoplankton) Major animals Human impacts Intertidal zones salt rich poor absent algae Mollusks, crabs, other invertebrates, small fish, pollution Oceanic pelagic zone salt rich poor May be present in some areas phytoplankton Fish, marine mammals Overfishing, pollution Coral reefs salt rich rich absent Algae that live in the corals Coral, fish, crabs, sharks medium rich absent none Mostly invertebrates Pollution, global warming, overfishing, damage from chemicals and dynamite Little impact from humans currently salt Marine benthic zone